Manual:CRS3xx series switches: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (136 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Versions| v6.41 +}} | {{Versions| v6.41 +}} | ||
{{Warning|This manual is moved to https://help.mikrotik.com/docs/display/ROS/CRS3xx%2C+CRS5xx%2C+CCR2116%2C+CCR2216+switch+chip+features}} | |||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
=Summary= | |||
The Cloud Router Switch series are highly integrated switches with high performance | The Cloud Router Switch series are highly integrated switches with high performance CPU and feature-rich packet processor. The CRS switches can be designed into various Ethernet applications including unmanaged switch, Layer 2 managed switch, carrier switch and wired unified packet processing. | ||
{{Warning | This article applies to CRS3xx series switches and not to CRS1xx/CRS2xx series switches.}} | {{Warning | This article applies to CRS3xx series switches and not to CRS1xx/CRS2xx series switches.}} | ||
==Features== | |||
<table class="styled_table"> | <table class="styled_table"> | ||
<tr><th width="25%">Features</th><th>Description</th></tr> | <tr><th width="25%">Features</th><th>Description</th></tr> | ||
| Line 17: | Line 20: | ||
<li>Configurable ports for switching or routing</li> | <li>Configurable ports for switching or routing</li> | ||
<li>Full non-blocking wirespeed switching</li> | <li>Full non-blocking wirespeed switching</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Large Unicast FDB for Layer 2 unicast forwarding</li> | ||
<li>Forwarding Databases works based on IVL</li> | <li>Forwarding Databases works based on IVL</li> | ||
<li>Jumbo frame support</li> | <li>Jumbo frame support</li> | ||
<li>IGMP Snooping support</li> | |||
</ul></td> | </ul></td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 25: | Line 29: | ||
<td>'''Mirroring'''</td> | <td>'''Mirroring'''</td> | ||
<td> | <td> | ||
<ul class="bullets"> | |||
<li>Various types of mirroring: | |||
<ul class="bullets"> | <ul class="bullets"> | ||
<li>Port based mirroring | <li>Port based mirroring | ||
<li>VLAN based mirroring | |||
<li>MAC based mirroring | |||
</ul> | |||
</ul></td> | </ul></td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 33: | Line 42: | ||
<td> | <td> | ||
<ul class="bullets"> | <ul class="bullets"> | ||
<li>Fully compatible with IEEE802.1Q</li> | <li>Fully compatible with IEEE802.1Q and IEEE802.1ad VLAN</li> | ||
<li>4k active VLANs</li> | <li>4k active VLANs</li> | ||
<li>Port based VLAN</ | <li>Flexible VLAN assignment: | ||
<ul class="bullets"> | |||
<li>Port based VLAN | |||
<li>Protocol based VLAN | |||
<li>MAC based VLAN | |||
</ul> | |||
<li>VLAN filtering</li> | <li>VLAN filtering</li> | ||
<li>From any to any VLAN translation</li> | |||
</ul></td> | </ul></td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 43: | Line 58: | ||
<td> | <td> | ||
<ul class="bullets"> | <ul class="bullets"> | ||
<li>Supports 802.3ad and balance-xor modes</li> | <li>Supports 802.3ad (LACP) and balance-xor modes</li> | ||
<li>Up 8 member ports per bonding interface</li> | <li>Up to 8 member ports per bonding interface</li> | ||
<li>Up to 30 bonding interfaces</li> | <li>Up to 30 bonding interfaces</li> | ||
<li>Hardware automatic failover and load balancing</li> | |||
</ul></td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>'''Quality of Service (QoS)'''</td> | |||
<td> | |||
<ul class="bullets"> | |||
<li>Ingress traffic limiting</li> | |||
<ul class="bullets"> | |||
<li>Port based</li> | |||
<li>MAC based</li> | |||
<li>IP based</li> | |||
<li>VLAN based</li> | |||
<li>Protocol based</li> | |||
<li>DSCP based</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
<li>Port based egress traffic limiting</li> | |||
</ul></td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>'''Port isolation'''</td> | |||
<td> | |||
<ul class="bullets"> | |||
<li>Applicable for Private VLAN implementation </li> | |||
</ul></td> | </ul></td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 52: | Line 91: | ||
<td><ul class="bullets"> | <td><ul class="bullets"> | ||
<li>Ingress ACL tables</li> | <li>Ingress ACL tables</li> | ||
<li>Classification based on ports, L2, L3, L4 protocol header fields</li> | <li>Classification based on ports, L2, L3, L4 protocol header fields</li> | ||
<li>ACL actions include filtering, forwarding and modifying of the protocol header fields</li> | <li>ACL actions include filtering, forwarding and modifying of the protocol header fields</li> | ||
| Line 59: | Line 97: | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
==Models== | |||
This table clarifies main differences between Cloud Router Switch models. | This table clarifies main differences between Cloud Router Switch models. | ||
| Line 69: | Line 107: | ||
| nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;* " | <b>Wireless</b> | | nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;* " | <b>Wireless</b> | ||
| nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;* " | <b>SFP+ port</b> | | nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;* " | <b>SFP+ port</b> | ||
| nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;* " | <b> | | nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;* " | <b>ACL rules</b> | ||
| nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;* " | <b>Unicast FDB entries</b> | |||
| nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;* " | <b>Jumbo Frame (Bytes)</b> | | nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;* " | <b>Jumbo Frame (Bytes)</b> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 78: | Line 117: | ||
| style="background-color: #F99;" | <b>-</b> | | style="background-color: #F99;" | <b>-</b> | ||
| <b>+</b> | | <b>+</b> | ||
| <b>128</b> | |||
| <b>16,000</b> | |||
| <b>10218</b> | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | CRS328-24P-4S+ | |||
| <b>Marvell-98DX3236</b> | |||
| <b>800MHz</b> | |||
| <b>1</b> | |||
| style="background-color: #F99;" | <b>-</b> | |||
| <b>+</b> | |||
| <b>128</b> | |||
| <b>16,000</b> | |||
| <b>10218</b> | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | CRS328-4C-20S-4S+ | |||
| <b>Marvell-98DX3236</b> | |||
| <b>800MHz</b> | |||
| <b>1</b> | |||
| style="background-color: #F99;" | <b>-</b> | |||
| <b>+</b> | |||
| <b>128</b> | |||
| <b>16,000</b> | |||
| <b>10218</b> | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | CRS305-1G-4S+ | |||
| <b>Marvell-98DX3236</b> | |||
| <b>800MHz</b> | |||
| <b>1</b> | |||
| style="background-color: #F99;" | <b>-</b> | |||
| <b>+</b> | |||
| <b>128</b> | |||
| <b>16,000</b> | |||
| <b>10218</b> | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | CRS309-1G-8S+ | |||
| <b>Marvell-98DX8208</b> | |||
| <b>800MHz</b> | |||
| <b>2</b> | |||
| style="background-color: #F99;" | <b>-</b> | |||
| <b>+</b> | | <b>+</b> | ||
| <b>680</b> | |||
| <b>32 000</b> | |||
| <b>10218</b> | | <b>10218</b> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 87: | Line 167: | ||
| style="background-color: #F99;" | <b>-</b> | | style="background-color: #F99;" | <b>-</b> | ||
| <b>+</b> | | <b>+</b> | ||
| <b>680</b> | |||
| <b>128,000</b> | |||
| <b>10218</b> | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | CRS312-4C+8XG | |||
| <b>Marvell-98DX8212</b> | |||
| <b>650MHz</b> | |||
| <b>1</b> | |||
| style="background-color: #F99;" | <b>-</b> | |||
| <b>+</b> | |||
| <b>341</b> | |||
| <b>32,000</b> | |||
| <b>10218</b> | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | CRS326-24S+2Q+ | |||
| <b>Marvell-98DX8332</b> | |||
| <b>650MHz</b> | |||
| <b>1</b> | |||
| style="background-color: #F99;" | <b>-</b> | |||
| <b>+</b> | |||
| <b>170</b> | |||
| <b>32,000</b> | |||
| <b>10218</b> | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | CRS354-48G-4S+2Q+ | |||
| <b>Marvell-98DX3257</b> | |||
| <b>650MHz</b> | |||
| <b>1</b> | |||
| style="background-color: #F99;" | <b>-</b> | |||
| <b>+</b> | |||
| <b>170</b> | |||
| <b>32,000</b> | |||
| <b>10218</b> | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | CRS354-48P-4S+2Q+ | |||
| <b>Marvell-98DX3257</b> | |||
| <b>650MHz</b> | |||
| <b>1</b> | |||
| style="background-color: #F99;" | <b>-</b> | |||
| <b>+</b> | | <b>+</b> | ||
| <b>170</b> | |||
| <b>32,000</b> | |||
| <b>10218</b> | | <b>10218</b> | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Abbreviations== | |||
* FDB - Forwarding Database | * FDB - Forwarding Database | ||
| Line 99: | Line 220: | ||
* PVID - Port VLAN ID | * PVID - Port VLAN ID | ||
* ACL - Access Control List | * ACL - Access Control List | ||
* CVID - Customer VLAN ID | |||
* SVID - Service VLAN ID | |||
=Port switching= | |||
In order to setup port switching on CRS3xx series switches, check the [[Manual:Interface/Bridge#Bridge_Hardware_Offloading | Bridge Hardware Offloading]] page. | |||
{{ Warning | Currently it is possible to create only one bridge with hardware offloading on CRS3xx series devices. Use the <code>hw</code> parameter to select which bridge will use hardware offloading.}} | |||
{{ Note | On CRS3xx series switches bridge STP/RSTP/MSTP, IGMP Snooping and VLAN filtering settings don't affect hardware offloading, since RouterOS v6.42 Bonding interfaces are also hardware offloaded.}} | |||
=VLAN= | |||
Since RouterOS v6.41 bridges provides VLAN aware Layer2 forwarding and VLAN tag modifications within the bridge. This set of features makes bridge operation more like a traditional Ethernet switch and allows to overcome Spanning Tree compatibilty issues compared to configuration when tunnel-like VLAN interfaces are bridged. Bridge VLAN Filtering configuration is highly recommended to comply with STP (802.1D), RSTP (802.1w) standards and is mandatory to enable MSTP (802.1s) support in RouterOS. | Since RouterOS v6.41 bridges provides VLAN aware Layer2 forwarding and VLAN tag modifications within the bridge. This set of features makes bridge operation more like a traditional Ethernet switch and allows to overcome Spanning Tree compatibilty issues compared to configuration when tunnel-like VLAN interfaces are bridged. Bridge VLAN Filtering configuration is highly recommended to comply with STP (802.1D), RSTP (802.1w) standards and is mandatory to enable MSTP (802.1s) support in RouterOS. | ||
==VLAN Filtering== | |||
The main VLAN setting is <code>vlan-filtering</code> which globally controls vlan-awareness and VLAN tag processing in the bridge. If <code>vlan-filtering=no</code>, bridge ignores VLAN tags, works in a shared-VLAN-learning (SVL) mode and cannot modify VLAN tags of packets. Turning on <code>vlan-filtering</code> enables all bridge VLAN related functionality and independent-VLAN-learning (IVL) mode. Besides joining the ports for Layer2 forwarding, bridge itself is also an interface therefore it has Port VLAN ID (pvid). | The main VLAN setting is <code>vlan-filtering</code> which globally controls vlan-awareness and VLAN tag processing in the bridge. If <code>vlan-filtering=no</code>, bridge ignores VLAN tags, works in a shared-VLAN-learning (SVL) mode and cannot modify VLAN tags of packets. Turning on <code>vlan-filtering</code> enables all bridge VLAN related functionality and independent-VLAN-learning (IVL) mode. Besides joining the ports for Layer2 forwarding, bridge itself is also an interface therefore it has Port VLAN ID (pvid). | ||
{{ Note | Since RouterOS v6.41 all VLAN switching related parameters are moved to the bridge section. On CRS3xx series devices VLAN switching must be configured under the bridge section as well, this will not limit the device's performance, CRS3xx is designed to use the built-in switch chip to work with bridge VLAN filtering, you are able to achieve full non-blocking wire-speed switching performance while using bridges and bridge VLAN filtering. Make sure that all bridge ports have the "H" flag, which indicates that the device is using the switch chip to forward packets. }} | |||
<p id="shbox"><b>Sub-menu:</b> <code>/interface bridge</code></p> | <p id="shbox"><b>Sub-menu:</b> <code>/interface bridge</code></p> | ||
| Line 222: | Line 267: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><var><b>frame-types</b></var> (<em>admit-all | admit-only-untagged-and-priority-tagged | admit-only-vlan-tagged</em>; Default: <b>admit-all</b>)</td> | <td><var><b>frame-types</b></var> (<em>admit-all | admit-only-untagged-and-priority-tagged | admit-only-vlan-tagged</em>; Default: <b>admit-all</b>)</td> | ||
<td>Specifies allowed ingress frame types on a bridge port.</td> | <td>Specifies allowed ingress frame types on a bridge port. Only has effect when <var>ingress-filtering</var> is enabled.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><var><b>ingress-filtering</b></var> (<em>yes | no</em>; Default: <b>no</b>)</td> | <td><var><b>ingress-filtering</b></var> (<em>yes | no</em>; Default: <b>no</b>)</td> | ||
<td>Enables or disables filtering which | <td>Enables or disables ingress filtering, which checks if an entry exists for the ingress port and the VLAN ID in the bridge VLAN table. Should be used with <var>frame-types</var> to specify if the ingress traffic should be tagged or untagged.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 234: | Line 279: | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
==VLAN Table== | |||
Bridge VLAN table represents per-VLAN port mapping with an egress VLAN tag action. | Bridge VLAN table represents per-VLAN port mapping with an egress VLAN tag action. | ||
| Line 271: | Line 316: | ||
==Setup examples== | |||
===Port Based VLAN=== | |||
* The configuration for CRS3xx switches is described | * The configuration for CRS3xx switches is described in the [[Manual:Interface/Bridge#VLAN_Example_.231_.28Trunk_and_Access_Ports.29 | Bridge VLAN FIltering]] section. | ||
{{ Note | It is possible to use the built-in switch chip and the CPU at the same time to create a Switch-Router setup, where a device acts as a switch and as a router at the same time. You can find a configuration example in the [[Manual:CRS_Router | CRS-Router]] guide. }} | |||
===MAC Based VLAN=== | |||
[[File:MAC-Based.png|center|frame|alt=Alt text|MAC Based VLAN]] | [[File:MAC-Based.png|center|frame|alt=Alt text|MAC Based VLAN]] | ||
{{ Note |The CRS3xx Switch Rule table is used for MAC Based VLAN functionality, | {{ Note |The CRS3xx Switch Rule table is used for MAC Based VLAN functionality, see [[Manual:CRS3xx_series_switches#Models | this table]] on how many rules each device supports.}} | ||
{{ Note |MAC-based VLANs will only work properly between switch ports and not between switch ports and CPU. When a packet is being forwarded to the CPU, the <var>pvid</var> property for the bridge port will be always used instead of <var>new-vlan-id</var> from ACL rules.}} | |||
* Enable switching on ports by creating a bridge with enabled hw-offloading. | * Enable switching on ports by creating a bridge with enabled hw-offloading. | ||
| Line 308: | Line 356: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
===( | ===Protocol Based VLAN=== | ||
[[File:Protocol-Based.png|center|frame|alt=Alt text|Protocol Based VLAN]] | |||
{{ Note |The CRS3xx Switch Rule table is used for Protocol Based VLAN functionality, see [[Manual:CRS3xx_series_switches#Models | this table]] on how many rules each device supports.}} | |||
* Enable switching on ports by creating a bridge with enabled hw-offloading. | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface bridge | |||
add name=bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes | |||
/interface bridge port | |||
add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether2 hw=yes | |||
add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether6 hw=yes | |||
add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether7 hw=yes | |||
add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether8 hw=yes | |||
</pre> | |||
* Add VLANs in the Bridge VLAN table and specify ports. | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface bridge vlan | |||
add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2 untagged=ether6 vlan-ids=200 | |||
add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2 untagged=ether7 vlan-ids=300 | |||
add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2 untagged=ether8 vlan-ids=400 | |||
</pre> | |||
* Add Switch rules which assign VLAN id based on MAC protocol. | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface ethernet switch rule | |||
add mac-protocol=ip new-vlan-id=200 ports=ether6 switch=switch1 | |||
add mac-protocol=ipx new-vlan-id=300 ports=ether7 switch=switch1 | |||
add mac-protocol=0x80F3 new-vlan-id=400 ports=ether8 switch=switch1 | |||
</pre> | |||
===VLAN Tunneling (Q-in-Q)=== | |||
Since RouterOS v6.43 it is possible to use a provider bridge (IEEE 802.1ad) VLAN filtering and hardware offloading at the same time on CRS3xx series switches. The configuration for CRS3xx switches is described in the [[Manual:Interface/Bridge#VLAN_Tunneling_.28Q-in-Q.29 | Bridge VLAN Tunneling (Q-in-Q)]] section. | |||
===Ingress VLAN translation=== | |||
It is possible to translate a certain VLAN ID to a different VLAN ID using ACL rules on an ingress port. In this example we create two ACL rules, allowing a bidirectional communication. This can be done by doing the following: | |||
[[File:crs3xx_vlan_translation.png|center|frame|alt=Alt text|CRS3xx Ingress VLAN translation]] | |||
* Create a new bridge and add ports to it with hardware offloading: | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface bridge | |||
add name=bridge1 vlan-filtering=no | |||
/interface bridge port | |||
add interface=ether1 bridge=bridge1 hw=yes | |||
add interface=ether2 bridge=bridge1 hw=yes | |||
</pre> | |||
* Add ACL rules to translate a VLAN ID in each direction: | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface ethernet switch rule | |||
add new-dst-ports=ether2 new-vlan-id=20 ports=ether1 switch=switch1 vlan-id=10 | |||
add new-dst-ports=ether1 new-vlan-id=10 ports=ether2 switch=switch1 vlan-id=20 | |||
</pre> | |||
* Add both VLAN IDs to the bridge VLAN table: | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface bridge vlan | |||
add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether1 vlan-ids=10 | |||
add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2 vlan-ids=20 | |||
</pre> | |||
* Enable bridge VLAN filtering: | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface bridge set bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes | |||
</pre> | |||
{{ Note | Bidirectional communication is limited only between two switch ports. Translating VLAN ID between more ports can cause traffic flooding or incorrect forwarding between same VLAN ports. }} | |||
{{ Warning | By enabling <code>vlan-filtering</code> you will be filtering out traffic destined to the CPU, before enabling VLAN filtering you should make sure that you set up a [[Manual:Interface/Bridge#Management_port| Management port]] }} | |||
=(R/M)STP= | |||
CRS3xx series switches are capable of running STP, RSTP and MSTP on a hardware level. For more detailed information you should check out the [[ Manual:Interface/Bridge#Spanning_Tree_Protocol | Spanning Tree Protocol]] manual page. | |||
=Bonding= | |||
Since RouterOS v6.42 all CRS3xx series switches support hardware offloading with bonding interfaces. Only ''802.3ad'' and ''balance-xor'' bonding modes are hardware offloaded, other bonding modes will use the CPU's resources. You can find more information about the bonding interfaces in the [[ Manual:Interface/Bonding | Bonding Interface ]] section. If 802.3ad mode is used, then LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) is supported. | |||
To create a hardware offloaded bonding interface, you must create a bonding interface with a supported bonding mode: | To create a hardware offloaded bonding interface, you must create a bonding interface with a supported bonding mode: | ||
| Line 349: | Line 450: | ||
add name=bridge | add name=bridge | ||
/interface bridge port | /interface bridge port | ||
add bridge=bridge interface=bond1 | add bridge=bridge interface=bond1 hw=yes | ||
add bridge=bridge interface=ether3 | add bridge=bridge interface=ether3 hw=yes | ||
add bridge=bridge interface=ether4 | add bridge=bridge interface=ether4 hw=yes | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
{{ Note | Don't add interfaces to a bridge that are already in a bond, RouterOS will not allow you to add an interface that is already a slave to a bridge as there is no need to do it since a bonding interface already contains the slave interfaces. }} | |||
Make sure that the bonding interface is hardware offloaded by checking the "H" flag: | Make sure that the bonding interface is hardware offloaded by checking the "H" flag: | ||
| Line 364: | Line 467: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
{{ Note | | {{ Note | With HW-offloaded bonding interfaces, the built-in switch chip will always use Layer2+Layer3+Layer4 for transmit hash policy, changing the transmit hash policy manually will have no effect. }} | ||
=L3 Hardware Offloading= | |||
Layer3 hardware offloading (otherwise known as IP switching or HW routing) will allow to offload some of the router features on to the switch chip. This allows to reach wire speeds when routing packets, which simply would not be possible with the CPU. | |||
At the moment of writing this article, only CRS317-1G-16S+ supports L3 HW Offloading and RouterOS v7beta6 or newer must be used. | |||
The feature can be enabled with: | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface ethernet switch | |||
set switch1 l3hw=yes | |||
</pre> | |||
{{Note| After turning off HW Offloading it is recommended to reboot the switch, to make sure that all HW related config is cleared from switch chip.}} | |||
Currently supported and unsupported feature list: | |||
{| border="1" class="wikitable collapsible sortable" style="text-align: left" | |||
| nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;text-align: center;* " | <b><u>Feature</u></b> | |||
| nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;text-align: center;* " | <b>Status</b> | |||
| nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;text-align: center;* " | <b>Description</b> | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | IPv4 Unicast | |||
| style="background-color: #0F0;font-weight: bold;" | HW | |||
| Depending on the complexity of routes in routing table, max HW accelerated route count could change (see table below for min-max supported route count for each hardware). Whole-byte IP prefixes (/8, /16, /24, etc.) occupy less HW space than others (e.g., /22). | |||
If HW route limit is reached new routes will fall back to CPU, except cases when newly added route overlaps with already existing routes processed by hardware. In this case destinations that were processed in hardware will continue to be processed in hardware. The user should choose the device with HW capability large-enough to store all the routes. | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | IPv6 Unicast | |||
| style="background-color: #FF0;font-weight: bold;" | CPU | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | IPv4 Multicast | |||
| style="background-color: #FF0;font-weight: bold;" | CPU | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | IPv6 Multicast | |||
| style="background-color: #FF0;font-weight: bold;" | CPU | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | ECMP | |||
| style="background-color: #0F0;font-weight: bold;" | HW | |||
| See hardware limits in the next table. | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | "blackhole" routes | |||
| style="background-color: #0F0;font-weight: bold;" | HW | |||
| This feature enables the possibility to drop D/DOS attacks at wire speed | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | "prohibit" routes | |||
| style="background-color: #FF0;font-weight: bold;" | CPU | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | "unreachable" routes | |||
| style="background-color: #FF0;font-weight: bold;" | CPU | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | gateway=<interface_name> | |||
| style="background-color: #FF0;font-weight: bold;" | HW/CPU | |||
| This works only for directly connected networks. Since HW does not know how to send ARP requests, CPU sends ARP request and waits for a reply to find out a DST MAC address on the first received packet of the connection that matches a DST IP address. After DST MAC is determined, HW entry is added and all further packets will be processed by switch chip. | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | Bridge | |||
| style="background-color: #0F0;font-weight: bold;" | HW | |||
| Routing from/to bridge interface | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | VLAN | |||
