Manual:IP/TFTP: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==TFTP== | |||
TFTP is a very simple protocol used to transfer files. It is from this that its name comes, Trivial File Transfer Protocol or TFTP. Each nonterminal packet is acknowledged separately. RouterOS has a built-in TFTP server since v3.22 | TFTP is a very simple protocol used to transfer files. It is from this that its name comes, Trivial File Transfer Protocol or TFTP. Each nonterminal packet is acknowledged separately. RouterOS has a built-in TFTP server since v3.22 | ||
| Line 14: | Line 16: | ||
== Examples == | == Examples == | ||
* if ''file'' is requested return file from store called ''sata1'': | * '''example 1''' if ''file'' is requested return file from store called ''sata1'': | ||
<pre><nowiki> | <pre><nowiki> | ||
/ip tftp add req-filename=file.txt real-filename=/sata1/file.txt allow=yes read-only=yes | /ip tftp add req-filename=file.txt real-filename=/sata1/file.txt allow=yes read-only=yes | ||
</nowiki></pre> | </nowiki></pre> | ||
* if we want to give out one precise ''file'' no matter what user is requesting: | * '''example 2''' if we want to give out one precise ''file'' no matter what user is requesting: | ||
<pre><nowiki> | <pre><nowiki> | ||
/ip tftp add req-filename=* real-filename=/sata1/file.txt allow=yes read-only=yes | /ip tftp add req-filename=* real-filename=/sata1/file.txt allow=yes read-only=yes | ||
</nowiki></pre> | </nowiki></pre> | ||
Revision as of 15:10, 3 April 2009
TFTP
TFTP is a very simple protocol used to transfer files. It is from this that its name comes, Trivial File Transfer Protocol or TFTP. Each nonterminal packet is acknowledged separately. RouterOS has a built-in TFTP server since v3.22
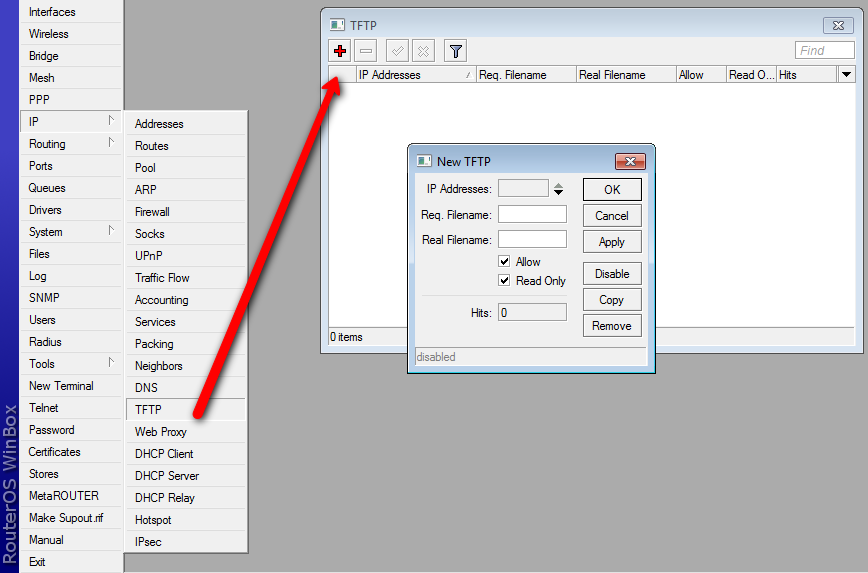
- ip-address (required) - range of IP addresses accepted as clients
- req-filename - requested filename as regular expression (regex)
- real-filename - if above two values are set and valid, the requested filename will be replaced with this. If this field is empty, the req-filename will be used. If multiple regex are specified in req-filename, with this field you can set which ones should match, so this rule is validated. real-filename format for using multiple regex is filename\0\5\6
- allow (default: yes) - to allow connection if above fields are set. if no, connection will be interrupted
- read-only (default: no) - sets if file can be written to, if set to "no" write attempt will fail with error
- hits - how many times this configuration entry has been executed (viewable only)
Examples
- example 1 if file is requested return file from store called sata1:
/ip tftp add req-filename=file.txt real-filename=/sata1/file.txt allow=yes read-only=yes
- example 2 if we want to give out one precise file no matter what user is requesting:
/ip tftp add req-filename=* real-filename=/sata1/file.txt allow=yes read-only=yes