Manual:IP/DNS: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (24 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Note| This page is out of date, please use the new documentation: [https://help.mikrotik.com/docs/display/ROS/DNS#DNS-DNSoverHTTPS(DoH)].}} | |||
{{Versions|v4.6}} | {{Versions|v4.6}} | ||
DNS cache is used to minimize DNS requests to an external DNS server as well as to minimize DNS resolution time. This is a simple | DNS cache is used to minimize DNS requests to an external DNS server as well as to minimize DNS resolution time. This is a simple DNS cache with local items. | ||
==Specifications== | ==Specifications== | ||
| Line 17: | Line 23: | ||
==DNS Cache Setup== | ==DNS Cache Setup== | ||
<p id="shbox"><b>Sub-menu:</b> <code>/ip dns</code></p> | |||
====Description==== | DNS facility is used to provide domain name resolution for router itself as well as for the clients connected to it. | ||
====Properties==== | |||
{{Mr-arg-table-h | |||
|prop=Property | |||
|desc=Description | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table | |||
|arg=allow-remote-requests | |||
|type=yes {{!}} no | |||
|default=no | |||
|desc=Specifies whether to allow network requests | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table | |||
|arg=cache-max-ttl | |||
|type=time | |||
|default=1w | |||
|desc=Maximum time-to-live for cache records. In other words, cache records will expire unconditionally after cache-max-ttl time. Shorter TTL received from DNS servers are respected. | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table | |||
|arg=cache-size | |||
|type=integer[64..4294967295] | |||
|default=2048 | |||
|desc=Specifies the size of DNS cache in KiB | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table | |||
|arg=max-concurrent-queries | |||
|type=integer | |||
|default=100 | |||
|desc=Specifies how much concurrent queries are allowed | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table | |||
|arg=max-concurrent-tcp-sessions | |||
|type=integer | |||
|default=20 | |||
|desc=Specifies how much concurrent TCP sessions are allowed | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table | |||
|arg=max-udp-packet-size | |||
|type=integer [50..65507] | |||
|default=4096 | |||
|desc=Maximum size of allowed UDP packet. | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table | |||
|arg=query-server-timeout | |||
|type=time | |||
|default=2s | |||
|desc=Specifies how long to wait for query response from one server | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table | |||
|arg=query-total-timeout | |||
|type=time | |||
|default=10s | |||
|desc=Specifies how long to wait for query response in total. Note that this setting must be configured taking into account <var>query-server-timeout</var> and number of used DNS server. | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table-end | |||
|arg=servers | |||
|type=list of IPv4/IPv6 addresses | |||
|default= | |||
|desc=List of DNS server IPv4/IPv6 addresses | |||
}} | |||
Read-only Properties | |||
{{Mr-arg-table-h | |||
|prop=Property | |||
|desc=Description | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-ro-table | |||
|arg=cache-used | |||
|type=integer | |||
|desc=Shows the currently used cache size in KiB | |||
}} | |||
DNS | {{Mr-arg-ro-table-end | ||
|arg=dynamic-server | |||
|type=IPv4/IPv6 list | |||
|desc=List of dynamically added DNS server from different services, for example, DHCP. | |||
}} | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
{{ Note| | |||
When both static and dynamic servers are set, static server entries are more preferred, however it does not indicate that static server will always be used (for example, previously query was received from dynamic server, but static was added later, then dynamic entry will be preferred). | |||
{{Note| If '''''allow-remote-requests''''' is used make sure that you limit access to your server over TCP and UDP protocol.}} | |||
====Example==== | ====Example==== | ||
| Line 134: | Line 208: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="border-bottom:1px solid gray;" valign="top"|'''name''' (text) | |style="border-bottom:1px solid gray;" valign="top"|'''name''' (text) | ||
|style="border-bottom:1px solid gray;" valign="top"|DNS name to be resolved to a given IP address. | |style="border-bottom:1px solid gray;" valign="top"|DNS name to be resolved to a given IP address. | ||
|- | |||
|style="border-bottom:1px solid gray;" valign="top"|'''regex''' (text) | |||
