Manual:Interface/EoIP: Difference between revisions
m →Properties: correct location |
m →Properties: value is in integer in seconds and messages are exchanged, typos |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><var><b>keepalive</b></var> (<em>integer</em>; Default: <b>not set</b>)</td> | <td><var><b>keepalive</b></var> (<em>integer</em>; Default: <b>not set</b>)</td> | ||
<td>keep-alive timer, sets time interval in what keep-alive messages should be received. If 3 | <td>keep-alive timer, sets time interval (seconds) in what keep-alive messages should be received. If 3 messages are missed, interface running flag is removed. For this to work, keepalive has to be set to same value on both ends of the tunnel, since one end is expecting messages from the other one and is sending keepalive messages in that direction.</td> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><var><b>l2mtu</b></var> (<em>integer</em>; Default: <b></b>)</td> | <td><var><b>l2mtu</b></var> (<em>integer</em>; Default: <b></b>)</td> | ||
Revision as of 15:34, 25 July 2011
Summary
Sub-menu: /interface eoip
Standards: GRE RFC 1701
Ethernet over IP (EoIP) Tunneling is a MikroTik RouterOS protocol that creates an Ethernet tunnel between two routers on top of an IP connection. The EoIP tunnel may run over IPIP tunnel, PPTP tunne or any other connection capable of transporting IP.
When the bridging function of the router is enabled, all Ethernet traffic (all Ethernet protocols) will be bridged just as if there where a physical Ethernet interface and cable between the two routers (with bridging enabled). This protocol makes multiple network schemes possible.
Network setups with EoIP interfaces:
- Possibility to bridge LANs over the Internet
- Possibility to bridge LANs over encrypted tunnels
- Possibility to bridge LANs over 802.11b 'ad-hoc' wireless networks
The EoIP protocol encapsulates Ethernet frames in GRE (IP protocol number 47) packets (just like PPTP) and sends them to the remote side of the EoIP tunnel.
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| arp (disabled | enabled | proxy-arp | reply-only; Default: enabled) | Address Resolution Protocol mode |
| keepalive (integer; Default: not set) | keep-alive timer, sets time interval (seconds) in what keep-alive messages should be received. If 3 messages are missed, interface running flag is removed. For this to work, keepalive has to be set to same value on both ends of the tunnel, since one end is expecting messages from the other one and is sending keepalive messages in that direction. |
| l2mtu (integer; Default: ) | Layer2 Maximum transmission unit. Not configurable for EoIP. Read more>> |
| mac-address (MAC; Default: ) | Media Access Control number of an interface. The address numeration authority allows to use MAC addresses in the range from 00:00:5E:80:00:00 - 00:00:5E:FF:FF:FF freely |
| mtu (integer; Default: 1500) | Layer3 Maximum transmission unit |
| name (string; Default: ) | Interface name |
| remote-address (IP; Default: ) | IP address of remote end of EoIP tunnel |
| tunnel-id (integer: 65536; Default: ) | Unique tunnel identifier, which must match other side of the tunnel |
Notes
tunnel-id is method of identifying tunnel. It must be unique for each EoIP tunnel.
mtu should be set to 1500 to eliminate packet refragmentation inside the tunnel (that allows transparent bridging of Ethernet-like networks, so that it would be possible to transport full-sized Ethernet frame over the tunnel).
When bridging EoIP tunnels, it is highly recommended to set unique MAC addresses for each tunnel for the bridge algorithms to work correctly. For EoIP interfaces you can use MAC addresses that are in the range from 00:00:5E:80:00:00 - 00:00:5E:FF:FF:FF , which IANA has reserved for such cases. Alternatively, you can set the second bit of the first byte to mark the address as locally administered address, assigned by network administrator, and use any MAC address, you just need to ensure they are unique between the hosts connected to one bridge.
Setup examples
Let us assume we want to bridge two networks: 'Office LAN' and 'Remote LAN'. By using EoIP setup can be made so that Office and Remote LANs are in the same Layer2 broadcast domain.
