Manual:MLPPP over single and multiple links: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Summary == | == Summary == | ||
<p id="shbox"><b>Standards:</b> <code>RFC 1990</code><br /> | |||
<b>Package:</b> <code>ppp</code> | |||
</p> | |||
Large packets are actually split into bits and sent evenly | |||
Multi-Link Point to Point Protocol (MP, Multi-Link PPP, MultiPPP or MLPPP) is a method of splitting, recombining, and sequencing data across multiple logical data links. | |||
In a situation where we have multiple DSL links a pair of devices, performance by “widening the pipe” between two devices can be increased by using Multi-Link PPP, without going to a newer, more expensive technology. | |||
Large packets are actually split into bits and sent evenly over ALL logical data links. This is done instantaneously with NO loss of bandwidth. It is important to understand that other end of the link needs to use the same protocol to recombine your data. | |||
Multilink is based on an [[LCP]] option negotiation that allows to indicate to its peer that it is capable of combining multiple physical links. | |||
== MLPPP over single link == | == MLPPP over single link == | ||
Typically size of the packet sent over PPP link is reduced due to overhead. MP can be used to transmit and receive full frame over single ppp link. To make it work the Multilink Protocol uses additional LCP configuration options '''Multilink Maximum Received Reconstructed Unit (MRRU)''' | |||
To enable Multi-link PPP over single link you must specify MRRU (Maximum Receive Reconstructed Unit) option. If both sides support this feature there are no need for MSS adjustment (in firewall mangle). Study shows that MRRU is less CPU expensive that 2 mangle rules per client. MRRU allows to divide packet to multiple channels therefore increasing possible MTU and MRU (up to 65535 bytes) | To enable Multi-link PPP over single link you must specify MRRU (Maximum Receive Reconstructed Unit) option. If both sides support this feature there are no need for MSS adjustment (in firewall mangle). Study shows that MRRU is less CPU expensive that 2 mangle rules per client. MRRU allows to divide packet to multiple channels therefore increasing possible MTU and MRU (up to 65535 bytes) | ||
Under Windows it can be enabled in Networking tag, Settings button, "Negotiate multi-link for single link connections". Their MRRU is hard coded to 1614. | Under Windows it can be enabled in Networking tag, Settings button, "Negotiate multi-link for single link connections". Their MRRU is hard coded to 1614. | ||
{{Note | MTU will be reduced by 4 bytes to work properly when MPPE encryption is enabled}} | |||
=== Configuration Example=== | === Configuration Example=== | ||
[[ | Let's configure pppoe server compatible with Windows clients and MRRU enabled. | ||
<pre> | |||
[admin@RB800] /interface pppoe-server server> add service-name=myPPP interface=ether1 mrru=1614 | |||
[admin@RB800] /interface pppoe-server server> print | |||
Flags: X - disabled | |||
0 service-name="myPPP" interface=ether1 max-mtu=1480 max-mru=1480 mrru=1614 | |||
authentication=pap,chap,mschap1,mschap2 keepalive-timeout=10 one-session-per-host=no | |||
max-sessions=0 default-profile=default | |||
</pre> | |||
In short - standard PPP link - just specify MRRU in both sides :) | In short - standard PPP link - just specify MRRU in both sides :) | ||
| Line 24: | Line 47: | ||
=== Configuration Example === | === Configuration Example === | ||
[[ | |||
[[File:mlppp.png|700px]] | |||
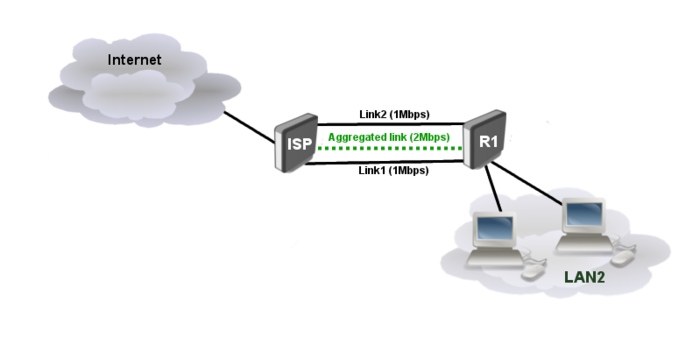
ISP gives to its client two physical links (DSL lines) 1Mbps each. To get aggregated 2Mbps pipe we have to set up MLPPP. Consider ISP router is pre-configured to support MLPPP. | |||
Configuration on Mikorotik router (R1) is: | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface pppoe-client | |||
add service-name=ISP interface=ether1,ether2 user=xxx password=yyy disabled=no \ | |||
add-default-route=yes use-peer-dns=yes | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
[admin@RB800] /interface pppoe-client> print | |||
Flags: X - disabled, R - running | |||
0 name="pppoe-out1" max-mtu=1480 max-mru=1480 mrru=disabled interface=ether1,ether2 | |||
user="xxx" password="yyy" profile=default service-name="ISP" ac-name="" add-default-route=yes | |||
dial-on-demand=no use-peer-dns=yes allow=pap,chap,mschap1,mschap2 | |||
</pre> | |||
Now when pppoe client is connected we can set up rest of configuration, local network address, enable dns requests, set up masquerade and firewall | |||
<pre> | |||
/ip address add address=192.168.88.1/24 interface=local | |||
/ip dns set allow-remote-request=yes | |||
/ip firewall nat | |||
add chain=src-nat action=masquerade out-interface=pppoe-out1 | |||
/ip firewall filter | |||
add chain=input connection-state=invalid action=drop \ | |||
comment="Drop Invalid connections" | |||
add chain=input connection-state=established action=accept \ | |||
comment="Allow Established connections" | |||
add chain=input protocol=icmp action=accept \ | |||
comment="Allow ICMP" | |||
add chain=input src-address=192.168.88.0/24 action=accept \ | |||
in-interface=!pppoe-out1 | |||
add chain=input action=drop comment="Drop everything else" | |||
</pre> | |||
For more advanced router and customer protection check [[Manual:IP/Firewall/Filter | firewall examples]]. | |||
==See Also== | |||
* [[Manual:Interface/PPPoE | PPPOE ]] | |||
* [[Manual:IP/Firewall | Firewall and NAT]] | |||
{{cont}} | |||
Latest revision as of 15:15, 31 July 2013
Summary
Standards: RFC 1990
Package: ppp
Multi-Link Point to Point Protocol (MP, Multi-Link PPP, MultiPPP or MLPPP) is a method of splitting, recombining, and sequencing data across multiple logical data links.
