Manual:Simple CAPsMAN setup: Difference between revisions
| (15 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__TOC__ | |||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
It is possible to create centralized Access Point management setup for home or office environment that is scalable to many Access Point. This can be done by setting up Controlled Access Point system Manager (CAPsMAN) on your router and connecting Controlled Access Points (CAPs) to it. There are multiple benefits of setting up CAPsMAN in your environment, the most important benefit is centralized configuration, you don't need to adjust changes to all CAPs in your network, but rather you need to specify changes in your CAPsMAN and all CAPs will receive these configuration changes. Another benefit is a centralized [[ Manual:Interface/Wireless#Registration_Table | Registration Table]], this will allow you to easily monitor devices and create [[ Manual:Interface/Wireless#Access_List | Access Lists]] for devices in your network from a single device (from CAPsMAN). There are a lot of customization options, you can read more about the possibilities in the [[ Manual:CAPsMAN | CAPsMAN]] manual page. This guide will provide you with a very easy, simple and fast way to setup CAPsMAN. | It is possible to create centralized Access Point management setup for home or office environment that is scalable to many Access Point. This can be done by setting up Controlled Access Point system Manager (CAPsMAN) on your router and connecting Controlled Access Points (CAPs) to it. There are multiple benefits of setting up CAPsMAN in your environment, the most important benefit is centralized configuration, you don't need to adjust changes to all CAPs in your network, but rather you need to specify changes in your CAPsMAN and all CAPs will receive these configuration changes. Another benefit is a centralized [[ Manual:Interface/Wireless#Registration_Table | Registration Table]], this will allow you to easily monitor devices and create [[ Manual:Interface/Wireless#Access_List | Access Lists]] for devices in your network from a single device (from CAPsMAN). There are a lot of customization options, you can read more about the possibilities in the [[ Manual:CAPsMAN | CAPsMAN]] manual page. This guide will provide you with a very easy, simple and fast way to setup CAPsMAN. | ||
{{ Note | It is not required that your router has a Wireless interface, but it is required that the "wireless" package is installed. }} | [[File:simple_capsman_topology.png|700px|thumb|center|alt=Alt text|Simple CAPsMAN Setup]] | ||