| style="background-color: #0F0;font-weight: bold;" | HW | |||
| Routing between VLAN interfaces | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | LACP | |||
| style="background-color: #0F0;font-weight: bold;" | HW | |||
| <code>/interface bonding</code> | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | Firewall | |||
| style="background-color: #7F7FFF;font-weight: bold;" | FW | |||
| Only Fasttrack connections gets processed by HW, which means that CPU is processing packets until connection gets fasttracked. | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | NAT | |||
| style="background-color: #7F7FFF;font-weight: bold;" | FW | |||
| NAT rules applied to the offloaded Fasttrack connections are processed by HW. | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | QoS | |||
| style="background-color: #F00;font-weight: bold;" | N/A | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
Where: | |||
* '''CPU''' - feature is supported but processed by CPU | |||
* '''HW''' - feature is supported and offloaded in hardware (works when l3hw=yes) | |||
* '''FW''' - feature is supported and offloaded in hardware (works when l3hw=fw) | |||
* '''N/A''' - feature is not available, meaning that L3 Hardware offloading MUST be disabled for these features to work | |||
{{Warning| Currently user must choose whether to use hardware accelerated routing or firewall. It is not possible to use both at the same time.}} | |||
'''List of supported devices and their limits:''' | |||
{| border="1" class="wikitable collapsible sortable" style="text-align: left" | |||
| nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;text-align: center;* " | <b><u></u></b> | |||
| nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;text-align: center;* " | <b>Release</b> | |||
| nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;text-align: center;* " | <b>Routes</b> | |||
| nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;text-align: center;* " | <b>Nexthops</b> | |||
| nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;text-align: center;* " | <b>ECMP Groups</b> | |||
| nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;text-align: center;* " | <b>Fasttrack connections(*1,*2)</b> | |||
| nowrap style="background-color: #CCC;text-align: center;* " | <b>NAT enties(*2)</b> | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | CRS317-1G-16S+ | |||
| 7.1beta1 | |||
| 150K - 240K | |||
| 8K | |||
| 4K | |||
| 4500 / 3750 (*3) | |||
| 4096 | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | CRS309-1G-8S+ | |||
| 7.1beta2 | |||
| 50K - 80K | |||
| 8K | |||
| 4K | |||
| 4500 / 3750 | |||
| 4096 | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | CRS312-4C+8XG | |||
| 7.1beta2 | |||
| 50K - 80K | |||
| 8K | |||
| 4K | |||
| 2250 / 1500 | |||
| 4096 (*4) | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color: #CCC;font-weight: bold;" | CRS326-24S+2Q+ | |||
| 7.1beta2 | |||
| 50K - 80K | |||
| 8K | |||
| 4K | |||
| 2250 / 1500 | |||
| 4096 | |||
|} | |||
<nowiki>*1</nowiki> ''When the HW limit of Fasttrack or NAT entries is reached, other connections will fall back to the CPU. MikroTik's smart connection offload algorithm ensures that the connections with the most traffic are offloaded to the hardware.'' | |||
<nowiki>*2</nowiki> ''Fasttrack connections share the same HW memory with ACL rules. Depending on the complexity, one ACL rule may occupy the memory of 3-6 Fasttrack connections. '' | |||
<nowiki>*3</nowiki> ''(Both MPLS and Bridge Port Extender are disabled) / (MPLS, Bridge Port Extender, or both are enabled). MPLS shares the HW memory with Fasttrack connections. Moreover, enabling MPLS requires the allocation of the entire memory region, which could store up to 750 Fasttrack connections otherwise. The same applies to Bridge Port Extender. However, MPLS and Bridge Port Extended may use the same memory region, so enabling them both doesn't double the limitation of Fasttrack connections. '' | |||
<nowiki>*4</nowiki> ''All NAT entries cannot be used due to the limited amount of Fasttrack connections.'' | |||
=Port isolation= | |||
Since RouterOS v6.43 it is possible to create a Private VLAN setup on CRS3xx series switches, example can be found in the [[Manual:Switch_Chip_Features#Port_isolation | Switch chip port isolation]] manual page. | |||
=IGMP Snooping= | |||
CRS3xx series switches are capable of using IGMP Snooping on a hardware level. To see more detailed information, you should check out the [[ Manual:Interface/Bridge#IGMP_Snooping | IGMP Snooping]] manual page. | |||
=DHCP Snooping and DHCP Option 82= | |||
CRS3xx series switches are capable of using DHCP Snooping with Option 82 on a hardware level. To see more detailed information, you should check out the [[ Manual:Interface/Bridge#DHCP_Snooping_and_DHCP_Option_82 | DHCP Snooping and DHCP Option 82]] manual page. | |||
=Mirroring= | |||
Mirroring lets the switch 'sniff' all traffic that is going in a switch chip and send a copy of those packets out to another port (mirror-target). This feature can be used to easily set up a 'tap' device that allows you to inspect the traffic on your network on a traffic analyzer device. It is possible to set up a simple port based mirroring where, but it is also possible to setup more complex mirroring based on various parameters. Note that mirror-target port has to belong to same switch. (See which port belong to which switch in <code>/interface ethernet</code> menu). Also mirror-target can have a special 'cpu' value, which means that 'sniffed' packets will be sent out of switch chips cpu port. There are many possibilities that can be used to mirror certain traffic, below you can find most common mirroring examples: | |||
* Port Based Mirroring | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
/interface | /interface ethernet switch | ||
set switch1 mirror-source=ether2 mirror-target=ether3 | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
{{ Note | Property <var>mirror-source</var> will send an ingress and egress packet copies to the <var>mirror-target</var> port. Both <var>mirror-source</var> and <var>mirror-target</var> are limited to a single interface.}} | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
/interface ethernet switch | |||
set switch1 mirror-source=none mirror-target=ether3 | |||
/interface ethernet switch rule | |||
add mirror=yes ports=ether1,ether2 switch=switch1 | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
{{ Note | Using ACL rules, it is possible to mirror packets from multiple <var>ports</var> interfaces. Only ingress packets are mirrored to <var>mirror-target</var> interface.}} | |||
* VLAN Based Mirroring | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface bridge | |||
set bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes | |||
/interface ethernet switch | |||
set switch1 mirror-target=ether3 mirror-source=none | |||
/interface ethernet switch rule | |||
add mirror=yes ports=ether1 switch=switch1 vlan-id=11 | |||
</pre> | |||
{{ Warning | By enabling <code>vlan-filtering</code> you will be filtering out traffic destined to the CPU, before enabling VLAN filtering you should make sure that you set up a [[Manual:Interface/Bridge#Management_port| Management port]] }} | |||
< | * MAC Based Mirroring | ||
< | <pre> | ||
/interface ethernet switch | |||
set switch1 mirror-target=ether3 mirror-source=none | |||
/interface ethernet switch rule | |||
add mirror=yes ports=ether1 switch=switch1 dst-mac-address=64:D1:54:D9:27:E6/FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF | |||
add mirror=yes ports=ether1 switch=switch1 src-mac-address=64:D1:54:D9:27:E6/FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF | |||
</pre> | |||
* Protocol Based Mirroring | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
/interface ethernet switch | |||
set switch1 mirror-target=ether3 mirror-source=none | |||
/interface ethernet switch rule | |||
add mirror=yes ports=ether1 switch=switch1 mac-protocol=ipx | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
* IP Based Mirroring | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
/interface ethernet switch set switch1 | /interface ethernet switch | ||
set switch1 mirror-target=ether3 mirror-source=none | |||
/interface ethernet switch rule | |||
add mirror=yes ports=ether1 switch=switch1 src-address=192.168.88.0/24 | |||
add mirror=yes ports=ether1 switch=switch1 dst-address=192.168.88.0/24 | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
== | There are other options as well, check the [[Manual:CRS3xx_series_switches#Switch_Rules_.28ACL.29 | ACL section]] to find out all possible parameters that can be used to match packets. | ||
=Traffic Shaping= | |||
It is possible to limit certain type of traffic using ACL rules. For CRS3xx series switches it is possible to limit ingress traffic that matches certain parameters and it is possible to limit ingress/egress traffic per port basis. For ingress traffic QoS policer is used, for egress traffic QoS shaper is used. | |||
Port | * Port Based Traffic Shaping | ||
<pre> | |||
/interface ethernet switch port | |||
set ether1 ingress-rate=10M egress-rate=5M | |||
</pre> | |||
* MAC Based Traffic Shaping | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
/interface ethernet switch | /interface ethernet switch rule | ||
set switch1 | add ports=ether1 switch=switch1 src-mac-address=64:D1:54:D9:27:E6/FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF rate=10M | ||
</pre> | |||
* VLAN Based Traffic Shaping | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface bridge | |||
set bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes | |||
/interface ethernet switch rule | |||
add ports=ether1 switch=switch1 vlan-id=11 rate=10M | |||
</pre> | |||
{{ Warning | By enabling <code>vlan-filtering</code> you will be filtering out traffic destined to the CPU, before enabling VLAN filtering you should make sure that you set up a [[Manual:Interface/Bridge#Management_port| Management port]] }} | |||
* Protocol Based Traffic Shaping | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface ethernet switch rule | |||
add ports=ether1 switch=switch1 mac-protocol=ipx rate=10M | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
== | There are other options as well, check the [[Manual:CRS3xx_series_switches#Switch_Rules_.28ACL.29 | ACL section]] to find out all possible parameters that can be used to match packets. | ||
{{ Note | The CRS3xx Switch Rule table is used for QoS functionality, see [[Manual:CRS3xx_series_switches#Models | this table]] on how many rules each device supports.}} | |||
=Traffic Storm Control= | |||
Since RouterOS v6.42 it is possible to enable traffic storm control on CRS3xx series devices. A traffic storm can emerge when certain frames are continuously flooded on the network. For example, if a network loop has been created and no loop avoidance mechanisms are used (e.g. [[Manual:Spanning_Tree_Protocol| Spanning Tree Protocol]]), broadcast or multicast frames can quickly overwhelm the network, causing degraded network performance or even complete network breakdown. With CRS3xx series switches it is possible to limit broadcast, unknown multicast and unknown unicast traffic. Unknown unicast traffic is considered when a switch does not contain a host entry for the destined MAC address. Unknown multicast traffic is considered when a switch does not contain a multicast group entry in the <code>/interface bridge mdb</code> menu. Storm control settings should be applied to ingress ports, the egress traffic will be limited. | |||
{{ Note | The storm control parameter is specified in percentage (%) of the link speed. If your link speed is 1Gbps, then specifying <code>storm-rate</code> as <code>10</code> will allow only 100Mbps of broadcast, unknown multicast and/or unknown unicast traffic to be forwarded. }} | |||
<p id="shbox"><b>Sub-menu:</b> <code>/interface ethernet switch port</code></p> | <p id="shbox"><b>Sub-menu:</b> <code>/interface ethernet switch port</code></p> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
{{Mr-arg-table-h | |||
|prop=Property | |||
|desc=Description | |||
}} | |||
</ | |||
< | {{Mr-arg-table | ||
|arg=limit-broadcasts | |||
|type=yes {{!}} no | |||
|default=yes | |||
|desc=Limit broadcast traffic on switch port. | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table | |||
|arg=limit-unknown-multicasts | |||
|type=yes {{!}} no | |||
|default=no | |||
|desc=Limit unknown multicast traffic on switch port. | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table | |||
|arg=limit-unknown-unicasts | |||
|type=yes {{!}} no | |||
|default=no | |||
|desc=Limit unknown unicast traffic on switch port. | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table-end | |||
|arg=storm-rate | |||
|type=integer 0..100 | |||
|default=100 | |||
|desc=Amount of broadcast, unknown multicast and/or unknown unicast traffic is limited to in percentage of the link speed. | |||
}} | |||
<br /> | |||
{{ Warning | Devices with Marvell-98DX3236 switch chip cannot distinguish unknown multicast traffic from all multicast traffic. For example, CRS326-24G-2S+ will limit all multicast traffic when <code>limit-unknown-multicasts</code> and <code>storm-rate</code> is used. For other devices, for example, CRS317-1G-16S+ the <code>limit-unknown-multicasts</code> parameter will limit only unknown multicast traffic (addresses that are not present in <code>/interface bridge mdb</code> }} | |||
* For example, to limit 1% (10Mbps) of broadcast and unknown unicast traffic on ether1 (1Gbps), use the following commands: | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface ethernet switch port | |||
set ether1 storm-rate=1 limit-broadcasts=yes limit-unknown-unicasts=yes | |||
</pre> | |||
=MPLS hardware offloading= | |||
Since RouterOS v6.41 it is possible to offload certain MPLS functions to the switch chip, the switch must be a (P)rovider router in a PE-P-PE setup in order to achieve hardware offloading. Setup example can be found in the [[Manual:Basic_MPLS_setup_example | Basic MPLS setup example]] manual page. | |||
{{ Note | Currently only <code>CRS317-1G-16S+</code> and <code>CRS309-1G-8S+</code> using RouterOS v6.41 and newer are capable of hardware offloading certain MPLS functions. <code>CRS317-1G-16S+</code> and <code>CRS309-1G-8S+</code> built-in switch chip is not capable of popping MPLS labels from packets, in a PE-P-PE setup you either have to use explicit null or disable TTL propagation in MPLS network to achieve hardware offloading. }} | |||
=Switch Rules (ACL)= | |||
Access Control List contains of ingress policy and egress policy engines. See [[Manual:CRS3xx_series_switches#Models | this table]] on how many rules each device supports (limited by RouterOS). It is advanced tool for wire-speed packet filtering, forwarding and modifying based on Layer2, Layer3 and Layer4 protocol header field conditions. | |||
{{ Note | ACL rules are checked for each received packet until a match has been found. If there are multiple rules that can match, then only the first rule will be triggered. A rule without any action parameters is a rule to accept the packet. }} | |||
<p id="shbox"><b>Sub-menu:</b> <code>/interface ethernet switch rule</code></p> | <p id="shbox"><b>Sub-menu:</b> <code>/interface ethernet switch rule</code></p> | ||
| Line 516: | Line 854: | ||
<td><var><b>protocol</b></var> (<em>dccp | ddp | egp | encap | etherip | ggp | gre | hmp | icmp | icmpv6 | idpr-cmtp | igmp | ipencap | ipip | ipsec-ah | ipsec-esp | ipv6 | ipv6-frag | ipv6-nonxt | ipv6-opts | ipv6-route | iso-tp4 | l2tp | ospf | pim | pup | rdp | rspf | rsvp | sctp | st | tcp | udp | udp-lite | vmtp | vrrp | xns-idp | xtp | or 0..255</em>)</td> | <td><var><b>protocol</b></var> (<em>dccp | ddp | egp | encap | etherip | ggp | gre | hmp | icmp | icmpv6 | idpr-cmtp | igmp | ipencap | ipip | ipsec-ah | ipsec-esp | ipv6 | ipv6-frag | ipv6-nonxt | ipv6-opts | ipv6-route | iso-tp4 | l2tp | ospf | pim | pup | rdp | rspf | rsvp | sctp | st | tcp | udp | udp-lite | vmtp | vrrp | xns-idp | xtp | or 0..255</em>)</td> | ||
<td>Matching particular IP protocol specified by protocol name or number.</td> | <td>Matching particular IP protocol specified by protocol name or number.</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><var><b>rate</b></var> (<em>0..4294967295</em>)</td> | |||
<td>Sets ingress traffic limitation (bits per second) for matched traffic.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 551: | Line 893: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><var><b>vlan-header</b></var> (<em>not-present | present</em>)</td> | <td><var><b>vlan-header</b></var> (<em>not-present | present</em>)</td> | ||
<td>Matching VLAN header, whether the VLAN header is present or not.</td> | <td>Matching VLAN header, whether the VLAN header is present or not. Requires <code>vlan-filtering=yes</code>.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 594: | Line 936: | ||
{{ Note | For VLAN related matchers or VLAN related action parameters to work, you need to enable <code>vlan-filtering</code> on the bridge interface and make sure that hardware offloading is enabled on those ports, otherwise these parameters will not have any effect. }} | {{ Note | For VLAN related matchers or VLAN related action parameters to work, you need to enable <code>vlan-filtering</code> on the bridge interface and make sure that hardware offloading is enabled on those ports, otherwise these parameters will not have any effect. }} | ||
== See also | {{ Warning | When <code>vlan-protocol</code> is set to 802.1Q, then VLAN related ACL rules are relevant to <code>0x8100</code> (CVID) packets, this includes <code>vlan-id</code> and <code>new-vlan-id</code>. When <code>vlan-protocol</code> is set to 802.1ad, then ACL rules are relevant to <code>0x88A8</code> (SVID) packets. For example, with 802.1Q the <code>vlan-id</code> matcher will match CVID packets, but with 802.1ad the <code>vlan-id</code> matcher will match SVID packets. }} | ||
=Port Security= | |||
It is possible to limit allowed MAC addresses on a single switch port on CRS3xx series switches. For example, to allow <code>64:D1:54:81:EF:8E</code> start by switching multiple ports together, in this example <code>64:D1:54:81:EF:8E</code> is going to be located behind '''ether1'''. | |||
* Create an ACL rule to allow the given MAC address and drop all other traffic on '''ether1''' (for ingress traffic): | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface ethernet switch rule | |||
add ports=ether1 src-mac-address=64:D1:54:81:EF:8E/FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF switch=switch1 | |||
add new-dst-ports="" ports=ether1 switch=switch1 | |||
</pre> | |||
* Switch all required ports together, disable MAC learning and disable unknown unicast flooding on '''ether1''': | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface bridge | |||
add name=bridge1 | |||
/interface bridge port | |||
add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether1 hw=yes learn=no unknown-unicast-flood=no | |||
add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether2 hw=yes | |||
</pre> | |||
* Add a static hosts entry for <code>64:D1:54:81:EF:8E</code> (for egress traffic): | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface bridge host | |||
add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether1 mac-address=64:D1:54:81:EF:8E | |||
</pre> | |||
{{ Warning | Broadcast traffic will still be sent out from '''ether1'''. To limit broadcast traffic flood on a bridge port, you can use the <code>broadcast-flood</code> parameter to toggle it. Do note that some protocols depend on broadcast traffic, such as streaming protocols and DHCP. }} | |||
=Dual Boot= | |||
“Dual boot” feature allows you to choose which operating system you prefer to use, RouterOS or SwOS. Device operating system could be changed using: | |||
* Serial Terminal (/''system routerboard settings set boot-os=swos'') | |||
* Winbox | |||
* Webfig | |||
* Serial Console | |||
{| | |||
|[[File:CRS317-dualboot.png|thumb|720x360px|alt=Alt text|Winbox]] | |||
|[[File:Daulboot-webfig.png|thumb|720x360px|alt=Alt text|Webfig]] | |||
|[[File:Dual-boot-option.png|thumb|720x360px|alt=Alt text|Serial Console]] | |||
|} | |||
More details about SwOS are described here: [https://wiki.mikrotik.com/wiki/SwOS SwOS manual] | |||
=Configuring SwOS using RouterOS= | |||
Since RouterOS 6.43 it is possible to load, save and reset SwOS configuration, as well as upgrade SwOS and set an IP address for the switch by using RouterOS. | |||
* Save configuration with <code>/system swos save-config</code> | |||
{{ Note | Configuration will be saved on the same device with <code>swos.config</code> as filename, make sure you download the file off your device since the configuration file will be removed after a reboot. }} | |||
* Load configuration with <code>/system swos load-config</code> | |||
* Change password with <code>/system swos password</code> | |||
* Reset configuration with <code>/system swos reset-config</code> | |||
* Upgrade SwOS from RouterOS using <code>/system swos upgrade</code> | |||
{{ Note | The upgrade command will automatically install the latest available SwOS version, make sure that your device has access to the Internet in order for the upgrade process to work properly. }} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table-h | |||
|prop=Property | |||
|desc=Description | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table | |||
|arg=address-acquisition-mode | |||
|type=dhcp-only {{!}} dhcp-with-fallback {{!}} static | |||
|default=dhcp-with-fallback | |||
|desc=Changes address acquisition method: | |||
* <var>dhcp-only</var> - uses only a DHCP client to acquire address | |||
* <var>dhcp-with-fallback</var> - for the first 10 seconds will try to acquire address using a DHCP client. If the request is unsuccessful, then address falls back to static as defined by <var>static-ip-address</var> property | |||
* <var>static</var> - address is set as defined by <var>static-ip-address</var> property | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table | |||
|arg=allow-from | |||
|type=IP/Mask | |||
|default=0.0.0.0/0 | |||
|desc=IP address or a network from which the switch is accessible. By default, the switch is accessible by any IP address. | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table | |||
|arg=allow-from-ports | |||
|type=name | |||
|default= | |||
|desc=List of switch ports from which the device is accessible. By default, all ports are allowed to access the switch | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table | |||
|arg=allow-from-vlan | |||
|type=integer: 0..4094 | |||
|default=0 | |||
|desc=VLAN ID from which the device is accessible. By defaull, all VLANs are allowed | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table | |||
|arg=identity | |||
|type=name | |||
|default=Mikrotik | |||
|desc=Name of the switch (used for Mikrotik Neighbor Discovery protocol) | |||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table-end | |||
|arg=static-ip-address | |||
|type=IP | |||
|default=192.168.88.1 | |||
|desc=IP address of the switch in case <var>address-acquisition-mode</var> is either set to <var>dhcp-with-fallback</var> or <var>static</var>. By setting a static IP address, the address acquisition process does not change, which is DHCP with fallback by default. This means that the configured static IP address will become active only when there is going to be no DHCP servers in the same broadcast domain | |||
}} | |||
=See also= | |||
* [[ | * [[Manual:CRS_Router | CRS Router]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Manual:CRS3xx_VLANs_with_Bonds | CRS3xx VLANs with Bonds]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Manual:Basic_VLAN_switching | Basic VLAN switching]] | ||
* [[Manual:Interface/Bridge#Bridge_Hardware_Offloading | Bridge Hardware Offloading]] | |||
* [[Manual:Interface/Bridge#Spanning_Tree_Protocol | Spanning Tree Protocol]] | |||
* [[Manual:Interface/Bridge#IGMP_Snooping | IGMP Snooping]] | |||
* [[Manual:Interface/Bridge#DHCP_Snooping_and_DHCP_Option_82 | DHCP Snooping and Option 82]] | |||
* [[M:Maximum_Transmission_Unit_on_RouterBoards | MTU on RouterBOARD]] | * [[M:Maximum_Transmission_Unit_on_RouterBoards | MTU on RouterBOARD]] | ||
* [[Manual:Layer2_misconfiguration | Layer2 misconfiguration]] | |||
* [[Manual:Bridge_VLAN_Table | Bridge VLAN Table]] | |||
{{cont}} | {{cont}} | ||
[[Category:Manual]] | [[Category:Manual]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Bridging and switching]] | ||
[[Category:Routerboard]] | |||
[[Category:Routerboard | |||
Latest revision as of 11:37, 22 September 2023