In a situation where we have multiple DSL links a pair of devices, performance by “widening the pipe” between two devices can be increased by using Multi-Link PPP, without going to a newer, more expensive technology.
Large packets are actually split into bits and sent evenly over ALL logical data links. This is done instantaneously with NO loss of bandwidth. It is important to understand that other end of the link needs to use the same protocol to recombine your data.
Multilink is based on an LCP option negotiation that allows to indicate to its peer that it is capable of combining multiple physical links.
MLPPP over single link
Typically size of the packet sent over PPP link is reduced due to overhead. MP can be used to transmit and receive full frame over single ppp link. To make it work the Multilink Protocol uses additional LCP configuration options Multilink Maximum Received Reconstructed Unit (MRRU)
To enable Multi-link PPP over single link you must specify MRRU (Maximum Receive Reconstructed Unit) option. If both sides support this feature there are no need for MSS adjustment (in firewall mangle). Study shows that MRRU is less CPU expensive that 2 mangle rules per client. MRRU allows to divide packet to multiple channels therefore increasing possible MTU and MRU (up to 65535 bytes)
Under Windows it can be enabled in Networking tag, Settings button, "Negotiate multi-link for single link connections". Their MRRU is hard coded to 1614.
Configuration Example
Let's configure pppoe server compatible with Windows clients and MRRU enabled.
[admin@RB800] /interface pppoe-server server> add service-name=myPPP interface=ether1 mrru=1614
[admin@RB800] /interface pppoe-server server> print
Flags: X - disabled
0 service-name="myPPP" interface=ether1 max-mtu=1480 max-mru=1480 mrru=1614
authentication=pap,chap,mschap1,mschap2 keepalive-timeout=10 one-session-per-host=no
max-sessions=0 default-profile=default
In short - standard PPP link - just specify MRRU in both sides :)
MLPPP over multiple links
MLPPP over multiple links allow to create a single ppp link over multiple physical connections. All PPP links must come from the same server (server must have MLPPP over multiple links support) and all PPP links must have same user name and password.
And to enable MLPPP you just need to create PPP client and specify multiple interfaces instead of single interface. Mikrotik RouterOS have MLPPP clent support starting from version 3.10. Presently there are no MLPPP server support available.
Configuration Example
ISP gives to its client two physical links (DSL lines) 1Mbps each. To get aggregated 2Mbps pipe we have to set up MLPPP. Consider ISP router is pre-configured to support MLPPP.
Configuration on Mikorotik router (R1) is:
/interface pppoe-client add service-name=ISP interface=ether1,ether2 user=xxx password=yyy disabled=no \ add-default-route=yes use-peer-dns=yes
[admin@RB800] /interface pppoe-client> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 name="pppoe-out1" max-mtu=1480 max-mru=1480 mrru=disabled interface=ether1,ether2
user="xxx" password="yyy" profile=default service-name="ISP" ac-name="" add-default-route=yes
dial-on-demand=no use-peer-dns=yes allow=pap,chap,mschap1,mschap2
Now when pppoe client is connected we can set up rest of configuration, local network address, enable dns requests, set up masquerade and firewall
/ip address add address=192.168.88.1/24 interface=local /ip dns set allow-remote-request=yes /ip firewall nat add chain=src-nat action=masquerade out-interface=pppoe-out1 /ip firewall filter add chain=input connection-state=invalid action=drop \ comment="Drop Invalid connections" add chain=input connection-state=established action=accept \ comment="Allow Established connections" add chain=input protocol=icmp action=accept \ comment="Allow ICMP" add chain=input src-address=192.168.88.0/24 action=accept \ in-interface=!pppoe-out1 add chain=input action=drop comment="Drop everything else"
For more advanced router and customer protection check firewall examples.
See Also
[ Top | Back to Content ]