{{ Note | It is not required that your router has a Wireless interface, but it is required that the "wireless" package is installed. For this setup a RB960 (hEX PoE) and two RB912 were used, but any router running RouterOS and any device having at least one Wireless interface and running RouterOS can be used. }} | |||
=Option #1, using | =Option #1, using Winbox= | ||
Before you can start configuring CAPsMAN, you must configure your selected CAPsMAN device as a router. Here we will assume that '''ether1''' is used as a WAN port and '''ether2-ether5''' are used as LAN ports. You can skip [[Manual:Simple_CAPsMAN_setup#Step_.231.2C_setup_router | Step1]] if you are already using the default configuration on your router. | Before you can start configuring CAPsMAN, you must configure your selected CAPsMAN device as a router. Here we will assume that '''ether1''' is used as a WAN port and '''ether2-ether5''' are used as LAN ports. You can skip [[Manual:Simple_CAPsMAN_setup#Step_.231.2C_setup_router | Step1]] if you are already using the default configuration on your router. | ||
==Step #1, setup router== | |||
'''Router''' | |||
* Get an IP address from WAN (or add a static IP address) | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step1_1.png | center]] | |||
* Create a bridge | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step1_2.png | center]] | |||
* Assign ports to the bridge | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step1_3.png | center]] | |||
* Repeat the step to add more ports to the bridge | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step1_4.png | center]] | |||
* Add an IP address to the bridge | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step1_5.png | center]] | |||
* Create a new address pool for the DHCP Server | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step1_6.png | center]] | |||
* Setup the DHCP Server | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step1_7.png | center]] | |||
<br /> | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step1_8.png | center]] | |||
* Setup NAT on your router | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step1_9.png | center]] | |||
<br /> | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step1_10.png | center]] | |||
{{ Note | You can skip these steps in case you have reset your device to defaults, these steps were only required for devices with no configuration at all (empty config). }} | |||
==Step #2, setup CAPsMAN== | |||
'''Router''' | |||
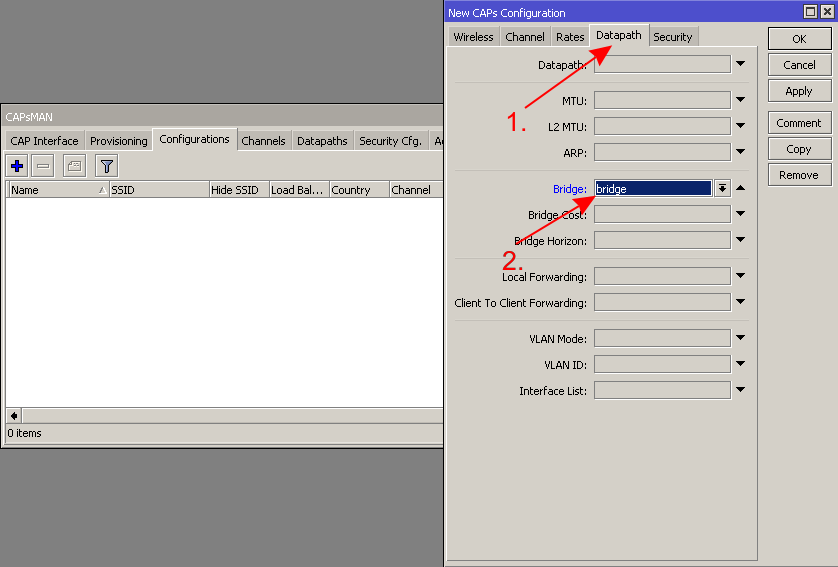
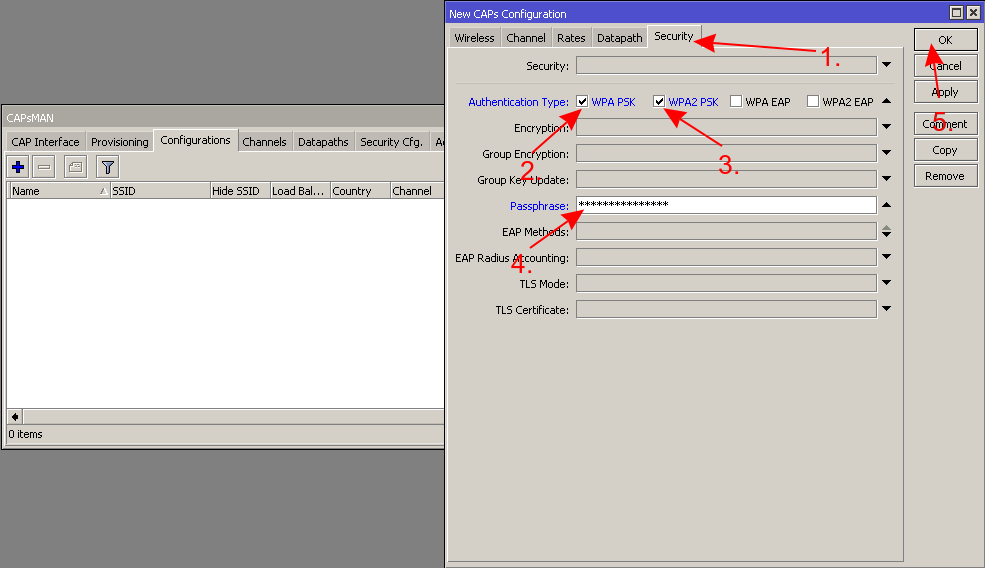
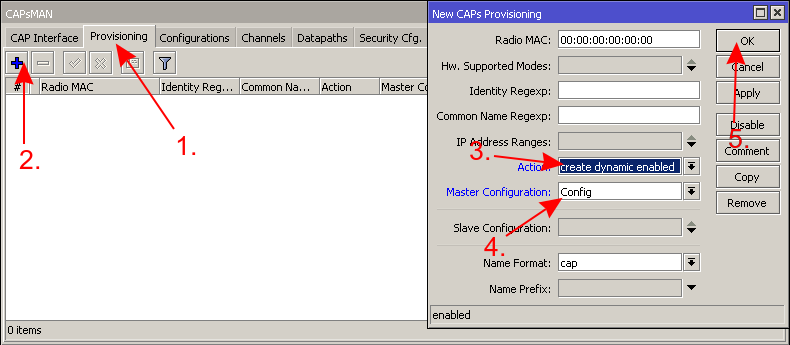
