Manual:OSPFv3 with Quagga: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(No difference)
| |
Latest revision as of 13:26, 31 May 2010
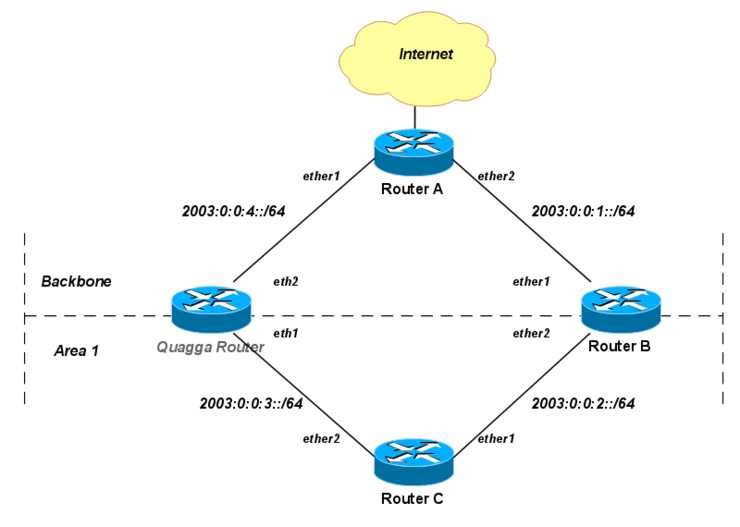
In this example we demonstrate interoperability of MikroTik 3.x with Quagga in multi-area OSPF setup with load balancing.
RouterOS version 3.16 and Quagga 0.99.11 are used respectively.
Router A
/ipv6 address add address=2003::1:0:0:0:1/64 advertise=no interface=ether2 add address=2003::4:0:0:0:1/64 advertise=no interface=ether1 add address=2003::1/64 advertise=no interface=ToInternet /routing ospf-v3 set router-id=0.0.0.1 distribute-default=always-as-type-1 /routing ospf-v3 interface add interface=ether1 area=backbone add interface=ether2 area=backbone
Router B
/ipv6 address add address=2003::1:0:0:0:2/64 advertise=no interface=ether1 add address=2003::2:0:0:0:2/64 advertise=no interface=ether2 /routing ospf-v3 set router-id=0.0.0.2 /routing ospf-v3 area add area-id=0.0.0.1 name=area1 /routing ospf-v3 interface add interface=ether1 area=backbone add interface=ether2 area=area1
Quagga Router
debian:~# ip -6 addr add 2003:0:0:3::4/64 dev eth1 debian:~# ip -6 addr add 2003:0:0:4::4/64 dev eth2 debian:~# debian:~# cat /etc/quagga/ospf6d.conf ... interface eth1 ipv6 ospf6 cost 10 interface eth2 ipv6 ospf6 cost 10 router ospf6 router-id 0.0.0.4 interface eth1 area 0.0.0.1 interface eth2 area 0.0.0.0 debian:~# telnet ::1 2606 Hello, this is Quagga (version 0.99.11). Copyright 1996-2005 Kunihiro Ishiguro, et al. ... quagga# show ipv6 ospf6 route *N E1 ::/0 fe80::1200:ff:fe00:100 eth2 00:33:50 *N IA 2003:0:0:1::/64 fe80::1200:ff:fe00:100 eth2 00:32:55 *N IE 2003:0:0:2::/64 fe80::1200:ff:fe00:100 eth2 00:02:44 *N IA 2003:0:0:2::/64 fe80::1200:ff:fe00:301 eth1 00:02:37 *N IE 2003:0:0:3::/64 fe80::1200:ff:fe00:100 eth2 00:02:39 N IA 2003:0:0:3::/64 :: eth1 00:02:46 *N IA 2003:0:0:4::/64 :: eth2 00:33:50
Router C
/ipv6 address add address=2003::2:0:0:0:3/64 advertise=no interface=ether1 add address=2003::3:0:0:0:3/64 advertise=no interface=ether2 /routing ospf-v3 set router-id=0.0.0.3 /routing ospf-v3 area add area-id=0.0.0.1 name=area1 /routing ospf-v3 interface add interface=ether1 area=area1 add interface=ether2 area=area1 [admin@C] /routing ospf-v3> route print # DESTINATION STATE COST 0 ::/0 ext-1 21 1 2003::1:0:0:0:0/64 inter-area 20 2 2003::2:0:0:0:0/64 intra-area 10 3 2003::3:0:0:0:0/64 intra-area 10 4 2003::4:0:0:0:0/64 inter-area 20 [admin@C] /routing ospf-v3> route print detail 0 destination=::/0 state=ext-1 gateway=fe80::1200:ff:fe00:201,fe80::1200:ff:fe00:ff00 interface=ether1,ether2 cost=21 area=external 1 destination=2003::1:0:0:0:0/64 state=inter-area gateway=fe80::1200:ff:fe00:201 interface=ether1 cost=20 area=area1 2 destination=2003::2:0:0:0:0/64 state=intra-area gateway=:: interface=ether1 cost=10 area=area1 3 destination=2003::3:0:0:0:0/64 state=intra-area gateway=:: interface=ether2 cost=10 area=area1 4 destination=2003::4:0:0:0:0/64 state=inter-area gateway=fe80::1200:ff:fe00:ff00 interface=ether2 cost=20 area=area1
Ping an "Internet" address from Router C (traffic will go through ECMP route):
[admin@C] > /ping 2003::1
2003::1 64 byte ping: ttl=63 time=20 ms
2003::1 64 byte ping: ttl=63 time=12 ms
2003::1 64 byte ping: ttl=63 time=9 ms
2003::1 64 byte ping: ttl=63 time=12 ms
4 packets transmitted, 4 packets received, 0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 9/13.2/20 ms
[admin@C] > /tool traceroute 2003::1
ADDRESS STATUS
1 2003::2:0:0:0:2 19ms 7ms 15ms
2 2003::1 13ms 13ms 12ms