Manual:Initial Configuration: Difference between revisions
m →Troubleshooting: choosing channel |
m →Choosing different frequency: name |
||
| Line 237: | Line 237: | ||
Wireless unnamed features in the guide that are good to know about. Configuration adjustments. | Wireless unnamed features in the guide that are good to know about. Configuration adjustments. | ||
====== | ======Channel frequencies and width====== | ||
It is possible to choose different frequency, here are frequencies that can be used and channel width settings to use 40MHz HT channel (for 802.11n). For example, using ''channel 1 or 2412MHz frequency'' setting ''20/40MHz HT below'' will not yield any results, since there are no 20MHz channel available below set frequency. | It is possible to choose different frequency, here are frequencies that can be used and channel width settings to use 40MHz HT channel (for 802.11n). For example, using ''channel 1 or 2412MHz frequency'' setting ''20/40MHz HT below'' will not yield any results, since there are no 20MHz channel available below set frequency. | ||
Revision as of 11:23, 29 September 2011
Summary
What to do when you have new MikroTik router and you need configuration different from default what routers are provided with?
Connecting wires
Router initial configuration is set up in the way that should work in most of the cases and it is described on the box you received your router in. It is good idea to connect wires in the way it is described on that box:
- Connect ethernet wire from your internet service provider (ISP) to port ether1, rest of the ports on the router are for local area network (LAN). At this moment, your router is protected by default firewall configuration so you should not worry about that.
- Connect LAN wires to the rest of the ports
Configuring router
Router initial configuration have DHCP client on WAN interface (ether1), rest of the ports are set as your local network with DHCP server configured for automatic configuration of devices that support that in your network. In that phase you have to set your computer to accept DHCP settings and connect to router port other than ether1 (please check routerboard.com for what port is what, or check front panel of the router).
Logging into the router
Router will have address 192.168.88.1 that you can open in your browser. When you do that you will be introduced with initial RouterOS page where you have to choose option WebFig.
You will be prompted with login screen into WebFig RouterOS configuration interface.
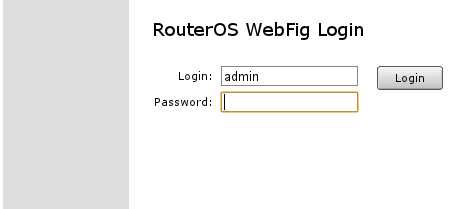
You have to fill in login name with admin and use blank password as it is already. After that you can login into the router.
Router user accounts
It is good idea to set up password for your default user admin and create new user for your use.
To do this, you have to go to 'System-> Users'
Afterwards click on Users menu:
You will see this screen, where you can manage users of the router.
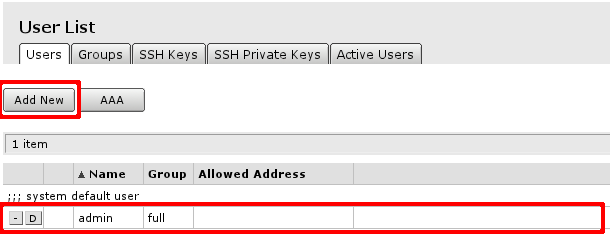
- By clicking on account name, in this case admin will open edit screen for the user
- Add new will open new user creation screen
Both screens are similar you can check that by selecting user name, afterwards clicking OK or Cancel you will be brought back to initial screen of user management.
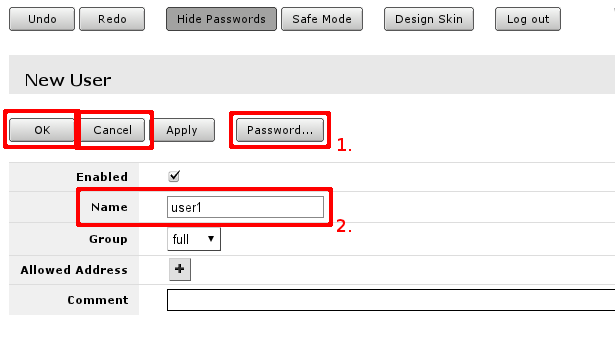
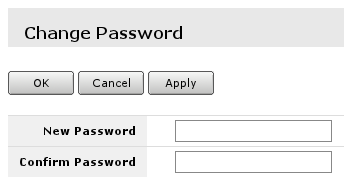
In user edit/Add new screen you can alter existing user or create new. Field marked with 2. is the user name, field 1. will open password screen.