|style="border-bottom:1px solid gray;" valign="top"|DNS regex | |||
|- | |- | ||
|style="border-bottom:1px solid gray;" valign="top"|'''ttl''' (time) | |style="border-bottom:1px solid gray;" valign="top"|'''ttl''' (time) | ||
|style="border-bottom:1px solid gray;" valign="top"|time-to-live of the DNS record | |style="border-bottom:1px solid gray;" valign="top"|time-to-live of the DNS record | ||
|- | |||
|style="border-bottom:1px solid gray;" valign="top"|'''type''' (text) | |||
|style="border-bottom:1px solid gray;" valign="top"|type of the DNS record. Available values are: A, AAAA, CNAME, FWD, MX, NS, NXDOMAIN, SRV, TXT | |||
|} | |} | ||
===Notes=== | ===Notes=== | ||
Reverse DNS lookup (Address to Name) of the regular expression entries is not possible. You can, however, add an additional plain record with the same IP address and specify some name for it. | Reverse DNS lookup (Address to Name) of the regular expression entries is not possible. You can, however, add an additional plain record with the same IP address and specify some name for it. | ||
Remember that the meaning of a dot (.) in regular expressions is any character, so the expression should be escaped properly. For example, if you need to match anything within example.com domain but not all the domains that just end with ''example.com'', like ''www.another-example.com'', use '' | Remember that the meaning of a dot (.) in regular expressions is any character, so the expression should be escaped properly. For example, if you need to match anything within example.com domain but not all the domains that just end with ''example.com'', like ''www.another-example.com'', use ''regexp=".*\\.example\\.com\$"'' | ||
Regular expression matching is significantly slower than of the plain entries, so it is advised to minimize the number of regular expression rules and optimize the expressions themselves. | Regular expression matching is significantly slower than of the plain entries, so it is advised to minimize the number of regular expression rules and optimize the expressions themselves. | ||
| Line 151: | Line 232: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
[admin@MikroTik] ip dns static> add name www.example.com address=10.0.0.1 | [admin@MikroTik] ip dns static> add name=www.example.com address=10.0.0.1 | ||
[admin@MikroTik] ip dns static> print | [admin@MikroTik] ip dns static> print | ||
Flags: D - dynamic, X - disabled, R - regexp | Flags: D - dynamic, X - disabled, R - regexp | ||
| Line 157: | Line 238: | ||
0 www.example.com 10.0.0.1 1d | 0 www.example.com 10.0.0.1 1d | ||
[admin@MikroTik] ip dns static> | [admin@MikroTik] ip dns static> | ||
</pre> | |||
It is also possible to forward specific DNS requests to a different server using <var>FWD</var> type. This will fordward all subdomains of "example.com" to server 10.0.0.1: | |||
<pre> | |||
[admin@MikroTik] ip dns static> add regexp=".*\\.example\\.com\$" forward-to=10.0.0.1 | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
{{Note| '''''regexp''''' entries are case sensitive, but since DNS requests are not case sensitive, RouterOS converts DNS names to lowercase, you should write regex only with lowercase letters.}} | |||
==Flushing DNS cache== | ==Flushing DNS cache== | ||
| Line 178: | Line 268: | ||
[admin@MikroTik] ip dns> cache flush | [admin@MikroTik] ip dns> cache flush | ||
[admin@MikroTik] ip dns> print | [admin@MikroTik] ip dns> print | ||
servers: 159.148.60.2 | |||
allow-remote-requests: yes | allow-remote-requests: yes | ||
cache-size: 2048 KiB | cache-size: 2048 KiB | ||
| Line 186: | Line 275: | ||
[admin@MikroTik] ip dns> | [admin@MikroTik] ip dns> | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
==DNS over HTTPS== | |||
Starting from RouterOS version v6.47 it is possible to use DNS over HTTPS (DoH). DoH uses HTTPS protocol to send and receive DNS requests for better data integrity. Its main goal is to provide privacy by eliminating the man in the middle attacks (MITM). Currently DoH is not compatible with FWD type static entries, in order to utilize FWD entries, DoH must not be configured. | |||
===Example=== | |||
It is advised to import the root CA certificate of the DoH server you have chosen to use for increased security. | |||
{{Warning | We strongly suggest not use third-party download links for certificate fetching. Use the Certificate Authority's own website.}} | |||
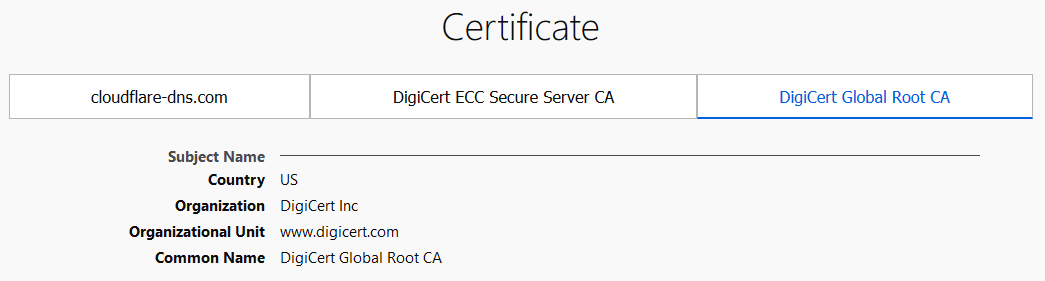
