Manual:Fast Path: Difference between revisions
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
=== IPv4 FastTrack handler=== | === IPv4 FastTrack handler=== | ||
IPv4 FastTrack handler is automatically used for marked connections. Use firewall action "fasttrack-connection" to mark connections for fasttrack. Currently only TCP and UDP connections can be actually fasttracked (even though any connection can be marked for fasttrack). IPv4 FastTrack handler supports NAT (SNAT, DNAT or both). FastTrack is supported on the [[M:Fast_Path#List_of_devices_with_FastPath_support | boards]] | IPv4 FastTrack handler is automatically used for marked connections. Use firewall action "fasttrack-connection" to mark connections for fasttrack. Currently only TCP and UDP connections can be actually fasttracked (even though any connection can be marked for fasttrack). IPv4 FastTrack handler supports NAT (SNAT, DNAT or both). FastTrack is supported on the specific [[M:Fast_Path#List_of_devices_with_FastPath_support | boards]]. | ||
Note that not all packets in a connection can be fasttracked, so it is likely to see some packets going through slow path even though connection is marked for fasttrack. Fasttracked packets bypass firewall, connection tracking, simple queues, queue tree with parent=global, <del>ip traffic-flow</del>(restriction removed in 6.33), ip accounting, ipsec, hotspot universal client, vrf assignment, so it is up to administrator to make sure fasttrack does not interfere with other configuration; | Note that not all packets in a connection can be fasttracked, so it is likely to see some packets going through slow path even though connection is marked for fasttrack. Fasttracked packets bypass firewall, connection tracking, simple queues, queue tree with parent=global, <del>ip traffic-flow</del>(restriction removed in 6.33), ip accounting, ipsec, hotspot universal client, vrf assignment, so it is up to administrator to make sure fasttrack does not interfere with other configuration; | ||
Revision as of 08:14, 27 November 2015
Summary
Fast path allows to forward packets without additional processing in the Linux kernel. It improves forwarding speeds significantly.
For fast path to work, interface support and specific configuration conditions are required.
List of devices with FastPath support
Interface FastPath support can be checked by doing "/interface print detail" and seeing fast-path property value.
| RouterBoard | Interfaces |
|---|---|
| RB6xx series | ether1,2 |
| RB7xx series | all ethernets |
| RB800 | ether1,2 |
| RB9xx series | all ethernets |
| RB1000 | all ethernets |
| RB1100 series | ether1-10,11 |
| RB2011 series | all ethernets and sfp |
| CCR series routers | all ethernets and sfps |
| All devices | wireless interfaces, if wireless-fp or wireless-cm2 package used |
| bridge interfaces (since 6.29) | |
| vlan, vrrp interfaces (since 6.30) | |
| bonding interfaces - rx only (since 6.30) | |
| eoip, gre, ipip interfaces (since 6.33). Eoip, gre, ipip interfaces have per interface setting "allow-fast-path". Allowing fast path on eoip, gre, ipip interfaces have side effect of bypassing firewall, connection tracking, simple queues, queue tree with parent=global, ip accounting, ipsec, hotspot universal client, vrf assignment for encapsulated packets that go trough fastpath. Note that allowing fast path for tunnel does not guarantee that all packets will go fastpath, so for slowpath packets regular processing happens as before |
FastPath Handlers
Currently RouterOS has following fast path handlers:
- ipv4
- ipv4 fasttrack
- traffic generator
- mpls
- bridge

Note: Packet can be forwarded by fast path handler only if at least source interface support fast path. For complete fast path forwarding destination interface support is also required. See the list of supported interfaces.
IPv4 handler
IPv4 fast path is automatically used if following conditions are met:
- firewal rules are not configured;
Traffic flow is disabledrestriction removed in 6.33;/ip traffic-flow enabled=no- Simple and queue trees with parent=global are not configured;
- no mesh, metarouter interface configuration;
- sniffer, torch and traffic generator is not running;
- connection tracking is not active;
- ip accounting is disabled (/ip accounting enabled=no);
- VRFs are not set (/ip route vrf is empty);
- Hotspot is not used (/ip hostspot has no interfaces);
- IpSec policies are not configured (ROS v6.8);
no active mac-ping, mac-telnet or mac-winbox sessionsrestriction removed in 6.33;- /tool mac-scan is not actively used;
- /tool ip-scan is not actively used;
/ip firewall connection tracking set enabled parameter has new auto value Which means that connection tracking is disabled by default until firewall rules are added.