Where old password for the user can be changed or added for new user.
Configure access to internet
If initial configuration did not work (your ISP is not providing DHCP server for automatic configuration) then you will have to have details from your ISP for static configuration of the router. These settings should include
- IP address you can use
- Network mask for the IP address
- Default gateway address
Less important settings regarding router configuration:
- DNS address for name resolution
- NTP server address for time automatic configuration
- Your previous MAC address of the interface facing ISP
DHCP Client
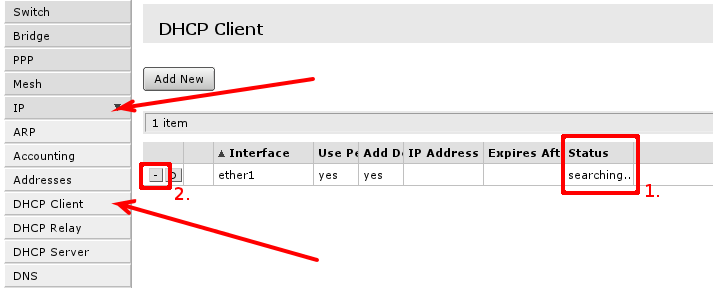
Default configuration is set up using DHCP-Client on interface facing your ISP or wide area network (WAN). It has to be disabled if your ISP is not providing this service in the network. Open 'IP -> DHCP Client' and inspect field 1. to see status of DHCP Client, if it is in state as displayed in screenshot, means your ISP is not providing you with automatic configuration and you can use button in selection 2. to remove DHCP-Client configured on the interface.
Static IP Address
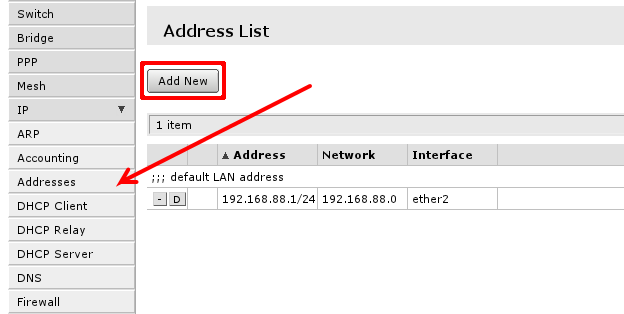
To manage IP addresses of the router open 'IP -> Address'
You will have one address here - address of your local area network (LAN) 192.168.88.1 one you are connected to router. Select Add new to add new static IP address to your router's configuration.
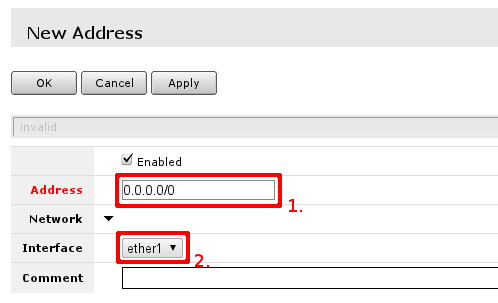
You have to fill only fields that are marked. Field 1. should contain IP address provided by your ISP and network mask'. Allowed notation examples:
- 172.16.88.67/24
- 172.16.88.67/255.255.255.0
both of these notations mean the same, if your ISP gave you address in one notation, or in the other, use one provided and router will do the rest of calculation.