There are various ways to find out what root CA certificate is necessary. The easiest way is by using your WEB browser, navigating to the DoH site and checking the websites security. Using Firefox we can see that DigiCert Global Root CA is used by CloudFlare DoH server. You can download the certificate straight from the browser or navigate to DigiCert website and fetch the certificate from a trusted source. | |||
[[file:Rootca.PNG]] | |||
Download the certificate and import it: | |||
<pre> | |||
/tool fetch url="https://cacerts.digicert.com/DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem" | |||
/certificate import file-name=DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem | |||
</pre> | |||
Configure the DoH server: | |||
<pre> | |||
/ip dns set use-doh-server=https://cloudflare-dns.com/dns-query verify-doh-cert=yes | |||
</pre> | |||
Note that you need at least one regular DNS server configured for the router to resolve the DoH hostname itself. If you do not have any dynamical or static DNS server configured, you can configure a static DNS entry like this: | |||
<pre> | |||
/ip dns static | |||
add address=1.1.1.1 name=cloudflare-dns.com | |||
</pre> | |||
{{Note| RouterOS prioritize DoH over DNS server if both are configured on the device. }} | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Regular_Expressions/POSIX_Basic_Regular_Expressions | |||
* http://www.freesoft.org/CIE/Course/Section2/3.htm | * http://www.freesoft.org/CIE/Course/Section2/3.htm | ||
* http://www.networksorcery.com/enp/protocol/dns.htm | * http://www.networksorcery.com/enp/protocol/dns.htm | ||
* [http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1035.txt?number=1035 RFC1035] | * [http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1035.txt?number=1035 RFC1035] | ||
[[Category:Manual]] | [[Category:Manual|D]] | ||
[[Category:IP]] | [[Category:IP|D]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:07, 9 January 2024

Note: This page is out of date, please use the new documentation: [1].
DNS cache is used to minimize DNS requests to an external DNS server as well as to minimize DNS resolution time. This is a simple DNS cache with local items.
Specifications
- Packages required: system
- License required: Level1
- Submenu level: /ip dns
- Standards and Technologies: DNS
- Hardware usage: Not significant
Description
A MikroTik router with DNS feature enabled can be set as a DNS server for any DNS-compliant client. Moreover, MikroTik router can be specified as a primary DNS server under its dhcp-server settings. When the remote requests are enabled, the MikroTik router responds to TCP and UDP DNS requests on port 53.
DNS Cache Setup
Sub-menu: /ip dns
DNS facility is used to provide domain name resolution for router itself as well as for the clients connected to it.
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| allow-remote-requests (yes | no; Default: no) | Specifies whether to allow network requests |
| cache-max-ttl (time; Default: 1w) | Maximum time-to-live for cache records. In other words, cache records will expire unconditionally after cache-max-ttl time. Shorter TTL received from DNS servers are respected. |
| cache-size (integer[64..4294967295]; Default: 2048) | Specifies the size of DNS cache in KiB |
| max-concurrent-queries (integer; Default: 100) | Specifies how much concurrent queries are allowed |
| max-concurrent-tcp-sessions (integer; Default: 20) | Specifies how much concurrent TCP sessions are allowed |
| max-udp-packet-size (integer [50..65507]; Default: 4096) | Maximum size of allowed UDP packet. |
| query-server-timeout (time; Default: 2s) | Specifies how long to wait for query response from one server |
| query-total-timeout (time; Default: 10s) | Specifies how long to wait for query response in total. Note that this setting must be configured taking into account query-server-timeout and number of used DNS server. |
| servers (list of IPv4/IPv6 addresses; Default: ) | List of DNS server IPv4/IPv6 addresses |
Read-only Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| cache-used (integer) | Shows the currently used cache size in KiB |
| dynamic-server (IPv4/IPv6 list) | List of dynamically added DNS server from different services, for example, DHCP. |
When both static and dynamic servers are set, static server entries are more preferred, however it does not indicate that static server will always be used (for example, previously query was received from dynamic server, but static was added later, then dynamic entry will be preferred).

Note: If allow-remote-requests is used make sure that you limit access to your server over TCP and UDP protocol.