* Create a configuration template for all your CAPs | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step2_1.png | center]] | |||
<br /> | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step2_2.png | center]] | |||
<br /> | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step2_3.png | center]] | |||
* Specify CAPsMAN to use the created configuration | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step2_4.png | center]] | |||
<br /> | |||
{{ Warning | Do NOT forget to change the country and the password. Select the right country or otherwise the CAP might select a frequency that is not supported in your area. }} | |||
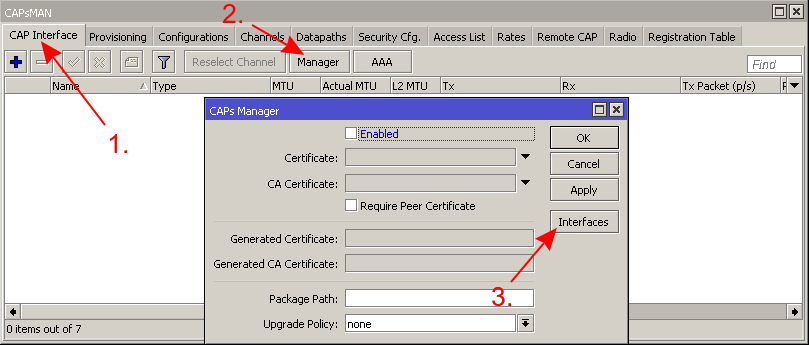
* For security reasons specify on which interfaces to listen to CAPs | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step2_5.png | center]] | |||
<br /> | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step2_6.png | center]] | |||
<br /> | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step2_7.png | center]] | |||
{{ Note | If default configuration is used, then specifying CAPsMAN ports can be skipped since the default firewall will block all incoming traffic from WAN side. This step can also be skipped if firewall is setup properly to block unwanted traffic from other ports. }} | |||
* Enable CAPsMAN manager to listen to CAPs | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step2_8.png | center]] | |||
==Step #3, setup CAPs== | |||
{{ Note | This step can be skipped if you connect your CAP while it is in CAPs mode, the device will automatically add configuration that will work with this CAPsMAN setup. You can read more about how to put your device into CAPs mode [[Manual:Reset_button | Here]]. Make sure that your device supports CAPs mode.}} | |||
'''CAPs''' | |||
* Connect to your CAP, create a bridge | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step1_2.png | center]] | |||
* Add the interface that is connected to the CAPsMAN in a bridge | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step3_1.png | center]] | |||
* Get an IP address from your router (or add a static IP address) | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step3_2.png | center]] | |||
* Enable CAP on Wireless interfaces | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step3_3.png | center]] | |||
* Connect more CAPs to your CAPsMAN and they should appear as CAP interfaces in your '''CAPsMAN Router''' | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step3_4.png | center]] | |||
'''That is it!''' Check your connectivity by using another Wireless device, for example, your smarthphone, your device should be visible in the '''CAPsMAN Router's''' registration table: | |||