Other field of interest is interface this address is going to be assigned. This should be interface your ISP is connected to, if you followed this guide - interface contains name - ether1

Note: While you type in the address, webfig will calculate if address you have typed is acceptable, if it is not label of the field will turn red, otherwise it will be blue

Note: It is good practice to add comments on the items to give some additional information for the future, but that is not required
Configuring network address translation (NAT)
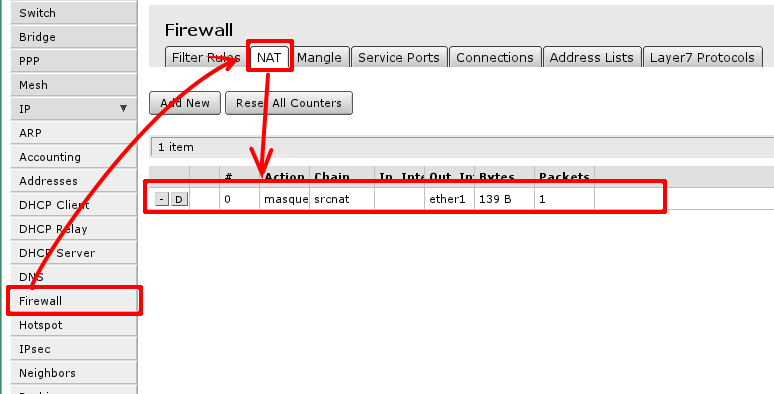
Since you are using local and global networks, you have to set up network masquerade, so that your LAN is hidden behind IP address provided by your ISP. That should be so, since your ISP does not know what LAN addresses you are going to use and your LAN will not be routed from global network.
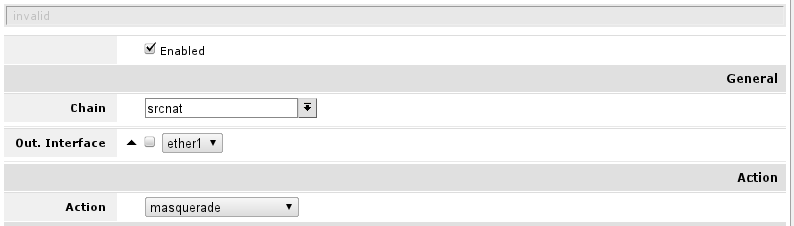
To check if you have the source NAT open 'IP -> Firewall -> tab NAT' and check if item highlighted (or similar) is in your configuration.
Essential fields for masquerade to work:
- enabled is checked;
- chain - should be srcnat;
- out-interface is set to interface connected to your ISP network, Following this guide ether1;
- action should be set to masquerade.
In screenshot correct rule is visible, note that irrelevant fields that should not have any value set here are hidden (and can be ignored)
Default gateway
under 'IP -> Routes' menu you have to add routing rule called default route. And select Add new to add new route.
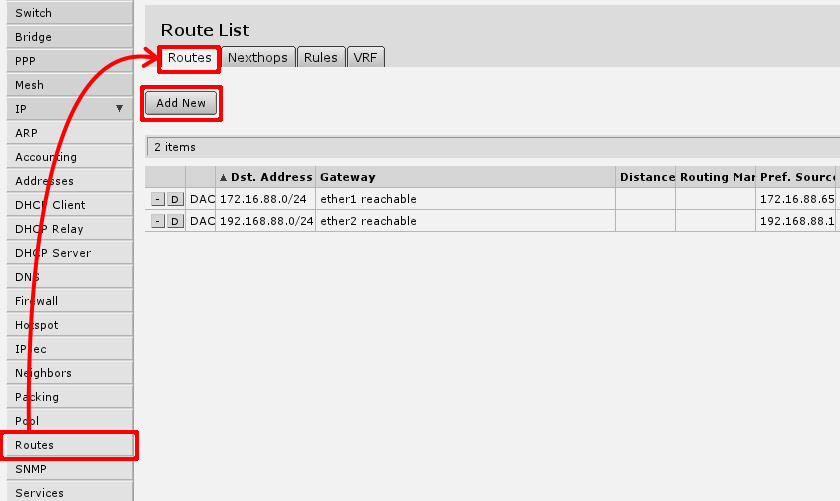
In screen presented you will see the following screen:
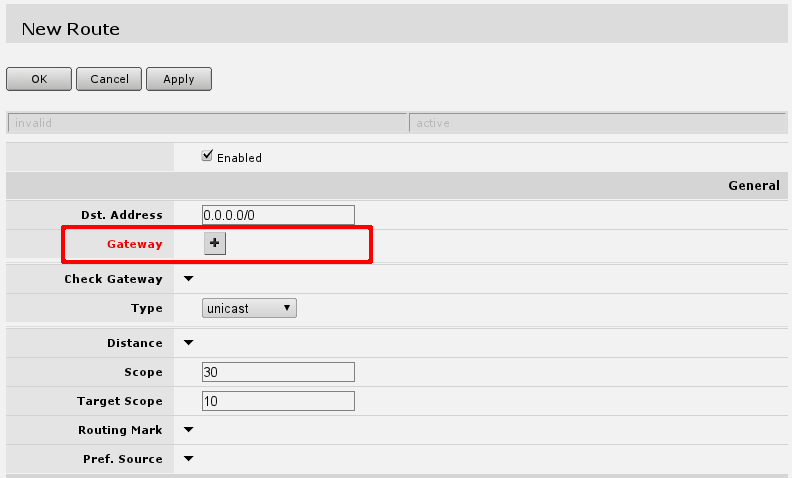 here you will have to press button with + near red Gateway label and enter in the field default gateway, or simply gateway given by your ISP.