Warning: This manual is moved to https://help.mikrotik.com/docs/display/ROS/CRS3xx%2C+CRS5xx%2C+CCR2116%2C+CCR2216+switch+chip+features
Summary
The Cloud Router Switch series are highly integrated switches with high performance CPU and feature-rich packet processor. The CRS switches can be designed into various Ethernet applications including unmanaged switch, Layer 2 managed switch, carrier switch and wired unified packet processing.
Features
| Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Forwarding |
|
| Mirroring |
|
| VLAN |
|
| Bonding |
|
| Quality of Service (QoS) |
|
| Port isolation |
|
| Access Control List |
|
Models
This table clarifies main differences between Cloud Router Switch models.
| Model | Switch Chip | CPU | Cores | Wireless | SFP+ port | ACL rules | Unicast FDB entries | Jumbo Frame (Bytes) |
| CRS326-24G-2S+ | Marvell-98DX3236 | 800MHz | 1 | - | + | 128 | 16,000 | 10218 |
| CRS328-24P-4S+ | Marvell-98DX3236 | 800MHz | 1 | - | + | 128 | 16,000 | 10218 |
| CRS328-4C-20S-4S+ | Marvell-98DX3236 | 800MHz | 1 | - | + | 128 | 16,000 | 10218 |
| CRS305-1G-4S+ | Marvell-98DX3236 | 800MHz | 1 | - | + | 128 | 16,000 | 10218 |
| CRS309-1G-8S+ | Marvell-98DX8208 | 800MHz | 2 | - | + | 680 | 32 000 | 10218 |
| CRS317-1G-16S+ | Marvell-98DX8216 | 800MHz | 2 | - | + | 680 | 128,000 | 10218 |
| CRS312-4C+8XG | Marvell-98DX8212 | 650MHz | 1 | - | + | 341 | 32,000 | 10218 |
| CRS326-24S+2Q+ | Marvell-98DX8332 | 650MHz | 1 | - | + | 170 | 32,000 | 10218 |
| CRS354-48G-4S+2Q+ | Marvell-98DX3257 | 650MHz | 1 | - | + | 170 | 32,000 | 10218 |
| CRS354-48P-4S+2Q+ | Marvell-98DX3257 | 650MHz | 1 | - | + | 170 | 32,000 | 10218 |
Abbreviations
- FDB - Forwarding Database
- MDB - Multicast Database
- SVL - Shared VLAN Learning
- IVL - Independent VLAN Learning
- PVID - Port VLAN ID
- ACL - Access Control List
- CVID - Customer VLAN ID
- SVID - Service VLAN ID
Port switching
In order to setup port switching on CRS3xx series switches, check the Bridge Hardware Offloading page.