[[File:Simple_CAPsMAN_Step3_5.png | center]] | |||
=Option #2, using CLI= | |||
Before you can start configuring CAPsMAN, you must configure your selected CAPsMAN device as a router. Here we will assume that '''ether1''' is used as a WAN port and '''ether2-ether5''' are used as LAN ports. You can skip [[Manual:Simple_CAPsMAN_setup#Step_.231.2C_setup_router_2 | Step1]] if you are already using the default configuration on your router. | |||
==Step #1, setup router== | ==Step #1, setup router== | ||
| Line 116: | Line 208: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
'''That is it!''' Check your connectivity by using another Wireless device, for example, your smarthphone, your device should be visible in the '''CAPsMAN's | '''That is it!''' Check your connectivity by using another Wireless device, for example, your smarthphone, your device should be visible in the '''CAPsMAN Router's''' registration table: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
/caps-man registration-table print | /caps-man registration-table print | ||
| Line 123: | Line 215: | ||
1 cap2 WiFi 4C:5E:0C:CB:0E:60 | 1 cap2 WiFi 4C:5E:0C:CB:0E:60 | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
=Case studies= | |||
==CAP in CAPsMAN== | |||
If your device has a Wireless interface and you want to use it as a CAPsMAN and a CAP, then it is possible, but it requires additional configuration. If you set your Wireless interface on your CAPsMAN to be managed by CAPsMAN, but the CAP interface is not showing up in CAPsMAN, then it is very likely that the Firewall on your Router is blocking traffic that is coming from the CAP interface. | |||
* In case you are using the default configuration | |||
<pre> | |||
/ip firewall filter | |||
add action=accept chain=input dst-address-type=local src-address-type=local place-before=[/ip firewall filter find where comment="defconf: drop all not coming from LAN"] | |||
</pre> | |||
* In case you are NOT using the default configuration | |||
<pre> | |||
/ip firewall filter | |||
add action=accept chain=input dst-address-type=local src-address-type=local | |||
</pre> | |||
* If you have limited the CAPsMAN manager on certain interfaces, then you will have enable all CAPsMAN on all interfaces and forbid any interface that you don't want CAPsMAN to listen to: | |||
<pre> | |||
/capsman manager interface | |||
remove [find where interface=bridge and forbid=no] | |||
set [find default=yes] forbid=no | |||
add forbid=yes interface=ether1 | |||
</pre> | |||
[[Category:Wireless]] | |||