here you will have to press button with + near red Gateway label and enter in the field default gateway, or simply gateway given by your ISP.
This should look like this, when you have pressed the + button and enter gateway into the field displayed.
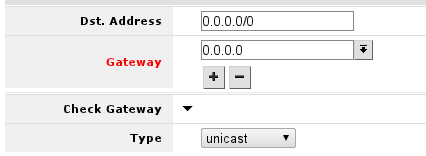
After this, you can press OK button to finish creation of the default route.
At this moment, you should be able to reach any globally available host on the Internet using IP address.
Domain name resolution
To be able to open web pages or access Internet hosts by domain name DNS should be configured, either on your router or your computer. In scope of this guide, i will present only option of router configuration, so that DNS addresses are given out by DHCP-Server that you are already using.
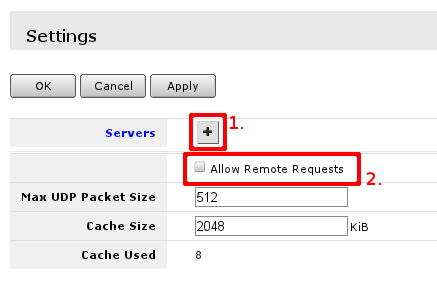
This can be done in 'IP -> DNS ->Settings', first Open 'IP ->DNS':
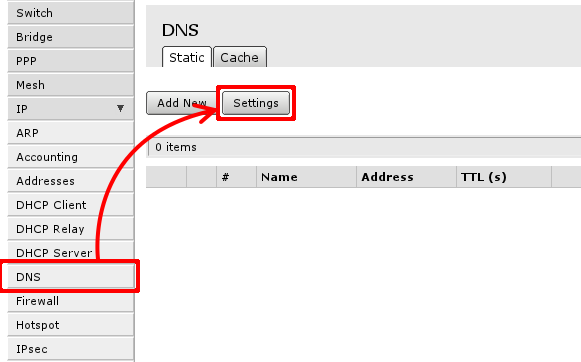
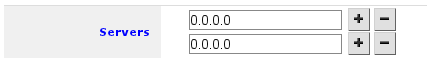
Then select Settings to set up DNS cacher on the router. You have to add field to enter DNS IP address, section 1. in image below. and check Allow Remote Requests marked with 2.
The result of pressing + twice will result in 2 fields for DNS IP addresses:

Note: Filling acceptable value in the field will turn field label blue, other way it will be marked red.
SNTP Client
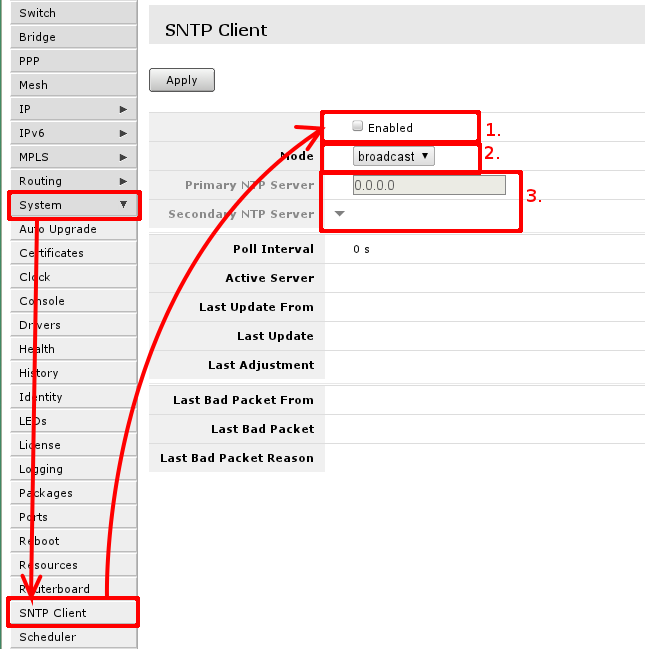
RouterBOARD routers do not keep time between restarts or power failuers. To have correct time on the router set up SNTP client if you require that.