Warning: Currently it is possible to create only one bridge with hardware offloading on CRS3xx series devices. Use the hw parameter to select which bridge will use hardware offloading.

Note: On CRS3xx series switches bridge STP/RSTP/MSTP, IGMP Snooping and VLAN filtering settings don't affect hardware offloading, since RouterOS v6.42 Bonding interfaces are also hardware offloaded.
VLAN
Since RouterOS v6.41 bridges provides VLAN aware Layer2 forwarding and VLAN tag modifications within the bridge. This set of features makes bridge operation more like a traditional Ethernet switch and allows to overcome Spanning Tree compatibilty issues compared to configuration when tunnel-like VLAN interfaces are bridged. Bridge VLAN Filtering configuration is highly recommended to comply with STP (802.1D), RSTP (802.1w) standards and is mandatory to enable MSTP (802.1s) support in RouterOS.
VLAN Filtering
The main VLAN setting is vlan-filtering which globally controls vlan-awareness and VLAN tag processing in the bridge. If vlan-filtering=no, bridge ignores VLAN tags, works in a shared-VLAN-learning (SVL) mode and cannot modify VLAN tags of packets. Turning on vlan-filtering enables all bridge VLAN related functionality and independent-VLAN-learning (IVL) mode. Besides joining the ports for Layer2 forwarding, bridge itself is also an interface therefore it has Port VLAN ID (pvid).