[[Category:Examples]] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:50, 31 May 2018
Introduction
It is possible to create centralized Access Point management setup for home or office environment that is scalable to many Access Point. This can be done by setting up Controlled Access Point system Manager (CAPsMAN) on your router and connecting Controlled Access Points (CAPs) to it. There are multiple benefits of setting up CAPsMAN in your environment, the most important benefit is centralized configuration, you don't need to adjust changes to all CAPs in your network, but rather you need to specify changes in your CAPsMAN and all CAPs will receive these configuration changes. Another benefit is a centralized Registration Table, this will allow you to easily monitor devices and create Access Lists for devices in your network from a single device (from CAPsMAN). There are a lot of customization options, you can read more about the possibilities in the CAPsMAN manual page. This guide will provide you with a very easy, simple and fast way to setup CAPsMAN.
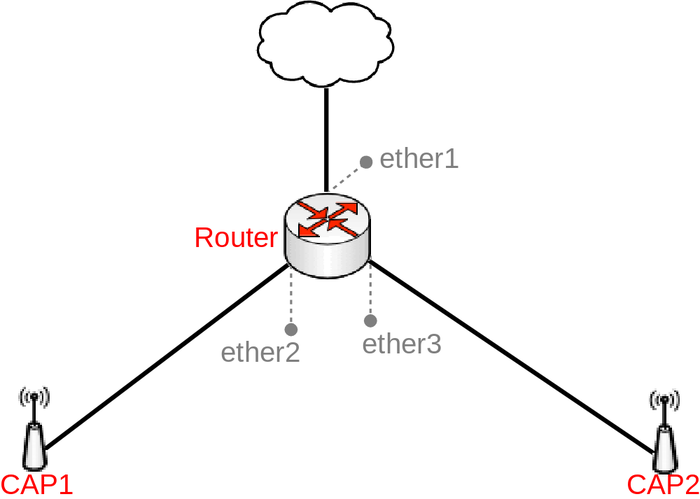

Note: It is not required that your router has a Wireless interface, but it is required that the "wireless" package is installed. For this setup a RB960 (hEX PoE) and two RB912 were used, but any router running RouterOS and any device having at least one Wireless interface and running RouterOS can be used.
Option #1, using Winbox
Before you can start configuring CAPsMAN, you must configure your selected CAPsMAN device as a router. Here we will assume that ether1 is used as a WAN port and ether2-ether5 are used as LAN ports. You can skip Step1 if you are already using the default configuration on your router.
Step #1, setup router
Router
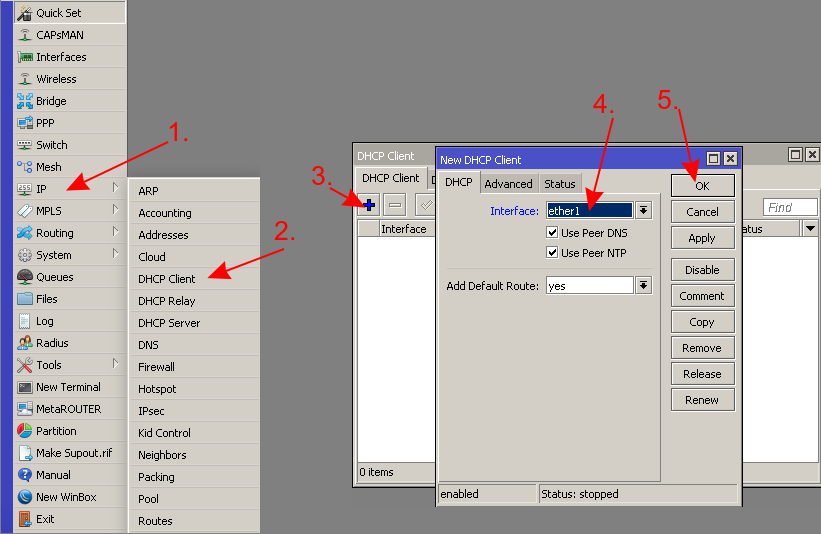
- Get an IP address from WAN (or add a static IP address)
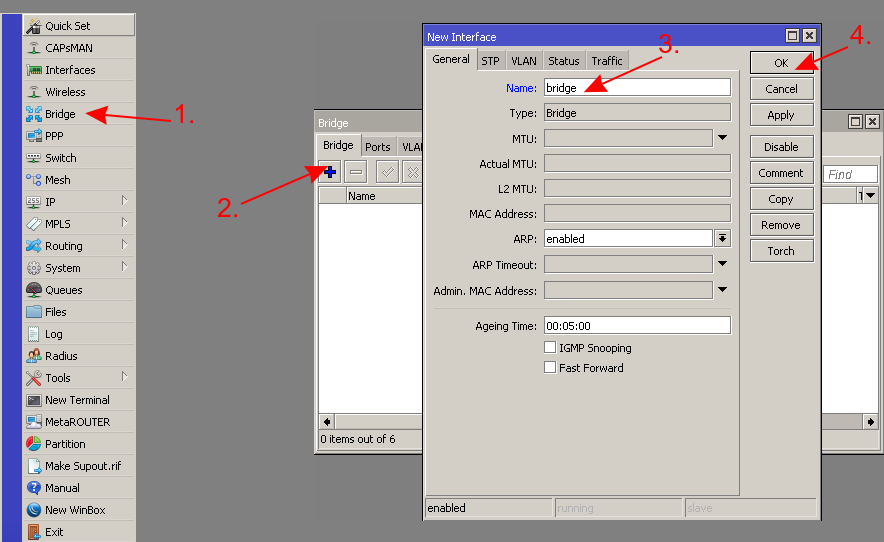
- Create a bridge
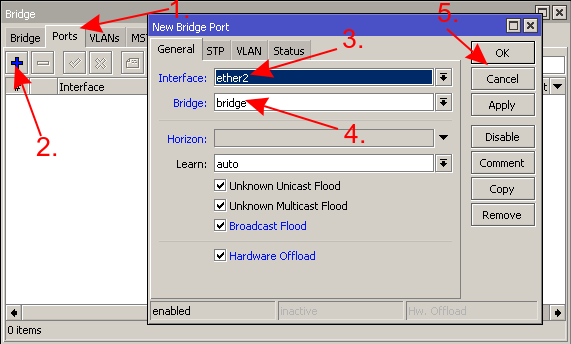
- Assign ports to the bridge
- Repeat the step to add more ports to the bridge
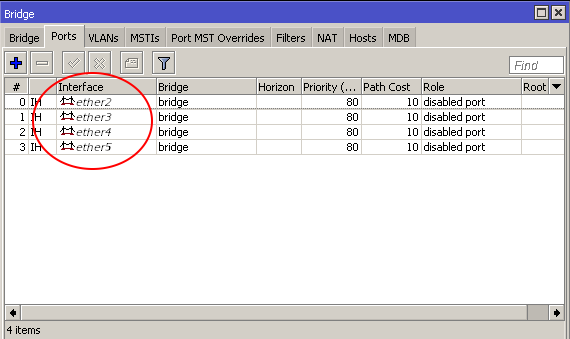
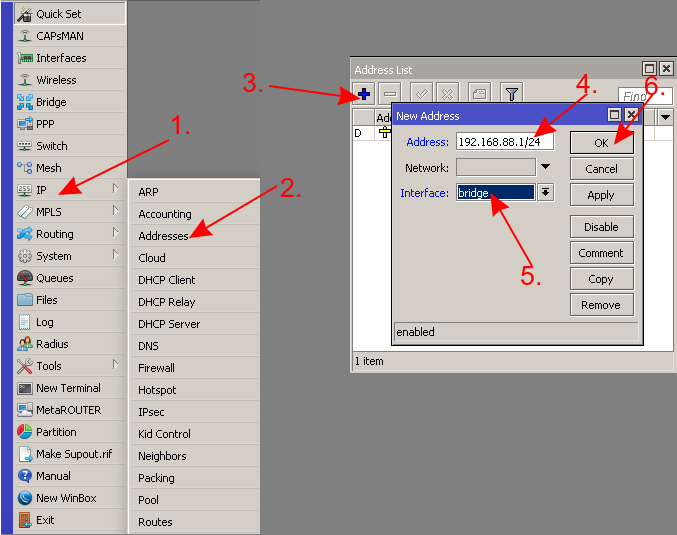
- Add an IP address to the bridge
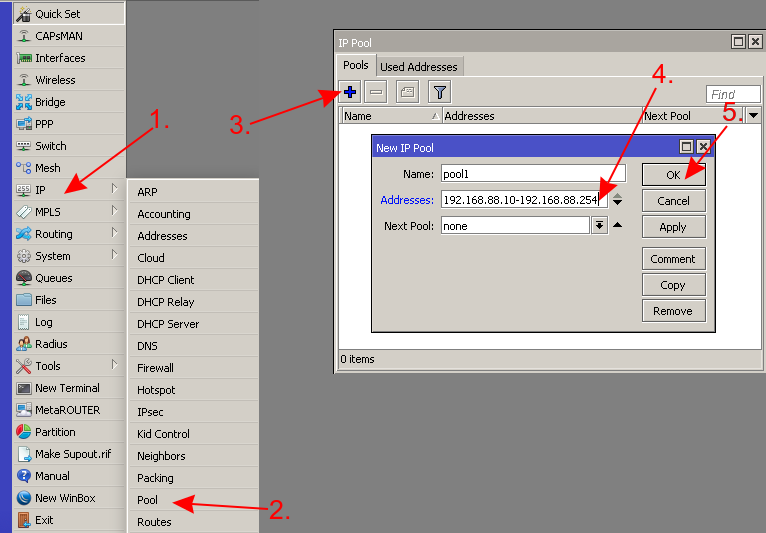
- Create a new address pool for the DHCP Server
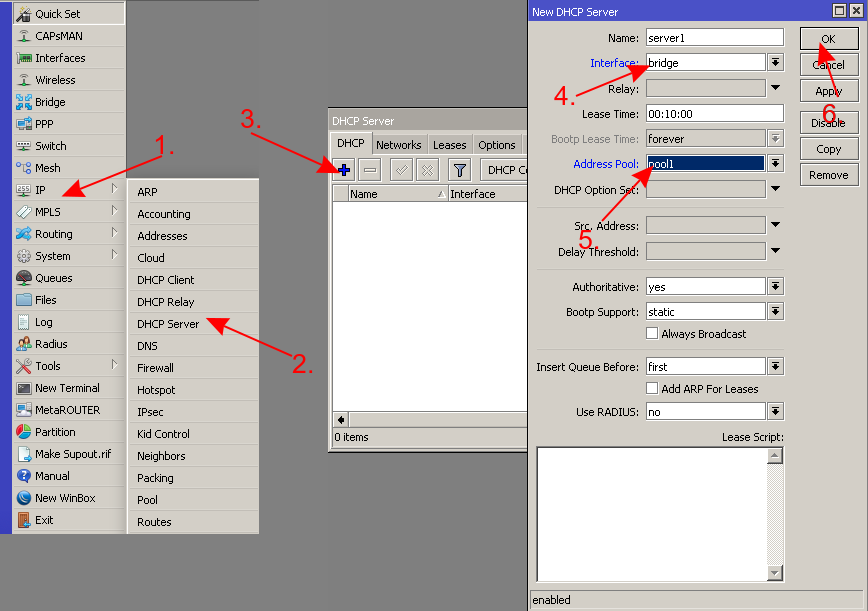
- Setup the DHCP Server
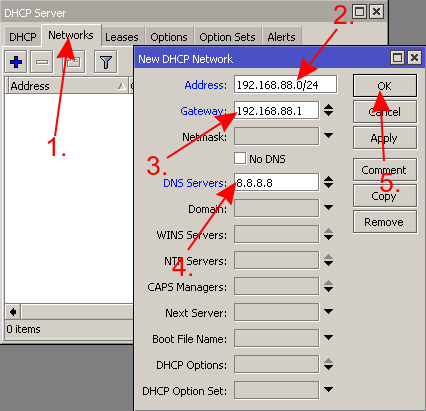
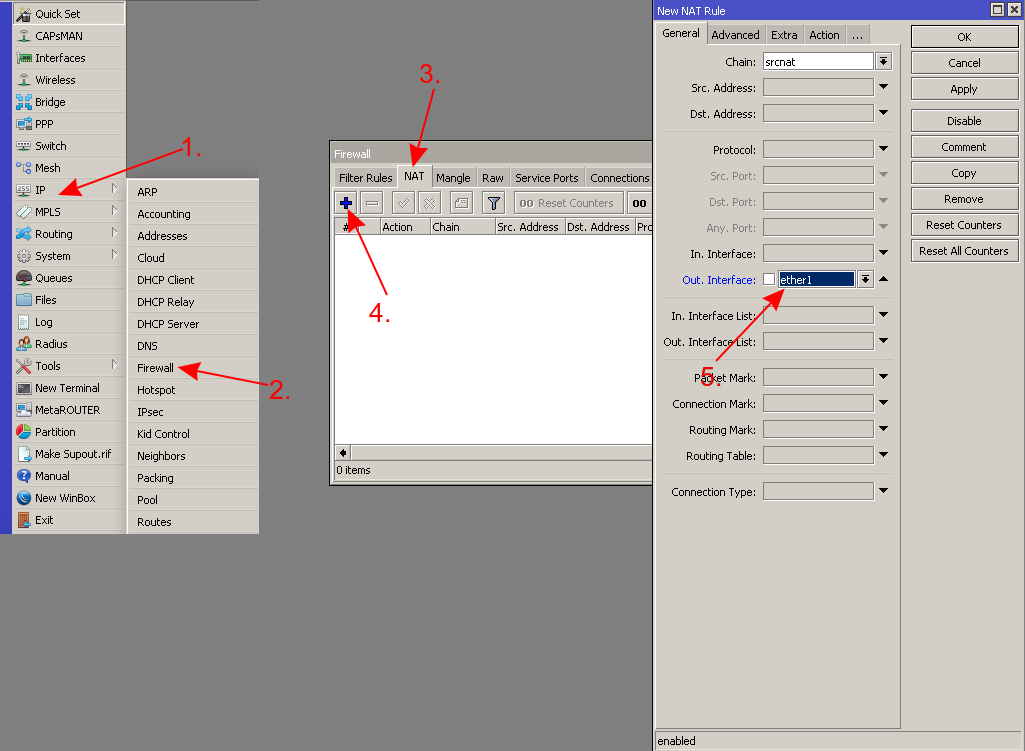
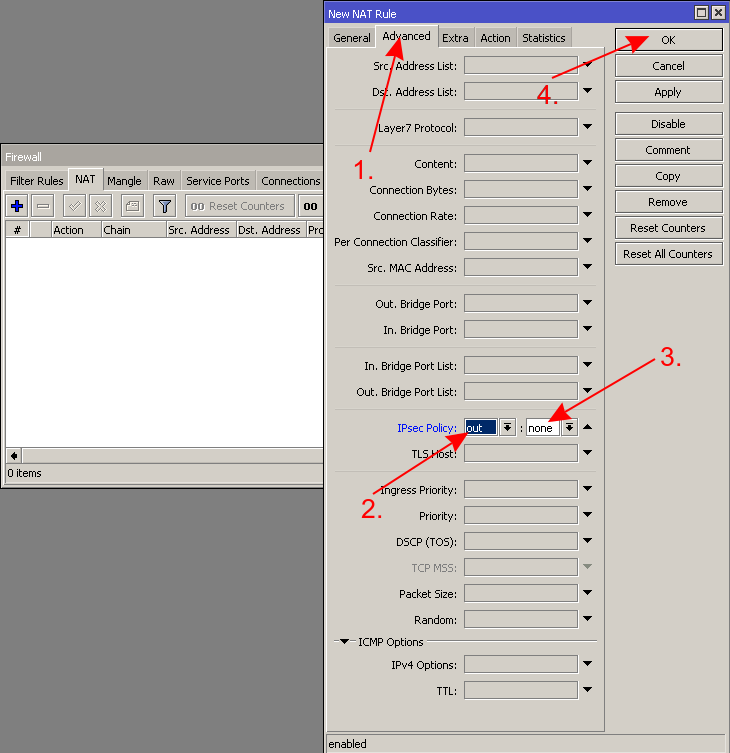
- Setup NAT on your router

Note: You can skip these steps in case you have reset your device to defaults, these steps were only required for devices with no configuration at all (empty config).