To do that, go to 'System -> SNTP' where you have to enable it, first mark, change mode from broadcast to unicast, so you can use global or ISP provided NTP servers, that will allow to enter NTP server IP addresses in third area.
Setting up Wireless
For ease of use bridged wireless setup will be used, so that your wired hosts will be in same ethernet broadcast domain as wireless clients.
To make this happen several things has to be checked:
- Ethernet interfaces designated for LAN are swtiched or bridged, or they are separate ports;
- If bridge interface exists;
- Wireless interface mode is set to ap-bridge (in case, router you have has level 4 or higher license level), if not, then mode has to be set to bridge and only one client (station) will be able to connect to the router using wireless network;
- There is appropriate security profile created and selected in interface settings.
Check Ethernet interface state

Warning: Changing settings may affect connectivity to your router and you can be disconnected from the router. Use Safe Mode so in case of disconnection made changes are reverted back to what they where before you entered safe mode
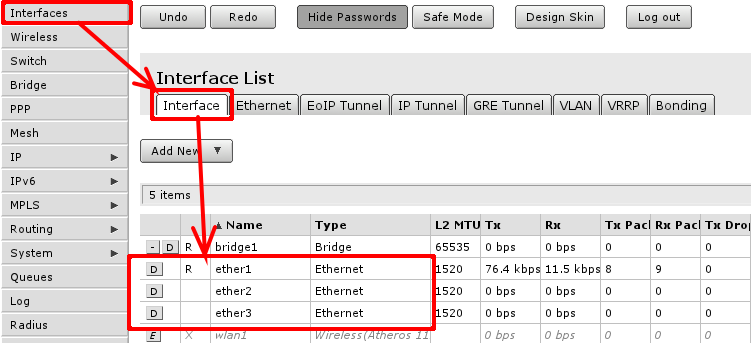
To check if ethernet port is switched, in other words, if ethernet port is set as slave to another port go to 'Interface' menu and open Ethernet interface details. They can be distinguished by Type column displaying Ethernet.
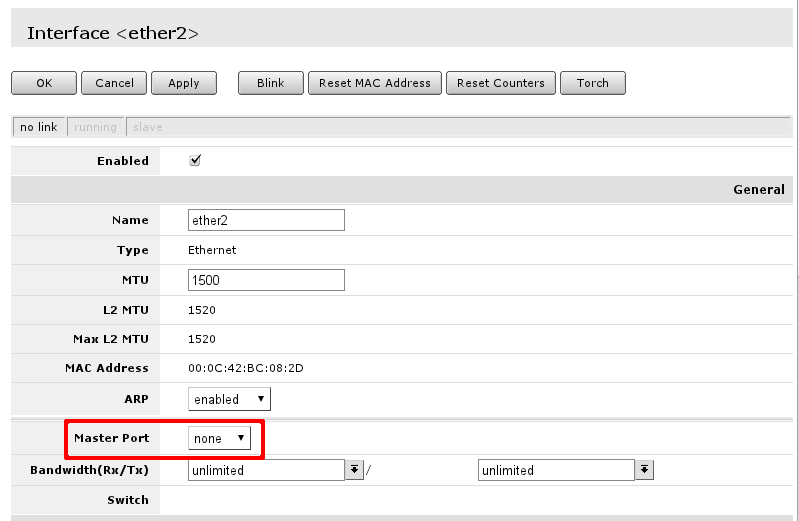
When interface details are opened, look up Master Port setting.
Available settings for the attribute are none, or one of Ethernet interface names. If name is set, that mean, that interface is set as slave port. Usually RouterBOARD routers will come with ether1 as intended WAN port and rest of ports will be set as slave ports of ether2 for LAN use.
Check if all intended LAN Ethernet ports are set as slave ports of the rest of one of the LAN ports. For example, if ether2. ether3, ether4 and ether5 are intended as LAN ports, set on ether3 to ether5 attribute Master Port to ether2.