Note: Since RouterOS v6.41 all VLAN switching related parameters are moved to the bridge section. On CRS3xx series devices VLAN switching must be configured under the bridge section as well, this will not limit the device's performance, CRS3xx is designed to use the built-in switch chip to work with bridge VLAN filtering, you are able to achieve full non-blocking wire-speed switching performance while using bridges and bridge VLAN filtering. Make sure that all bridge ports have the "H" flag, which indicates that the device is using the switch chip to forward packets.
Sub-menu: /interface bridge
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| vlan-filtering (yes | no; Default: no) | Globally enables or disables VLAN functionality for bridge. |
| pvid (1..4094; Default: 1) | Port VLAN ID (pvid) specifies which VLAN the untagged ingress traffic is assigned to. It applies e.g. to frames sent from bridge IP and destined to a bridge port. |
Sub-menu: /interface bridge port
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| frame-types (admit-all | admit-only-untagged-and-priority-tagged | admit-only-vlan-tagged; Default: admit-all) | Specifies allowed ingress frame types on a bridge port. Only has effect when ingress-filtering is enabled. |
| ingress-filtering (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables ingress filtering, which checks if an entry exists for the ingress port and the VLAN ID in the bridge VLAN table. Should be used with frame-types to specify if the ingress traffic should be tagged or untagged. |
| pvid (1..4094; Default: 1) | Port VLAN ID (pvid) specifies which VLAN the untagged ingress traffic is assigned to. |
VLAN Table
Bridge VLAN table represents per-VLAN port mapping with an egress VLAN tag action.
tagged ports send out frames with a learned VLAN ID tag.
untagged ports remove VLAN tag before sending out frames if the learned VLAN ID matches the port pvid.
Sub-menu: /interface bridge vlan
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| bridge (name) | The bridge interface which the respective VLAN entry is intended for. |
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables Bridge VLAN entry. |
| tagged (interfaces; Default: none) | Interface list with a VLAN tag adding action in egress. This setting accepts comma separated values. E.g. tagged=ether1,ether2. |
| untagged (interfaces; Default: none) | Interface list with a VLAN tag removing action in egress. This setting accepts comma separated values. E.g. tagged=ether3,ether4. |
| vlan-ids (1..4094) | The list of VLAN IDs for certain port configuration. This setting accepts VLAN ID range as well as comma separated values. E.g. vlan-ids=100-115,120,122,128-130. |
Setup examples
Port Based VLAN
- The configuration for CRS3xx switches is described in the Bridge VLAN FIltering section.