Step #2, setup CAPsMAN
Router
- Create a configuration template for all your CAPs
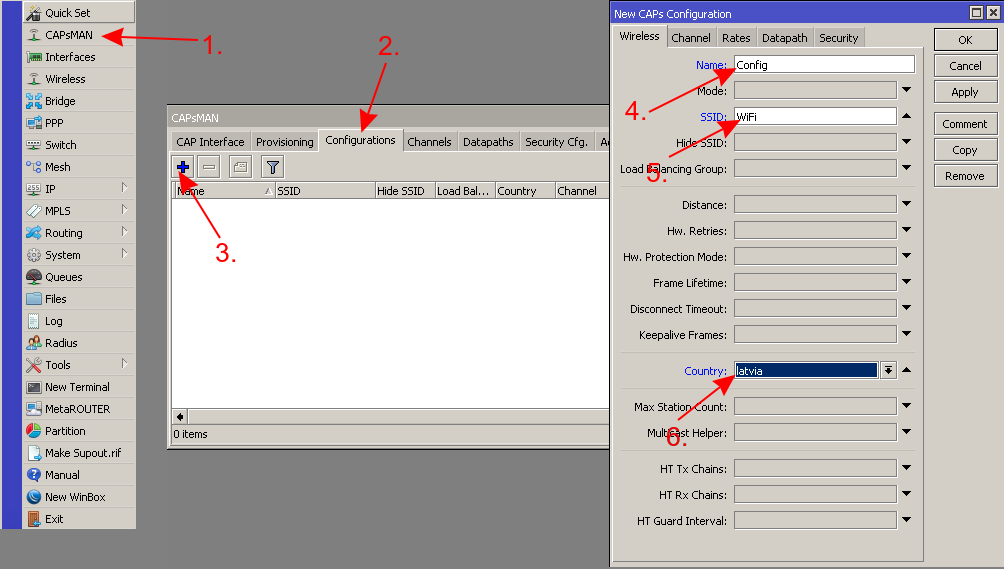
- Specify CAPsMAN to use the created configuration

Warning: Do NOT forget to change the country and the password. Select the right country or otherwise the CAP might select a frequency that is not supported in your area.
- For security reasons specify on which interfaces to listen to CAPs
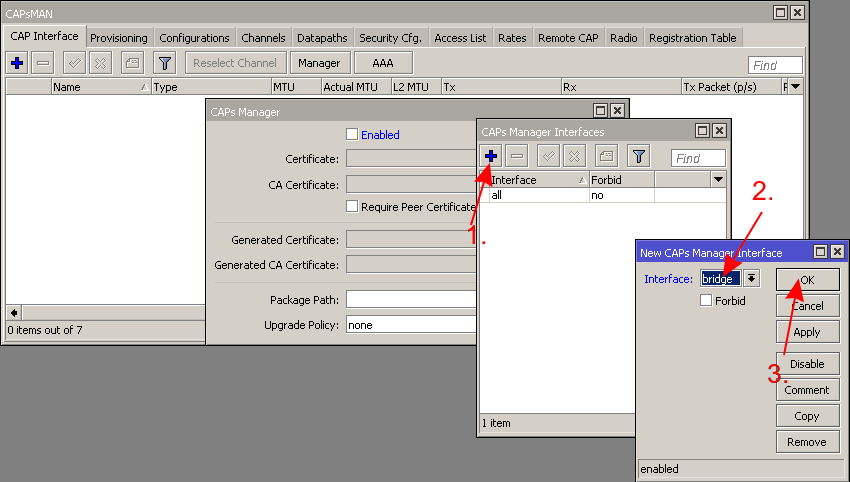
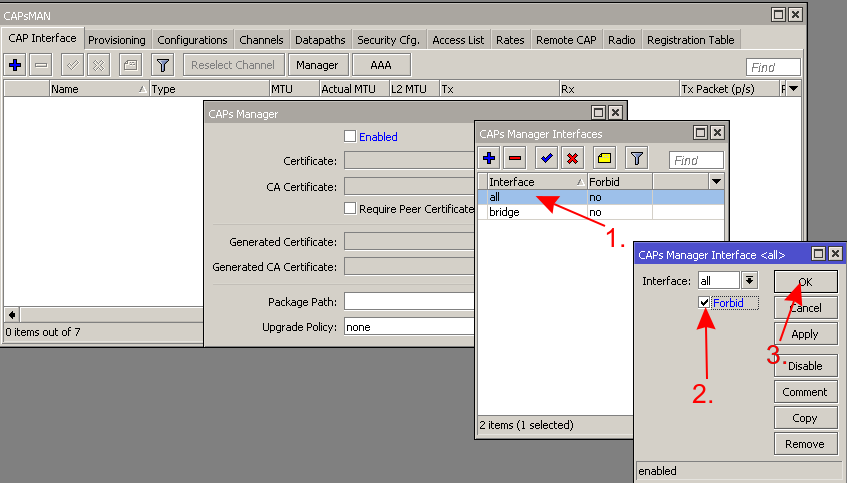

Note: If default configuration is used, then specifying CAPsMAN ports can be skipped since the default firewall will block all incoming traffic from WAN side. This step can also be skipped if firewall is setup properly to block unwanted traffic from other ports.
- Enable CAPsMAN manager to listen to CAPs
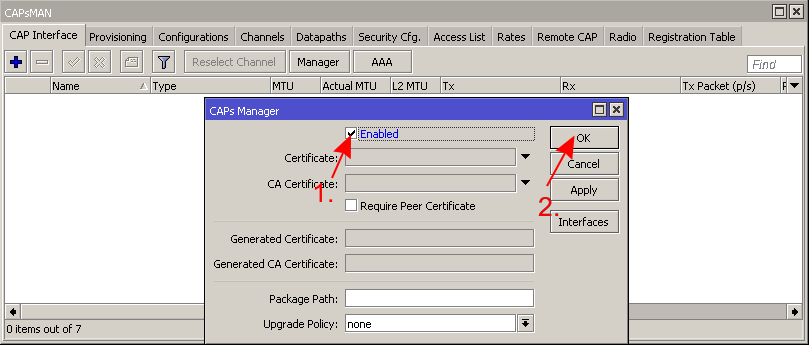
Step #3, setup CAPs

Note: This step can be skipped if you connect your CAP while it is in CAPs mode, the device will automatically add configuration that will work with this CAPsMAN setup. You can read more about how to put your device into CAPs mode Here. Make sure that your device supports CAPs mode.