Example
To set 159.148.60.2 as the primary DNS server and allow the router to be used as a DNS server, do the following:
[admin@MikroTik] ip dns> set servers=159.148.60.2 \
\... allow-remote-requests=yes
[admin@MikroTik] ip dns> print
servers: 159.148.60.2
allow-remote-requests: yes
cache-size: 2048KiB
cache-max-ttl: 1w
cache-used: 7KiB
[admin@MikroTik] ip dns>
Cache Monitoring
- Submenu level: /ip dns cache
Description
This menu provides a list with all address (DNS type "A") records stored on the server
Property Description
| Property | Desciption |
|---|---|
| address (read-only: IP address) | IP address of the host |
| name (read-only: name) | DNS name of the host |
| ttl (read-only: time) | remaining time-to-live for the record |
All DNS Entries
- Submenu level: /ip dns cache all
Description
This menu provides a complete list with all DNS records stored on the server
Property Description
| Property | Desciption |
|---|---|
| data (read-only: text) | DNS data field. IP address for type "A" records. Other record types may have different contents of the data field (like hostname or arbitrary text) |
| name (read-only: name) | DNS name of the host |
| ttl (read-only: time) | remaining time-to-live for the record |
| type (read-only: text) | DNS record type |
Static DNS Entries
- Submenu level: /ip dns static
Description
The MikroTik RouterOS has an embedded DNS server feature in DNS cache. It allows you to link the particular domain names with the respective IP addresses and advertize these links to the DNS clients using the router as their DNS server. This feature can also be used to provide fake DNS information to your network clients. For example, resolving any DNS request for a certain set of domains (or for the whole Internet) to your own page.
The server is capable of resolving DNS requests based on POSIX basic regular expressions, so that multiple requets can be matched with the same entry. In case an entry does not conform with DNS naming standards, it is considered a regular expression and marked with ‘R’ flag. The list is ordered and is checked from top to bottom. Regular expressions are checked first, then the plain records.
Property Description
| Property | Desciption |
|---|---|
| address (IP address) | IP address to resolve domain name with |
| name (text) | DNS name to be resolved to a given IP address. |
| regex (text) | DNS regex |
| ttl (time) | time-to-live of the DNS record |
| type (text) | type of the DNS record. Available values are: A, AAAA, CNAME, FWD, MX, NS, NXDOMAIN, SRV, TXT |
Notes
Reverse DNS lookup (Address to Name) of the regular expression entries is not possible. You can, however, add an additional plain record with the same IP address and specify some name for it.
Remember that the meaning of a dot (.) in regular expressions is any character, so the expression should be escaped properly. For example, if you need to match anything within example.com domain but not all the domains that just end with example.com, like www.another-example.com, use regexp=".*\\.example\\.com\$"
Regular expression matching is significantly slower than of the plain entries, so it is advised to minimize the number of regular expression rules and optimize the expressions themselves. Example
To add a static DNS entry for www.example.com to be resolved to 10.0.0.1 IP address:
[admin@MikroTik] ip dns static> add name=www.example.com address=10.0.0.1 [admin@MikroTik] ip dns static> print Flags: D - dynamic, X - disabled, R - regexp # NAME ADDRESS TTL 0 www.example.com 10.0.0.1 1d [admin@MikroTik] ip dns static>
It is also possible to forward specific DNS requests to a different server using FWD type. This will fordward all subdomains of "example.com" to server 10.0.0.1:
[admin@MikroTik] ip dns static> add regexp=".*\\.example\\.com\$" forward-to=10.0.0.1

Note: regexp entries are case sensitive, but since DNS requests are not case sensitive, RouterOS converts DNS names to lowercase, you should write regex only with lowercase letters.
Flushing DNS cache
- Command name: /ip dns cache flush
Command Description
| Command | Desciption |
|---|---|
| flush | clears internal DNS cache |
Example
[admin@MikroTik] ip dns> cache flush
[admin@MikroTik] ip dns> print
servers: 159.148.60.2
allow-remote-requests: yes
cache-size: 2048 KiB
cache-max-ttl: 1w
cache-used: 10 KiB
[admin@MikroTik] ip dns>
DNS over HTTPS
Starting from RouterOS version v6.47 it is possible to use DNS over HTTPS (DoH). DoH uses HTTPS protocol to send and receive DNS requests for better data integrity. Its main goal is to provide privacy by eliminating the man in the middle attacks (MITM). Currently DoH is not compatible with FWD type static entries, in order to utilize FWD entries, DoH must not be configured.
Example
It is advised to import the root CA certificate of the DoH server you have chosen to use for increased security.

Warning: We strongly suggest not use third-party download links for certificate fetching. Use the Certificate Authority's own website.
There are various ways to find out what root CA certificate is necessary. The easiest way is by using your WEB browser, navigating to the DoH site and checking the websites security. Using Firefox we can see that DigiCert Global Root CA is used by CloudFlare DoH server. You can download the certificate straight from the browser or navigate to DigiCert website and fetch the certificate from a trusted source.
Download the certificate and import it:
/tool fetch url="https://cacerts.digicert.com/DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem" /certificate import file-name=DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem
Configure the DoH server:
/ip dns set use-doh-server=https://cloudflare-dns.com/dns-query verify-doh-cert=yes
Note that you need at least one regular DNS server configured for the router to resolve the DoH hostname itself. If you do not have any dynamical or static DNS server configured, you can configure a static DNS entry like this:
/ip dns static add address=1.1.1.1 name=cloudflare-dns.com