Note: It is possible to use the built-in switch chip and the CPU at the same time to create a Switch-Router setup, where a device acts as a switch and as a router at the same time. You can find a configuration example in the CRS-Router guide.
MAC Based VLAN
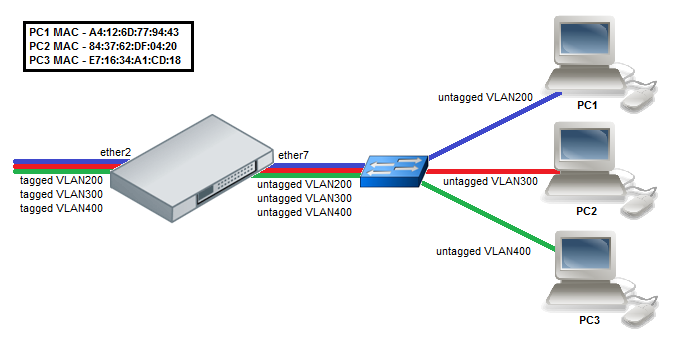

Note: The CRS3xx Switch Rule table is used for MAC Based VLAN functionality, see this table on how many rules each device supports.

Note: MAC-based VLANs will only work properly between switch ports and not between switch ports and CPU. When a packet is being forwarded to the CPU, the pvid property for the bridge port will be always used instead of new-vlan-id from ACL rules.
- Enable switching on ports by creating a bridge with enabled hw-offloading.
/interface bridge add name=bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes /interface bridge port add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether2 hw=yes add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether7 hw=yes
- Add VLANs in the Bridge VLAN table and specify ports.
/interface bridge vlan add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2 untagged=ether7 vlan-ids=200,300,400
- Add Switch rules which assign VLAN id based on MAC address.
/interface ethernet switch rule add switch=switch1 ports=ether7 src-mac-address=A4:12:6D:77:94:43/FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF new-vlan-id=200 add switch=switch1 ports=ether7 src-mac-address=84:37:62:DF:04:20/FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF new-vlan-id=300 add switch=switch1 ports=ether7 src-mac-address=E7:16:34:A1:CD:18/FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF new-vlan-id=400
Protocol Based VLAN
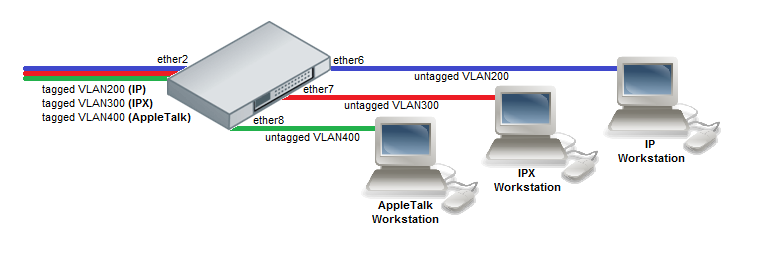

Note: The CRS3xx Switch Rule table is used for Protocol Based VLAN functionality, see this table on how many rules each device supports.
- Enable switching on ports by creating a bridge with enabled hw-offloading.
/interface bridge add name=bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes /interface bridge port add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether2 hw=yes add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether6 hw=yes add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether7 hw=yes add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether8 hw=yes
- Add VLANs in the Bridge VLAN table and specify ports.
/interface bridge vlan add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2 untagged=ether6 vlan-ids=200 add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2 untagged=ether7 vlan-ids=300 add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2 untagged=ether8 vlan-ids=400
- Add Switch rules which assign VLAN id based on MAC protocol.
/interface ethernet switch rule add mac-protocol=ip new-vlan-id=200 ports=ether6 switch=switch1 add mac-protocol=ipx new-vlan-id=300 ports=ether7 switch=switch1 add mac-protocol=0x80F3 new-vlan-id=400 ports=ether8 switch=switch1
VLAN Tunneling (Q-in-Q)
Since RouterOS v6.43 it is possible to use a provider bridge (IEEE 802.1ad) VLAN filtering and hardware offloading at the same time on CRS3xx series switches. The configuration for CRS3xx switches is described in the Bridge VLAN Tunneling (Q-in-Q) section.
Ingress VLAN translation
It is possible to translate a certain VLAN ID to a different VLAN ID using ACL rules on an ingress port. In this example we create two ACL rules, allowing a bidirectional communication. This can be done by doing the following:
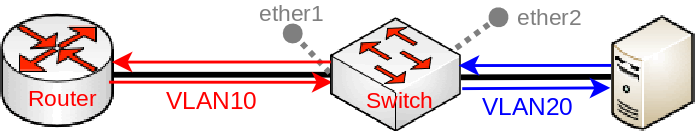
- Create a new bridge and add ports to it with hardware offloading:
/interface bridge add name=bridge1 vlan-filtering=no /interface bridge port add interface=ether1 bridge=bridge1 hw=yes add interface=ether2 bridge=bridge1 hw=yes
- Add ACL rules to translate a VLAN ID in each direction:
/interface ethernet switch rule add new-dst-ports=ether2 new-vlan-id=20 ports=ether1 switch=switch1 vlan-id=10 add new-dst-ports=ether1 new-vlan-id=10 ports=ether2 switch=switch1 vlan-id=20
- Add both VLAN IDs to the bridge VLAN table:
/interface bridge vlan add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether1 vlan-ids=10 add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2 vlan-ids=20
- Enable bridge VLAN filtering:
/interface bridge set bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes

Note: Bidirectional communication is limited only between two switch ports. Translating VLAN ID between more ports can cause traffic flooding or incorrect forwarding between same VLAN ports.

Warning: By enabling vlan-filtering you will be filtering out traffic destined to the CPU, before enabling VLAN filtering you should make sure that you set up a Management port
(R/M)STP
CRS3xx series switches are capable of running STP, RSTP and MSTP on a hardware level. For more detailed information you should check out the Spanning Tree Protocol manual page.
Bonding
Since RouterOS v6.42 all CRS3xx series switches support hardware offloading with bonding interfaces. Only 802.3ad and balance-xor bonding modes are hardware offloaded, other bonding modes will use the CPU's resources. You can find more information about the bonding interfaces in the Bonding Interface section. If 802.3ad mode is used, then LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) is supported.
To create a hardware offloaded bonding interface, you must create a bonding interface with a supported bonding mode:
/interface bonding add mode=802.3ad name=bond1 slaves=ether1,ether2
This interface can be added to a bridge alongside with other interfaces:
/interface bridge add name=bridge /interface bridge port add bridge=bridge interface=bond1 hw=yes add bridge=bridge interface=ether3 hw=yes add bridge=bridge interface=ether4 hw=yes

Note: Don't add interfaces to a bridge that are already in a bond, RouterOS will not allow you to add an interface that is already a slave to a bridge as there is no need to do it since a bonding interface already contains the slave interfaces.
Make sure that the bonding interface is hardware offloaded by checking the "H" flag:
/interface bridge port print Flags: X - disabled, I - inactive, D - dynamic, H - hw-offload # INTERFACE BRIDGE HW 0 H bond1 bridge yes 1 H ether3 bridge yes 2 H ether4 bridge yes

Note: With HW-offloaded bonding interfaces, the built-in switch chip will always use Layer2+Layer3+Layer4 for transmit hash policy, changing the transmit hash policy manually will have no effect.
L3 Hardware Offloading
Layer3 hardware offloading (otherwise known as IP switching or HW routing) will allow to offload some of the router features on to the switch chip. This allows to reach wire speeds when routing packets, which simply would not be possible with the CPU.
At the moment of writing this article, only CRS317-1G-16S+ supports L3 HW Offloading and RouterOS v7beta6 or newer must be used.
The feature can be enabled with:
/interface ethernet switch set switch1 l3hw=yes