In case this operation fails - means that Ethernet interface is used as port in bridge, you have to remove them from bridge to enable hardware packet switching between Ethernet ports. To do this, go to Bridge -> Ports and remove slave ports (in example, ether3 to ether5) from the tab.
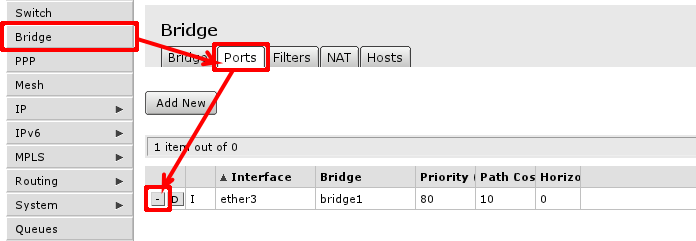

Note: If master port is present as bridge port, that is fine, intended configuration requires it there, same applies to wireless interface (wlan)
Security profile
It is important to protect your wireless network, so no malicious acts can be performed by 3rd parties using your wireless access-point.
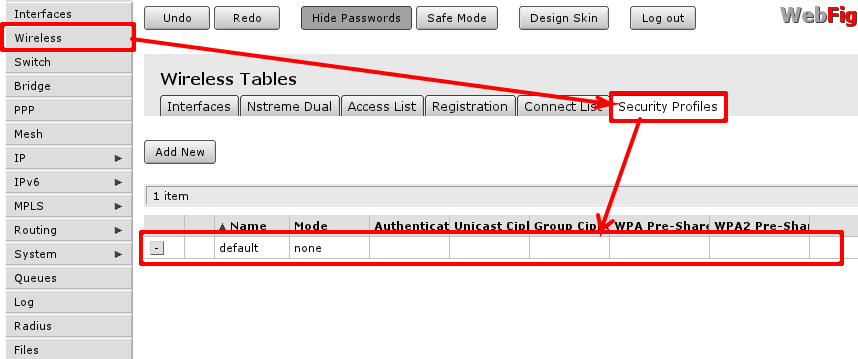
To edit or create new security profile head to 'Wireless -> tab 'Security Prodiles' and choose one of two options:
- Using Add new create new profile;
- Using highlighted path in screenshot edit default profile that is already assigned to wireless interface.
In This example i will create new security profile, editing it is quite similar. Options that has to be set are highlighted with read and recommended options are outlined by red boxes and pre-set to recommended values. WPA and WPA2 is used since there are still legacy equipment around (Laptops with Windows XP, that do not support WPA2 etc.)
WPA Pre- shared key and WPA2 Pre- shared key should be entered with sufficient length. If key length is too short field label will indicate that by turning red, when sufficient length is reached it will turn blue.
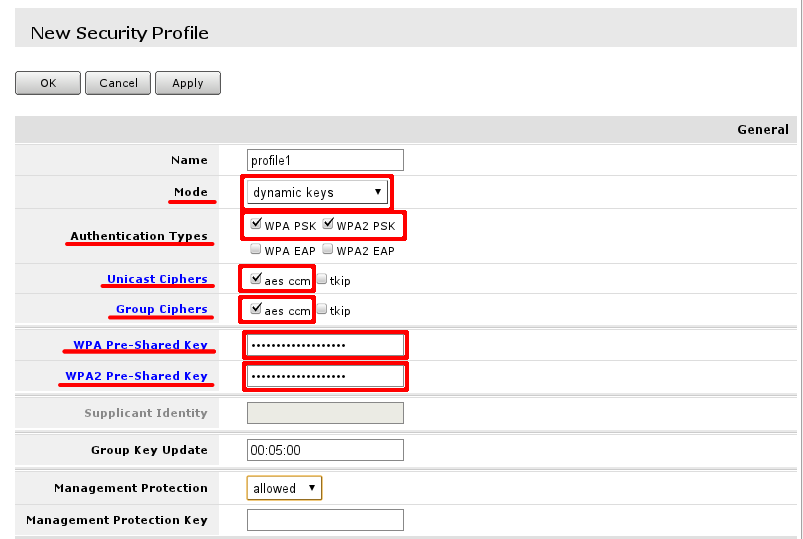

Note: When configuring this, you can deselect Hide passwords in page header to see the actual values of the fields, so they can be successfully entered into device configuration that are going to connect to wireless access-point