CAPs
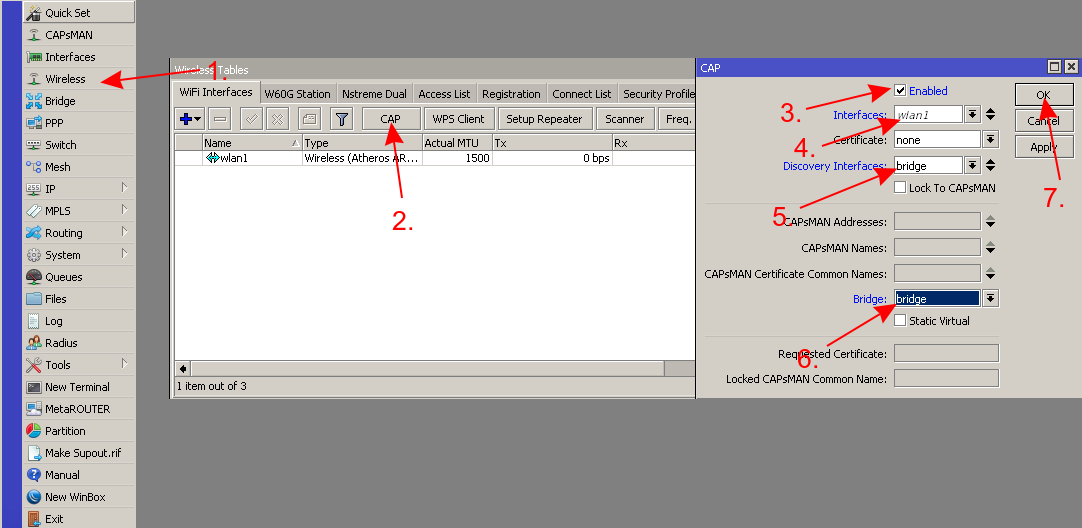
- Connect to your CAP, create a bridge

- Add the interface that is connected to the CAPsMAN in a bridge
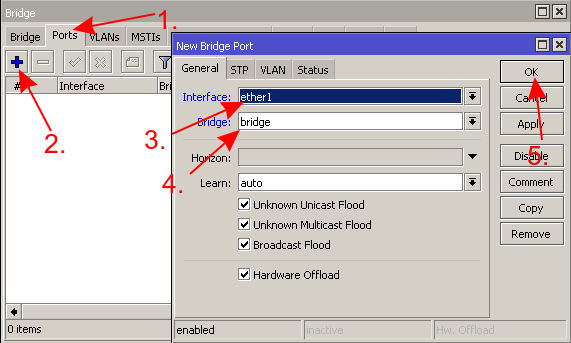
- Get an IP address from your router (or add a static IP address)
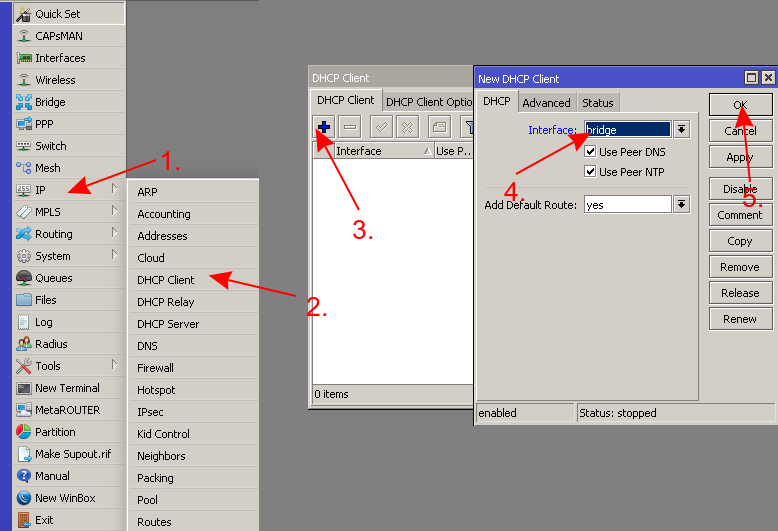
- Enable CAP on Wireless interfaces
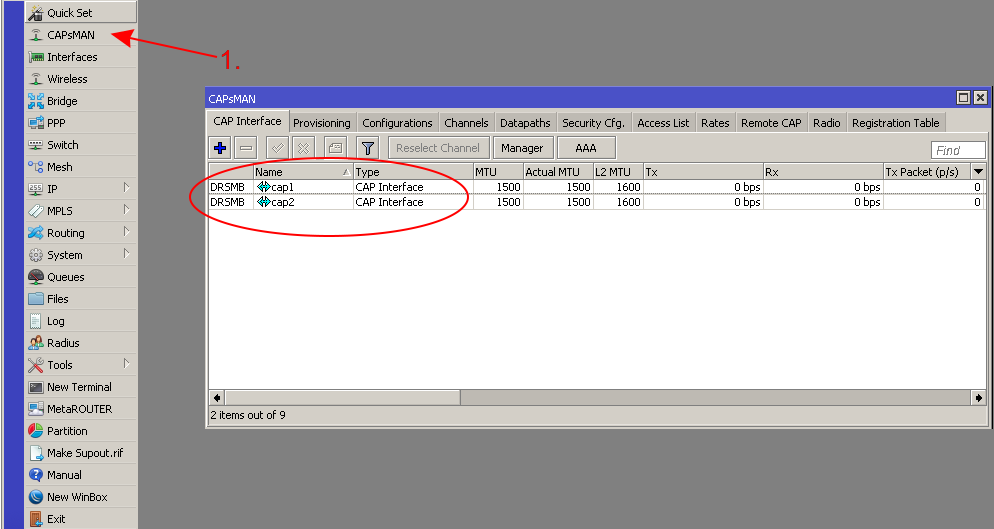
- Connect more CAPs to your CAPsMAN and they should appear as CAP interfaces in your CAPsMAN Router
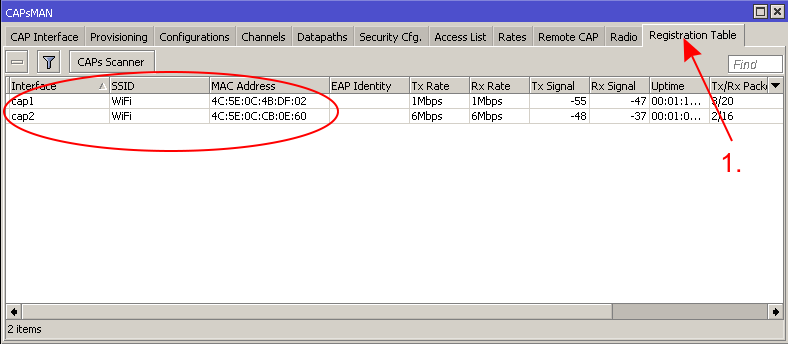
That is it! Check your connectivity by using another Wireless device, for example, your smarthphone, your device should be visible in the CAPsMAN Router's registration table:
Option #2, using CLI
Before you can start configuring CAPsMAN, you must configure your selected CAPsMAN device as a router. Here we will assume that ether1 is used as a WAN port and ether2-ether5 are used as LAN ports. You can skip Step1 if you are already using the default configuration on your router.