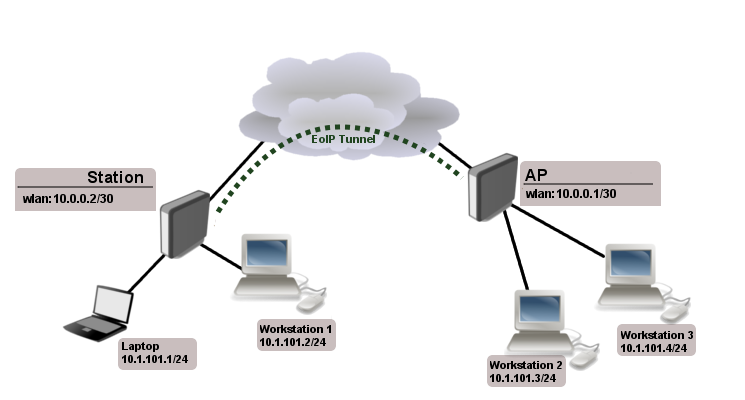
Consider following setup:
As you know wireless station cannot be bridged, to overcome this limitation (not involving WDS) we will create EoIP tunnel over the wireless link and bridge it with interfaces connected to local networks.
We will not cower wireless configuration in this example, lets assume that wireless link is already established
At first we create EoIP tunnel on our gateway ...
[admin@Our_GW] interface eoip> add name="eoip-remote" tunnel-id=0 \ \... remote-address=10.0.0.2 [admin@Our_GW] interface eoip> enable eoip-remote [admin@Our_GW] interface eoip> print Flags: X - disabled, R - running 0 name=eoip-remote mtu=1500 arp=enabled remote-address=10.0.0.2 tunnel-id=0 [admin@Our_GW] interface eoip>
... and on Remote router
[admin@Remote] interface eoip> add name="eoip" tunnel-id=0 \ \... remote-address=10.0.0.1 [admin@Remote] interface eoip> enable eoip-main [admin@Remote] interface eoip> print Flags: X - disabled, R - running 0 name=eoip mtu=1500 arp=enabled remote-address=10.0.0.1 tunnel-id=0 [admin@Remote] interface eoip>
Next step is to bridge local interfaces with EoIP tunnel On Our GW ...
[admin@Our_GW] interface bridge> add
[admin@Our_GW] interface bridge> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 R name="bridge1" mtu=1500 arp=enabled mac-address=00:00:00:00:00:00
protocol-mode=none priority=0x8000 auto-mac=yes
admin-mac=00:00:00:00:00:00 max-message-age=20s forward-delay=15s
transmit-hold-count=6 ageing-time=5m
[admin@Our_GW] interface bridge> port add bridge=bridge1 interface=eoip-remote
[admin@Our_GW] interface bridge> port add bridge=bridge1 interface=office-eth
[admin@Our_GW] interface bridge> port print
Flags: X - disabled, I - inactive, D - dynamic
# INTERFACE BRIDGE PRIORITY PATH-COST
0 eoip-remote bridge1 128 10
1 office-eth bridge1 128 10
[admin@Our_GW] interface bridge>
... and Remote router:
[admin@Remote] interface bridge> add
[admin@Remote] interface bridge> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 R name="bridge1" mtu=1500 arp=enabled mac-address=00:00:00:00:00:00
protocol-mode=none priority=0x8000 auto-mac=yes
admin-mac=00:00:00:00:00:00 max-message-age=20s forward-delay=15s
transmit-hold-count=6 ageing-time=5m
[admin@Remote] interface bridge> port add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether
[admin@Remote] interface bridge> port add bridge=bridge1 interface=eoip-main
[admin@Remote] interface bridge> port print
Flags: X - disabled, I - inactive, D - dynamic
# INTERFACE BRIDGE PRIORITY PATH-COST
0 ether bridge1 128 10
1 eoip-main bridge1 128 10
[admin@Remote] interface bridge>
Now both sites are in the same Layer2 broadcast domain. You can set up IP addresses from the same network on both sites.
[ Top | Back to Content ]