Wireless settings
Adjusting wireless settings. That can be done here:
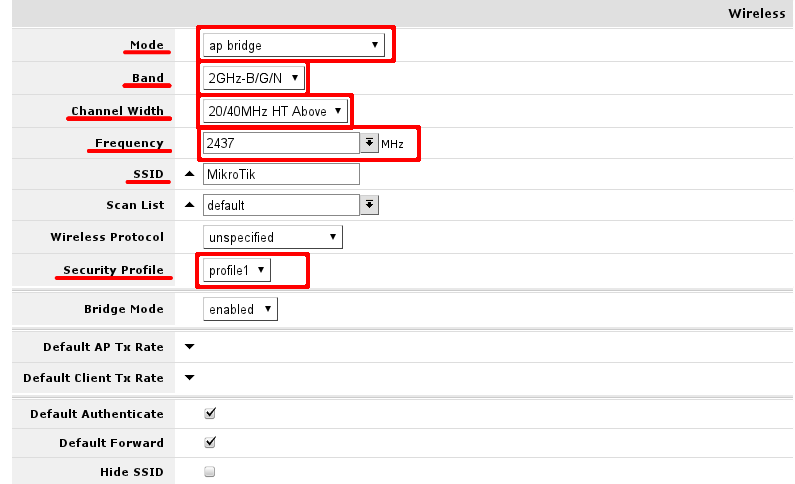
In General section adjust settings to settings as shown in screenshot. Consider these safe, however it is possible, that these has to be adjusted slightly.
Interface mode has to be set to ap-bridge, if that is not possible (license resctrictions) set to bridge, so one client will be able to connect to device.
WiFI devices usually are designed with 2.4GHz modes in mind, setting band to 2GHz-b/g/n will enable clients with 802.11b, 802.11g and 802.11n to connect to the access point
Adjust channel width to enable faster data rates for 802.11n clients. In example channel 6 is used, as result, 20/40MHz HT Above or 20/40 MHz HT Below can be used. Choose either of them.
Set SSID - the name of the access point. It will be visible when you scan for networks using your WiFi equipment.
[[File:File:Example.jpg]]
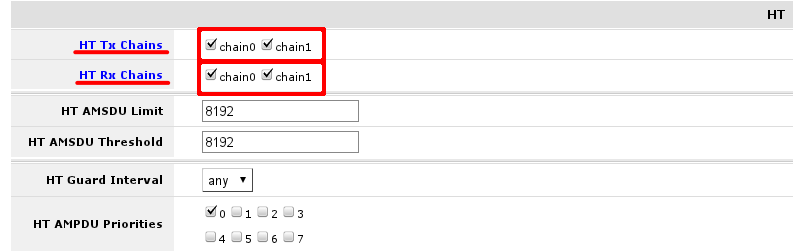
In section HT set change HT transmit and receive chains. It is good practice to enable all chains that are available
When settings are set accordingly it is time to enable our protected wireless access-point
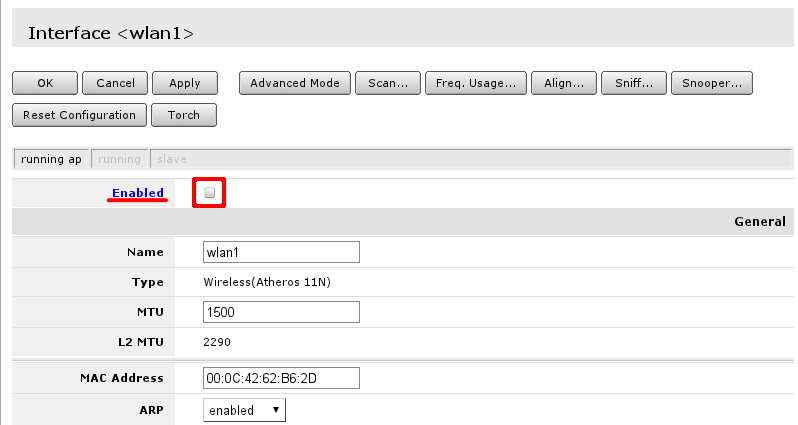
Bridge LAN with Wireless
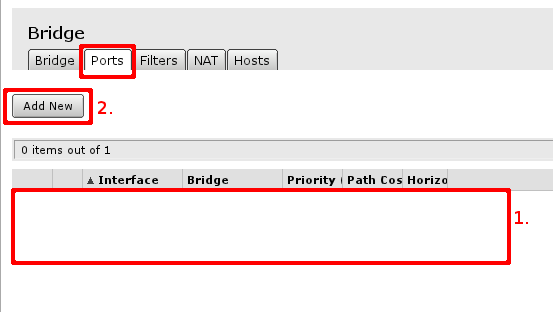
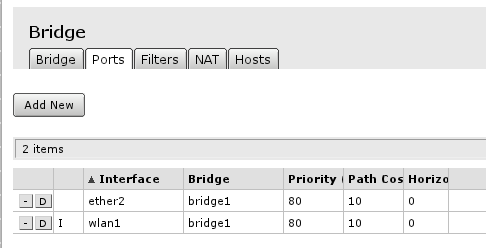
Open Bridge menu and check if there are any bridge interface available first mark. If there is not, select Add New marked with second mark and in the screen that opens just accept the default settings and create interface. When bridge interface is availbe continue to Ports tab where master LAN interface and WiFI interface have to be added.