Step #1, setup router
Router
- Get an IP address from WAN (or add a static IP address)
/ip dhcp-client add disabled=no interface=ether1
- Create a bridge and add bridge ports to it
/interface bridge add name=bridge /interface bridge port add bridge=bridge interface=ether2 add bridge=bridge interface=ether3 add bridge=bridge interface=ether4 add bridge=bridge interface=ether5
- Add an IP address to the bridge
/ip address add address=192.168.88.1/24 interface=bridge
- Setup DHCP Server
/ip pool add name=pool1 ranges=192.168.88.10-192.168.88.254 /ip dhcp-server add address-pool=pool1 disabled=no interface=bridge /ip dhcp-server network add address=192.168.88.0/24 dns-server=8.8.8.8 gateway=192.168.88.1
- Setup NAT on your router
/ip firewall nat add action=masquerade chain=srcnat ipsec-policy=out,none out-interface=ether1

Note: You can skip these steps in case you have reset your device to defaults, these steps were only required for devices with no configuration at all (empty config).
Step #2, setup CAPsMAN
Router
- Create a configuration template for all your CAPs
/caps-man configuration add country=latvia datapath.bridge=bridge name=Config security.authentication-types=wpa-psk,wpa2-psk security.passphrase=secret_wifi_password ssid=WiFi /caps-man provisioning add action=create-dynamic-enabled master-configuration=Config

Warning: Do NOT forget to change the country and the password. Select the right country or otherwise the CAP might select a frequency that is not supported in your area.
- For security reasons specify on which interfaces to listen to CAPs
/caps-man manager interface set [ find default=yes ] forbid=yes add disabled=no interface=bridge

Note: If default configuration is used, then specifying CAPsMAN ports can be skipped since the default firewall will block all incoming traffic from WAN side. This step can also be skipped if firewall is setup properly to block unwanted traffic from other ports.
- Enable CAPsMAN manager to listen to CAPs
/caps-man manager set enabled=yes
Step #3, setup CAPs

Note: This step can be skipped if you connect your CAP while it is in CAPs mode, the device will automatically add configuration that will work with this CAPsMAN setup. You can read more about how to put your device into CAPs mode Here. Make sure that your device supports CAPs mode.
CAPs
- Connect to your CAP, create a bridge and add the interface that is connected to the CAPsMAN in a bridge
/interface bridge add name=bridge /interface bridge port add bridge=bridge interface=ether1
- Get an IP address from your router (or add a static IP address)
/ip dhcp-client add disabled=no interface=bridge
- Enable CAP on Wireless interfaces
/interface wireless cap set bridge=bridge discovery-interfaces=bridge enabled=yes interfaces=wlan1
- Connect more CAPs to your CAPsMAN and they should appear as CAP interfaces in your CAPsMAN Router
/caps-man interface print Flags: M - master, D - dynamic, B - bound, X - disabled, I - inactive, R - running # NAME RADIO-MAC 0 MDBR cap1 4C:5E:0C:0F:C8:48 1 MDBR cap2 4C:5E:0C:C0:D9:AA
That is it! Check your connectivity by using another Wireless device, for example, your smarthphone, your device should be visible in the CAPsMAN Router's registration table:
/caps-man registration-table print # INTERFACE SSID MAC-ADDRESS 0 cap1 WiFi 4C:5E:0C:4B:DF:02 1 cap2 WiFi 4C:5E:0C:CB:0E:60
Case studies
CAP in CAPsMAN
If your device has a Wireless interface and you want to use it as a CAPsMAN and a CAP, then it is possible, but it requires additional configuration. If you set your Wireless interface on your CAPsMAN to be managed by CAPsMAN, but the CAP interface is not showing up in CAPsMAN, then it is very likely that the Firewall on your Router is blocking traffic that is coming from the CAP interface.
- In case you are using the default configuration
/ip firewall filter add action=accept chain=input dst-address-type=local src-address-type=local place-before=[/ip firewall filter find where comment="defconf: drop all not coming from LAN"]
- In case you are NOT using the default configuration
/ip firewall filter add action=accept chain=input dst-address-type=local src-address-type=local
- If you have limited the CAPsMAN manager on certain interfaces, then you will have enable all CAPsMAN on all interfaces and forbid any interface that you don't want CAPsMAN to listen to:
/capsman manager interface remove [find where interface=bridge and forbid=no] set [find default=yes] forbid=no add forbid=yes interface=ether1