Manual:Basic VLAN switching: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Versions| v6.41 +}} | {{Versions| v6.41 +}} | ||
{{Warning|This manual is moved to https://help.mikrotik.com/docs/display/ROS/Basic+VLAN+switching}} | |||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| Line 65: | Line 67: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
/interface bridge | /interface bridge | ||
add name=bridge1 | add name=bridge1 | ||
/interface bridge port | /interface bridge port | ||
add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether1 hw=yes | add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether1 hw=yes | ||
| Line 88: | Line 90: | ||
{{ Note | This type of configuration should be used on RouterBOARD series devices, this includes RB4xx, RB9xx, RB2011, RB3011, hAP, hEX, cAP and other devices. }} | {{ Note | This type of configuration should be used on RouterBOARD series devices, this includes RB4xx, RB9xx, RB2011, RB3011, hAP, hEX, cAP and other devices. }} | ||
{{ Note | By default, the bridge interface is configured with <var>protocol-mode</var> set to <code>rstp</code>. For some devices, this can disable hardware offloading because specific switch chips do not support this feature. See the [[Manual:Interface/Bridge#Bridge_Hardware_Offloading | Bridge Hardware Offloading]] section with supported features. }} | |||
{{ Note | For devices that have multiple switch chips (for example, RB2011, RB3011, RB1100), each switch chip is only able to switch VLAN traffic between ports that are on the same switch chip, VLAN filtering will not work on a hardware level between ports that are on different switch chips, this means you should not add all ports to a single bridge if you are intending to use VLAN filtering using the switch chip, VLANs between switch chips will not get filtered. You can connect a single cable between both switch chips to work around this hardware limitation, another option is to use [[Manual:Basic_VLAN_switching#Other_devices_without_a_built-in_switch_chip | Bridge VLAN Filtering]], but it disables hardware offloading (and lowers the total throughput). }} | {{ Note | For devices that have multiple switch chips (for example, RB2011, RB3011, RB1100), each switch chip is only able to switch VLAN traffic between ports that are on the same switch chip, VLAN filtering will not work on a hardware level between ports that are on different switch chips, this means you should not add all ports to a single bridge if you are intending to use VLAN filtering using the switch chip, VLANs between switch chips will not get filtered. You can connect a single cable between both switch chips to work around this hardware limitation, another option is to use [[Manual:Basic_VLAN_switching#Other_devices_without_a_built-in_switch_chip | Bridge VLAN Filtering]], but it disables hardware offloading (and lowers the total throughput). }} | ||
Latest revision as of 11:03, 17 January 2022

Warning: This manual is moved to https://help.mikrotik.com/docs/display/ROS/Basic+VLAN+switching
Introduction
Many MikroTik devices come with a built-in switch chips that usually have an option to do VLAN switching on a hardware level, this means that you can achieve wire-speed performance using VLANs if a proper configuration method is used. The configuration method changes across different models, this guide will focus on setting up a basic trunk/access port setup with a management port from the trunk port using different devices with the right configuration to achieve best performance and to fully utilize the available hardware components.
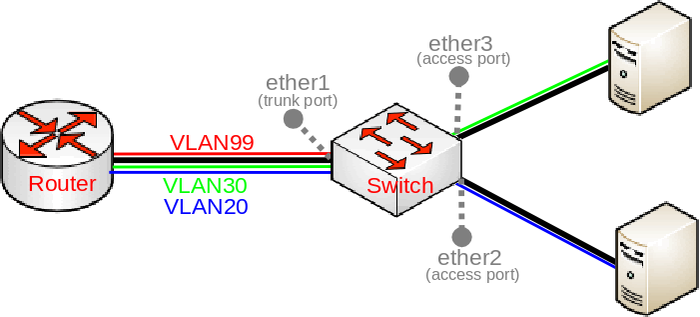
CRS3xx series switches
/interface bridge add name=bridge1 /interface bridge port add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether1 hw=yes add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether2 hw=yes pvid=20 add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether3 hw=yes pvid=30 /interface bridge vlan add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether1 untagged=ether2 vlan-ids=20 add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether1 untagged=ether3 vlan-ids=30 add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether1,bridge1 vlan-ids=99 /interface vlan add interface=bridge1 vlan-id=99 name=MGMT /ip address add address=192.168.99.1/24 interface=MGMT /interface bridge set bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes
More detailed examples can be found here.
CRS1xx/CRS2xx series switches
/interface bridge add name=bridge1 /interface bridge port add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether1 hw=yes add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether2 hw=yes add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether3 hw=yes /interface ethernet switch ingress-vlan-translation add ports=ether2 customer-vid=0 new-customer-vid=20 sa-learning=yes add ports=ether3 customer-vid=0 new-customer-vid=30 sa-learning=yes /interface ethernet switch egress-vlan-tag add tagged-ports=ether1 vlan-id=20 add tagged-ports=ether1 vlan-id=30 add tagged-ports=ether1,switch1-cpu vlan-id=99 /interface ethernet switch vlan add ports=ether1,ether2 vlan-id=20 learn=yes add ports=ether1,ether3 vlan-id=30 learn=yes add ports=ether1,switch1-cpu vlan-id=99 learn=yes /interface vlan add interface=bridge1 vlan-id=99 name=MGMT /ip address add address=192.168.99.1/24 interface=MGMT /interface ethernet switch set drop-if-invalid-or-src-port-not-member-of-vlan-on-ports=ether1,ether2,ether3
More detailed examples can be found here.
Other devices with built-in switch chip