IPv4 FastTrack handler
IPv4 FastTrack handler is automatically used for marked connections. Use firewall action "fasttrack-connection" to mark connections for fasttrack. Currently only TCP and UDP connections can be actually fasttracked (even though any connection can be marked for fasttrack). IPv4 FastTrack handler supports NAT (SNAT, DNAT or both). FastTrack is supported on the specific boards.
Note that not all packets in a connection can be fasttracked, so it is likely to see some packets going through slow path even though connection is marked for fasttrack. Fasttracked packets bypass firewall, connection tracking, simple queues, queue tree with parent=global, ip traffic-flow(restriction removed in 6.33), ip accounting, ipsec, hotspot universal client, vrf assignment, so it is up to administrator to make sure fasttrack does not interfere with other configuration;
IPv4 FastTrack is active if following conditions are met:
- no mesh, metarouter interface configuration;
- sniffer, torch and traffic generator is not running;
no active mac-ping, mac-telnet or mac-winbox sessionsrestriction removed in 6.33;- /tool mac-scan is not actively used;
- /tool ip-scan is not actively used;
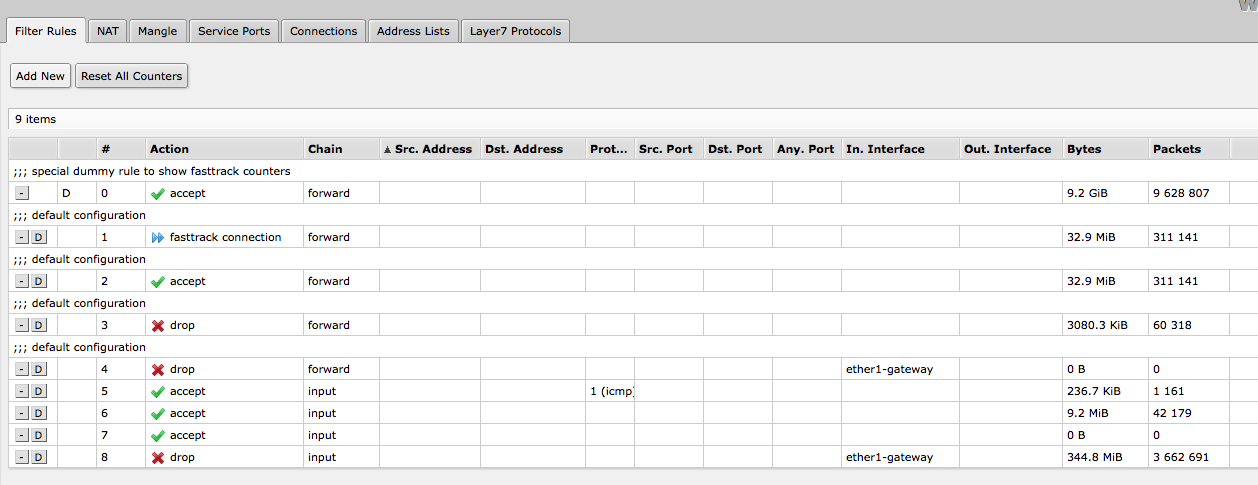
For example, in home routers with factory default configuration, you could Fasttrack all LAN traffic with this one rule placed at the top of the Firewall Filter. The same configuration accept rule is required:
/ip firewall filter add chain=forward action=fasttrack-connection connection-state=established,related /ip firewall filter add chain=forward action=accept connection-state=established,related
Note, that this will break any filtering and Queues you apply for LAN traffic, you will have to mark traffic first, if you want to only fasttrack specific traffic.
This is how a default configuration looks with fastpath rule added on top (and auto-added dummy rule above it):
Traffic Generator handler
Traffic Generator fast path is automatically used for interfaces that support this feature.
MPLS handler
MPLS fast path is automatically used for interfaces that support this feature.
Currently MPLS fast-path applies only to MPLS switched traffic (frames that enter router as MPLS and must leave router as MPLS) - MPLS ingress and egress (including VPLS tunnel endpoints that do VPLS encap/decap) will operate as before.
Bridge handler
Bridge fast path is automatically used if following conditions are met:
- no bridge firewall rules (
/interface bridge filter, /interface bridge nat) are configured, /interface bridge settings use-ip-firwall=no,- no mesh, metarouter interface configuration,
- sniffer, torch and traffic generator is not running,
[ Top | Back to Content ]