Note: After turning off HW Offloading it is recommended to reboot the switch, to make sure that all HW related config is cleared from switch chip.
Currently supported and unsupported feature list:
| Feature | Status | Description |
| IPv4 Unicast | HW | Depending on the complexity of routes in routing table, max HW accelerated route count could change (see table below for min-max supported route count for each hardware). Whole-byte IP prefixes (/8, /16, /24, etc.) occupy less HW space than others (e.g., /22).
If HW route limit is reached new routes will fall back to CPU, except cases when newly added route overlaps with already existing routes processed by hardware. In this case destinations that were processed in hardware will continue to be processed in hardware. The user should choose the device with HW capability large-enough to store all the routes. |
| IPv6 Unicast | CPU | |
| IPv4 Multicast | CPU | |
| IPv6 Multicast | CPU | |
| ECMP | HW | See hardware limits in the next table. |
| "blackhole" routes | HW | This feature enables the possibility to drop D/DOS attacks at wire speed |
| "prohibit" routes | CPU | |
| "unreachable" routes | CPU | |
| gateway=<interface_name> | HW/CPU | This works only for directly connected networks. Since HW does not know how to send ARP requests, CPU sends ARP request and waits for a reply to find out a DST MAC address on the first received packet of the connection that matches a DST IP address. After DST MAC is determined, HW entry is added and all further packets will be processed by switch chip. |
| Bridge | HW | Routing from/to bridge interface |
| VLAN | HW | Routing between VLAN interfaces |
| LACP | HW | /interface bonding
|
| Firewall | FW | Only Fasttrack connections gets processed by HW, which means that CPU is processing packets until connection gets fasttracked. |
| NAT | FW | NAT rules applied to the offloaded Fasttrack connections are processed by HW. |
| QoS | N/A |
Where:
- CPU - feature is supported but processed by CPU
- HW - feature is supported and offloaded in hardware (works when l3hw=yes)
- FW - feature is supported and offloaded in hardware (works when l3hw=fw)
- N/A - feature is not available, meaning that L3 Hardware offloading MUST be disabled for these features to work

Warning: Currently user must choose whether to use hardware accelerated routing or firewall. It is not possible to use both at the same time.
List of supported devices and their limits:
| Release | Routes | Nexthops | ECMP Groups | Fasttrack connections(*1,*2) | NAT enties(*2) | |
| CRS317-1G-16S+ | 7.1beta1 | 150K - 240K | 8K | 4K | 4500 / 3750 (*3) | 4096 |
| CRS309-1G-8S+ | 7.1beta2 | 50K - 80K | 8K | 4K | 4500 / 3750 | 4096 |
| CRS312-4C+8XG | 7.1beta2 | 50K - 80K | 8K | 4K | 2250 / 1500 | 4096 (*4) |
| CRS326-24S+2Q+ | 7.1beta2 | 50K - 80K | 8K | 4K | 2250 / 1500 | 4096 |
*1 When the HW limit of Fasttrack or NAT entries is reached, other connections will fall back to the CPU. MikroTik's smart connection offload algorithm ensures that the connections with the most traffic are offloaded to the hardware.
*2 Fasttrack connections share the same HW memory with ACL rules. Depending on the complexity, one ACL rule may occupy the memory of 3-6 Fasttrack connections.
*3 (Both MPLS and Bridge Port Extender are disabled) / (MPLS, Bridge Port Extender, or both are enabled). MPLS shares the HW memory with Fasttrack connections. Moreover, enabling MPLS requires the allocation of the entire memory region, which could store up to 750 Fasttrack connections otherwise. The same applies to Bridge Port Extender. However, MPLS and Bridge Port Extended may use the same memory region, so enabling them both doesn't double the limitation of Fasttrack connections.
*4 All NAT entries cannot be used due to the limited amount of Fasttrack connections.
Port isolation
Since RouterOS v6.43 it is possible to create a Private VLAN setup on CRS3xx series switches, example can be found in the Switch chip port isolation manual page.
IGMP Snooping
CRS3xx series switches are capable of using IGMP Snooping on a hardware level. To see more detailed information, you should check out the IGMP Snooping manual page.
DHCP Snooping and DHCP Option 82
CRS3xx series switches are capable of using DHCP Snooping with Option 82 on a hardware level. To see more detailed information, you should check out the DHCP Snooping and DHCP Option 82 manual page.
Mirroring
Mirroring lets the switch 'sniff' all traffic that is going in a switch chip and send a copy of those packets out to another port (mirror-target). This feature can be used to easily set up a 'tap' device that allows you to inspect the traffic on your network on a traffic analyzer device. It is possible to set up a simple port based mirroring where, but it is also possible to setup more complex mirroring based on various parameters. Note that mirror-target port has to belong to same switch. (See which port belong to which switch in /interface ethernet menu). Also mirror-target can have a special 'cpu' value, which means that 'sniffed' packets will be sent out of switch chips cpu port. There are many possibilities that can be used to mirror certain traffic, below you can find most common mirroring examples:
- Port Based Mirroring
/interface ethernet switch set switch1 mirror-source=ether2 mirror-target=ether3

Note: Property mirror-source will send an ingress and egress packet copies to the mirror-target port. Both mirror-source and mirror-target are limited to a single interface.
/interface ethernet switch set switch1 mirror-source=none mirror-target=ether3 /interface ethernet switch rule add mirror=yes ports=ether1,ether2 switch=switch1

Note: Using ACL rules, it is possible to mirror packets from multiple ports interfaces. Only ingress packets are mirrored to mirror-target interface.
- VLAN Based Mirroring
/interface bridge set bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes /interface ethernet switch set switch1 mirror-target=ether3 mirror-source=none /interface ethernet switch rule add mirror=yes ports=ether1 switch=switch1 vlan-id=11

Warning: By enabling vlan-filtering you will be filtering out traffic destined to the CPU, before enabling VLAN filtering you should make sure that you set up a Management port
- MAC Based Mirroring
/interface ethernet switch set switch1 mirror-target=ether3 mirror-source=none /interface ethernet switch rule add mirror=yes ports=ether1 switch=switch1 dst-mac-address=64:D1:54:D9:27:E6/FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF add mirror=yes ports=ether1 switch=switch1 src-mac-address=64:D1:54:D9:27:E6/FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF
- Protocol Based Mirroring
/interface ethernet switch set switch1 mirror-target=ether3 mirror-source=none /interface ethernet switch rule add mirror=yes ports=ether1 switch=switch1 mac-protocol=ipx
- IP Based Mirroring
/interface ethernet switch set switch1 mirror-target=ether3 mirror-source=none /interface ethernet switch rule add mirror=yes ports=ether1 switch=switch1 src-address=192.168.88.0/24 add mirror=yes ports=ether1 switch=switch1 dst-address=192.168.88.0/24
There are other options as well, check the ACL section to find out all possible parameters that can be used to match packets.
Traffic Shaping
It is possible to limit certain type of traffic using ACL rules. For CRS3xx series switches it is possible to limit ingress traffic that matches certain parameters and it is possible to limit ingress/egress traffic per port basis. For ingress traffic QoS policer is used, for egress traffic QoS shaper is used.
- Port Based Traffic Shaping
/interface ethernet switch port set ether1 ingress-rate=10M egress-rate=5M
- MAC Based Traffic Shaping
/interface ethernet switch rule add ports=ether1 switch=switch1 src-mac-address=64:D1:54:D9:27:E6/FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF rate=10M
- VLAN Based Traffic Shaping
/interface bridge set bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes /interface ethernet switch rule add ports=ether1 switch=switch1 vlan-id=11 rate=10M

Warning: By enabling vlan-filtering you will be filtering out traffic destined to the CPU, before enabling VLAN filtering you should make sure that you set up a Management port
- Protocol Based Traffic Shaping
/interface ethernet switch rule add ports=ether1 switch=switch1 mac-protocol=ipx rate=10M
There are other options as well, check the ACL section to find out all possible parameters that can be used to match packets.

Note: The CRS3xx Switch Rule table is used for QoS functionality, see this table on how many rules each device supports.
Traffic Storm Control
Since RouterOS v6.42 it is possible to enable traffic storm control on CRS3xx series devices. A traffic storm can emerge when certain frames are continuously flooded on the network. For example, if a network loop has been created and no loop avoidance mechanisms are used (e.g. Spanning Tree Protocol), broadcast or multicast frames can quickly overwhelm the network, causing degraded network performance or even complete network breakdown. With CRS3xx series switches it is possible to limit broadcast, unknown multicast and unknown unicast traffic. Unknown unicast traffic is considered when a switch does not contain a host entry for the destined MAC address. Unknown multicast traffic is considered when a switch does not contain a multicast group entry in the /interface bridge mdb menu. Storm control settings should be applied to ingress ports, the egress traffic will be limited.

Note: The storm control parameter is specified in percentage (%) of the link speed. If your link speed is 1Gbps, then specifying storm-rate as 10 will allow only 100Mbps of broadcast, unknown multicast and/or unknown unicast traffic to be forwarded.
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch port
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| limit-broadcasts (yes | no; Default: yes) | Limit broadcast traffic on switch port. |
| limit-unknown-multicasts (yes | no; Default: no) | Limit unknown multicast traffic on switch port. |
| limit-unknown-unicasts (yes | no; Default: no) | Limit unknown unicast traffic on switch port. |
| storm-rate (integer 0..100; Default: 100) | Amount of broadcast, unknown multicast and/or unknown unicast traffic is limited to in percentage of the link speed. |

Warning: Devices with Marvell-98DX3236 switch chip cannot distinguish unknown multicast traffic from all multicast traffic. For example, CRS326-24G-2S+ will limit all multicast traffic when limit-unknown-multicasts and storm-rate is used. For other devices, for example, CRS317-1G-16S+ the limit-unknown-multicasts parameter will limit only unknown multicast traffic (addresses that are not present in /interface bridge mdb
- For example, to limit 1% (10Mbps) of broadcast and unknown unicast traffic on ether1 (1Gbps), use the following commands:
/interface ethernet switch port set ether1 storm-rate=1 limit-broadcasts=yes limit-unknown-unicasts=yes
MPLS hardware offloading
Since RouterOS v6.41 it is possible to offload certain MPLS functions to the switch chip, the switch must be a (P)rovider router in a PE-P-PE setup in order to achieve hardware offloading. Setup example can be found in the Basic MPLS setup example manual page.