Warning: Not all devices with a switch chip are capable of VLAN switching on a hardware level, check the supported features for each switch chip, the compatibility table can be found Here. If a device has VLAN table support, then it is capable of VLAN switching using the built-in switch chip. You can check the device's switch chip either in the provided link or by using /interface ethernet switch print
/interface bridge add name=bridge1 /interface bridge port add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether1 hw=yes add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether2 hw=yes add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether3 hw=yes /interface ethernet switch vlan add ports=ether1,ether2 switch=switch1 vlan-id=20 add ports=ether1,ether3 switch=switch1 vlan-id=30 add ports=ether1,switch1-cpu switch=switch1 vlan-id=99 /interface vlan add interface=bridge1 vlan-id=99 name=MGMT /ip address add address=192.168.99.1/24 interface=MGMT /interface ethernet switch port set ether1 vlan-mode=secure vlan-header=add-if-missing set ether2 vlan-mode=secure vlan-header=always-strip default-vlan-id=20 set ether3 vlan-mode=secure vlan-header=always-strip default-vlan-id=30 set switch1-cpu vlan-header=leave-as-is vlan-mode=secure
More detailed examples can be found here.

Note: This type of configuration should be used on RouterBOARD series devices, this includes RB4xx, RB9xx, RB2011, RB3011, hAP, hEX, cAP and other devices.

Note: By default, the bridge interface is configured with protocol-mode set to rstp. For some devices, this can disable hardware offloading because specific switch chips do not support this feature. See the Bridge Hardware Offloading section with supported features.

Note: For devices that have multiple switch chips (for example, RB2011, RB3011, RB1100), each switch chip is only able to switch VLAN traffic between ports that are on the same switch chip, VLAN filtering will not work on a hardware level between ports that are on different switch chips, this means you should not add all ports to a single bridge if you are intending to use VLAN filtering using the switch chip, VLANs between switch chips will not get filtered. You can connect a single cable between both switch chips to work around this hardware limitation, another option is to use Bridge VLAN Filtering, but it disables hardware offloading (and lowers the total throughput).
Other devices without a built-in switch chip
It is possible to do VLAN filtering using the CPU, there are multiple ways to do it, but it is highly recommended by using bridge VLAN filtering.
/interface bridge add name=bridge1 /interface bridge port add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether1 hw=no add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether2 hw=no pvid=20 add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether3 hw=no pvid=30 /interface bridge vlan add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether1 untagged=ether2 vlan-ids=20 add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether1 untagged=ether3 vlan-ids=30 add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether1,bridge1 vlan-ids=99 /interface vlan add interface=bridge1 vlan-id=99 name=MGMT /ip address add address=192.168.99.1/24 interface=MGMT /interface bridge set bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes
More detailed examples can be found here.