First marked area is where interfaces that are added as ports to bridge interface are visible. If there are no ports added, choose Add New to add new ports to created bridge interfaces.
When new bridge port is added, select that it is enabled (part of active configuration), select correct bridge interface, following this guide - there should be only 1 interface. And select correct port - LAN interface master port and WiFi port
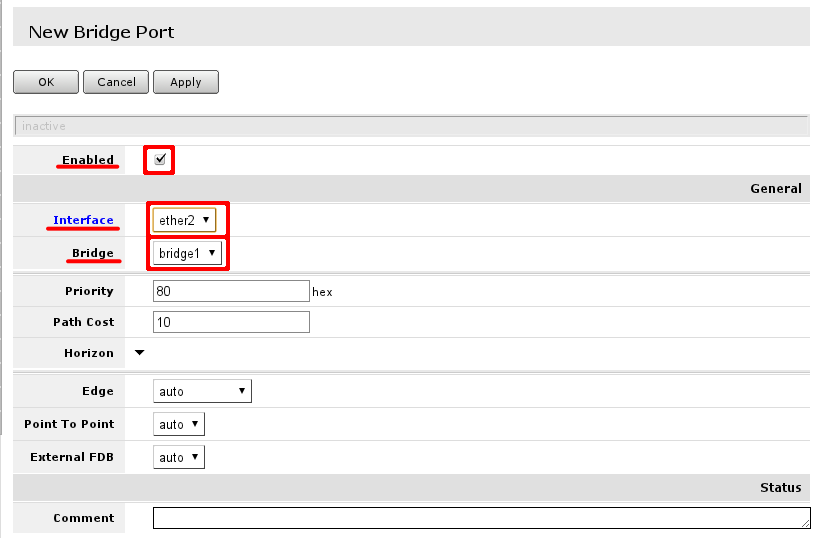
Finished look of bridge configured with all ports required
Troubleshooting
This section is here to make some deviations from configuration described in the guide itself. It can require more understanding of networking, wireless networks in general.
Wireless
Wireless unnamed features in the guide that are good to know about. Configuration adjustments.
Channel frequencies and width
It is possible to choose different frequency, here are frequencies that can be used and channel width settings to use 40MHz HT channel (for 802.11n). For example, using channel 1 or 2412MHz frequency setting 20/40MHz HT below will not yield any results, since there are no 20MHz channel available below set frequency.
| Channel | Frequency | Below | Above |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2412 MHz | no | yes |
| 2 | 2417 MHz | no | yes |
| 3 | 2422 MHz | no | yes |
| 4 | 2427 MHz | no | yes |
| 5 | 2432 MHz | yes | yes |
| 6 | 2437 MHz | yes | yes |
| 7 | 2442 MHz | yes | yes |
| 8 | 2447 MHz | yes | yes |
| 9 | 2452 MHz | yes | yes |
| 10 | 2457 MHz | yes | yes |
| 11 | 2462 MHz | yes | no |
| 12 | 2467 MHz | yes | no |
| 13 | 2472 MHz | yes | no |