Note: Currently only CRS317-1G-16S+ and CRS309-1G-8S+ using RouterOS v6.41 and newer are capable of hardware offloading certain MPLS functions. CRS317-1G-16S+ and CRS309-1G-8S+ built-in switch chip is not capable of popping MPLS labels from packets, in a PE-P-PE setup you either have to use explicit null or disable TTL propagation in MPLS network to achieve hardware offloading.
Switch Rules (ACL)
Access Control List contains of ingress policy and egress policy engines. See this table on how many rules each device supports (limited by RouterOS). It is advanced tool for wire-speed packet filtering, forwarding and modifying based on Layer2, Layer3 and Layer4 protocol header field conditions.

Note: ACL rules are checked for each received packet until a match has been found. If there are multiple rules that can match, then only the first rule will be triggered. A rule without any action parameters is a rule to accept the packet.
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch rule
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| copy-to-cpu (no | yes; Default: no) | Clones the matching packet and sends it to the CPU. |
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables ACL entry. |
| dscp (0..63) | Matching DSCP field of the packet. |
| dst-address (IP address/Mask) | Matching destination IP address and mask. |
| dst-address6 (IPv6 address/Mask) | Matching destination IPv6 address and mask. |
| dst-mac-address (MAC address/Mask) | Matching destination MAC address and mask. |
| dst-port (0..65535) | Matching destination protocol port number. |
| flow-label (0..1048575) | Matching IPv6 flow label. |
| mac-protocol (802.2 | arp | homeplug-av | ip | ipv6 | ipx | lldp | loop-protect | mpls-multicast | mpls-unicast | packing-compr | packing-simple | pppoe | pppoe-discovery | rarp | service-vlan | vlan | or 0..65535 | or 0x0000-0xffff) | Matching particular MAC protocol specified by protocol name or number |
| mirror (no | yes) | Clones the matching packet and sends it to the mirror-target port. |
| new-dst-ports (ports) | Changes the destination port as specified. An empty setting will drop the packet. A specified port will redirect the packet to it. When the parameter is not used, the packet will be accepted. Multiple "new-dst-ports" are not supported on CRS3xx series switches. |
| new-vlan-id (0..4095) | Changes the VLAN ID to the specified value. Requires vlan-filtering=yes. |
| new-vlan-priority (0..7) | Changes the VLAN priority tag. Requires vlan-filtering=yes. |
| ports (ports) | Matching ports on which will the rule apply on received traffic. |
| protocol (dccp | ddp | egp | encap | etherip | ggp | gre | hmp | icmp | icmpv6 | idpr-cmtp | igmp | ipencap | ipip | ipsec-ah | ipsec-esp | ipv6 | ipv6-frag | ipv6-nonxt | ipv6-opts | ipv6-route | iso-tp4 | l2tp | ospf | pim | pup | rdp | rspf | rsvp | sctp | st | tcp | udp | udp-lite | vmtp | vrrp | xns-idp | xtp | or 0..255) | Matching particular IP protocol specified by protocol name or number. |
| rate (0..4294967295) | Sets ingress traffic limitation (bits per second) for matched traffic. |
| redirect-to-cpu (no | yes) | Changes the destination port of a matching packet to the CPU. |
| src-address (IP address/Mask) | Matching source IP address and mask. |
| src-address6 (IPv6 address/Mask) | Matching source IPv6 address and mask. |
| src-mac-address (MAC address/Mask) | Matching source MAC address and mask. |
| src-port (0..65535) | Matching source protocol port number. |
| switch (switch group) | Matching switch group on which will the rule apply. |
| traffic-class (0..255) | Matching IPv6 traffic class. |
| vlan-id (0..4095) | Matching VLAN ID. Requires vlan-filtering=yes. |
| vlan-header (not-present | present) | Matching VLAN header, whether the VLAN header is present or not. Requires vlan-filtering=yes. |
| vlan-priority (0..7) | Matching VLAN priority. |
Action parameters:
- copy-to-cpu
- redirect-to-cpu
- mirror
- new-dst-ports (can be used to drop packets)
- new-vlan-id
- new-vlan-priority
- rate
Conditional parameters:
- Layer2 conditions:
- dst-mac-address
- mac-protocol
- src-mac-address
- vlan-id
- vlan-header
- vlan-priority
- Layer3 conditions:
- dscp
- protocol
- IPv4 conditions:
- dst-address
- src-address
- IPv6 conditions:
- dst-address6
- flow-label
- src-address6
- traffic-class
- Layer4 conditions:
- dst-port
- src-port

Note: For VLAN related matchers or VLAN related action parameters to work, you need to enable vlan-filtering on the bridge interface and make sure that hardware offloading is enabled on those ports, otherwise these parameters will not have any effect.

Warning: When vlan-protocol is set to 802.1Q, then VLAN related ACL rules are relevant to 0x8100 (CVID) packets, this includes vlan-id and new-vlan-id. When vlan-protocol is set to 802.1ad, then ACL rules are relevant to 0x88A8 (SVID) packets. For example, with 802.1Q the vlan-id matcher will match CVID packets, but with 802.1ad the vlan-id matcher will match SVID packets.
Port Security
It is possible to limit allowed MAC addresses on a single switch port on CRS3xx series switches. For example, to allow 64:D1:54:81:EF:8E start by switching multiple ports together, in this example 64:D1:54:81:EF:8E is going to be located behind ether1.
- Create an ACL rule to allow the given MAC address and drop all other traffic on ether1 (for ingress traffic):
/interface ethernet switch rule add ports=ether1 src-mac-address=64:D1:54:81:EF:8E/FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF switch=switch1 add new-dst-ports="" ports=ether1 switch=switch1
- Switch all required ports together, disable MAC learning and disable unknown unicast flooding on ether1:
/interface bridge add name=bridge1 /interface bridge port add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether1 hw=yes learn=no unknown-unicast-flood=no add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether2 hw=yes
- Add a static hosts entry for
64:D1:54:81:EF:8E(for egress traffic):
/interface bridge host add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether1 mac-address=64:D1:54:81:EF:8E

Warning: Broadcast traffic will still be sent out from ether1. To limit broadcast traffic flood on a bridge port, you can use the broadcast-flood parameter to toggle it. Do note that some protocols depend on broadcast traffic, such as streaming protocols and DHCP.
Dual Boot
“Dual boot” feature allows you to choose which operating system you prefer to use, RouterOS or SwOS. Device operating system could be changed using:
- Serial Terminal (/system routerboard settings set boot-os=swos)
- Winbox
- Webfig
- Serial Console
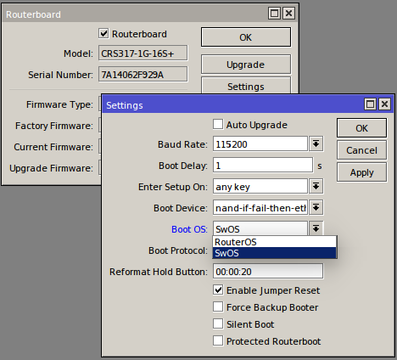 |
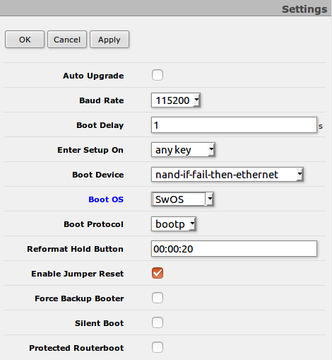 |
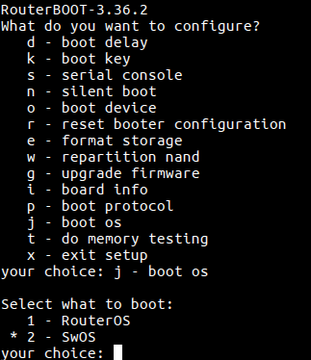 |
More details about SwOS are described here: SwOS manual
Configuring SwOS using RouterOS
Since RouterOS 6.43 it is possible to load, save and reset SwOS configuration, as well as upgrade SwOS and set an IP address for the switch by using RouterOS.
- Save configuration with
/system swos save-config

Note: Configuration will be saved on the same device with swos.config as filename, make sure you download the file off your device since the configuration file will be removed after a reboot.
- Load configuration with
/system swos load-config
- Change password with
/system swos password
- Reset configuration with
/system swos reset-config
- Upgrade SwOS from RouterOS using
/system swos upgrade

Note: The upgrade command will automatically install the latest available SwOS version, make sure that your device has access to the Internet in order for the upgrade process to work properly.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| address-acquisition-mode (dhcp-only | dhcp-with-fallback | static; Default: dhcp-with-fallback) | Changes address acquisition method:
|
| allow-from (IP/Mask; Default: 0.0.0.0/0) | IP address or a network from which the switch is accessible. By default, the switch is accessible by any IP address. |
| allow-from-ports (name; Default: ) | List of switch ports from which the device is accessible. By default, all ports are allowed to access the switch |
| allow-from-vlan (integer: 0..4094; Default: 0) | VLAN ID from which the device is accessible. By defaull, all VLANs are allowed |
| identity (name; Default: Mikrotik) | Name of the switch (used for Mikrotik Neighbor Discovery protocol) |
| static-ip-address (IP; Default: 192.168.88.1) | IP address of the switch in case address-acquisition-mode is either set to dhcp-with-fallback or static. By setting a static IP address, the address acquisition process does not change, which is DHCP with fallback by default. This means that the configured static IP address will become active only when there is going to be no DHCP servers in the same broadcast domain |
See also
- CRS Router
- CRS3xx VLANs with Bonds
- Basic VLAN switching
- Bridge Hardware Offloading
- Spanning Tree Protocol
- IGMP Snooping
- DHCP Snooping and Option 82
- MTU on RouterBOARD
- Layer2 misconfiguration
- Bridge VLAN Table
[ Top | Back to Content ]
