Manual:CRS1xx/2xx series switches examples: Difference between revisions
| Line 447: | Line 447: | ||
'''This example requires a group of switched ports. Assume that all ports used in this example are in one switch group configured with master-port setting.''' | '''This example requires a group of switched ports. Assume that all ports used in this example are in one switch group configured with master-port setting.''' | ||
<pre> | |||
/interface ethernet | |||
set ether6 master-port=ether2 | |||
set ether7 master-port=ether2 | |||
set ether8 master-port=ether2 | |||
set ether9 master-port=ether2 | |||
set ether10 master-port=ether2 | |||
</pre> | |||
The first part of port isolation configuration is setting the Uplink port – set port profile to 0 for ether2. | The first part of port isolation configuration is setting the Uplink port – set port profile to 0 for ether2. | ||
Revision as of 11:33, 9 June 2016
Summary
Basic use cases and configuration examples for Cloud Router Switch features.
Management IP Configuration
- Untagged (VLAN 0) Management IP address has to be assigned to the master-port.
/interface ethernet set ether3 master-port=ether2 set ether4 master-port=ether2 set ether5 master-port=ether2 /ip address add address=192.168.88.1/24 interface=ether2 network=192.168.88.0
- For tagged VLAN Management IP address add VLAN 99 interface and assign IP address to it. Since the master-port receives all the traffic coming from switch-cpu port, VLAN interface has to be configured on the master-port, in this case "ether2" port. Now from switch-chip point there also has to be VLAN 99 tagging on switch1-cpu port.
/interface vlan add name=vlan99 vlan-id=99 interface=ether2 /ip address add address=192.168.88.1/24 interface=vlan99 network=192.168.88.0
/interface ethernet switch egress-vlan-tag add tagged-ports=switch1-cpu vlan-id=99 /interface ethernet switch vlan add ports=switch1-cpu vlan-id=99 learn=yes
VLAN

Note: It is recommended to get Serial Console cable and test it before configuring VLANs because you may lose access to the CPU and/or the port you are connected to.

Note: Some changes may take some time to take effect due to already learned MAC addreses. In such cases flushing Unicast Forwarding Database can help: /interface ethernet switch unicast-fdb flush

Note: Multiple master-port configuration is designed as fast and simple port isolation solution, but it limits part of VLAN functionality supported by CRS switch-chip. For advanced configurations use one master-port within CRS switch chip for all ports, configure VLANs and isolate port groups with port isolation profile configuration.
Port Based VLAN
Example 1 (Trunk and Access ports)
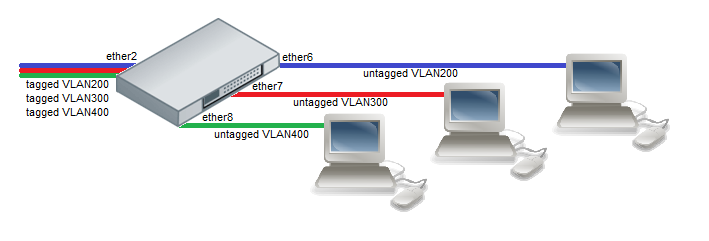
- Choose a master port and enslave the ports you need to be in the same switch group.
/interface ethernet set ether6 master-port=ether2 set ether7 master-port=ether2 set ether8 master-port=ether2
- Add initial VLAN assignments (PVID) to VLAN access ports.
/interface ethernet switch ingress-vlan-translation add ports=ether6 customer-vid=0 new-customer-vid=200 sa-learning=yes add ports=ether7 customer-vid=0 new-customer-vid=300 sa-learning=yes add ports=ether8 customer-vid=0 new-customer-vid=400 sa-learning=yes
- Add VLAN 200, VLAN 300 and VLAN 400 tagging on ether2 port to create it as VLAN trunk port. Egress-VLAN-Tag entry is mandatory for every VLAN to make VLAN access ports work. If VLAN trunk port has not been chosen yet, Egress-VLAN-Tag entry has to be added with tagged-ports="".
/interface ethernet switch egress-vlan-tag add tagged-ports=ether2 vlan-id=200 add tagged-ports=ether2 vlan-id=300 add tagged-ports=ether2 vlan-id=400
- VLAN membership definitions in the VLAN table are required for proper isolation. Adding entries with VLAN id and ports makes that VLAN traffic valid on those ports.
/interface ethernet switch vlan add ports=ether2,ether6 vlan-id=200 learn=yes add ports=ether2,ether7 vlan-id=300 learn=yes add ports=ether2,ether8 vlan-id=400 learn=yes
- After valid VLAN configuration unknown/invalid VLAN forwarding can be disabled in global switch settings.
/interface ethernet switch set drop-if-invalid-or-src-port-not-member-of-vlan-on-ports=ether2,ether6,ether7,ether8
Example 2 (Trunk and Hybrid ports)
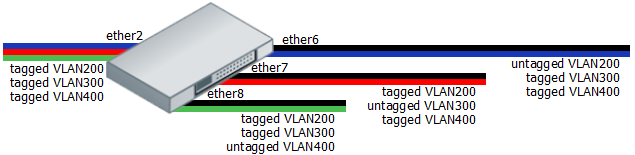
- Create a group of switched ports.
/interface ethernet set ether6 master-port=ether2 set ether7 master-port=ether2 set ether8 master-port=ether2
- Add initial VLAN assignments (PVID) for untagged traffic on ether6, ether7, ether8 ports.
/interface ethernet switch ingress-vlan-translation add ports=ether6 customer-vid=0 new-customer-vid=200 sa-learning=yes add ports=ether7 customer-vid=0 new-customer-vid=300 sa-learning=yes add ports=ether8 customer-vid=0 new-customer-vid=400 sa-learning=yes
- Add VLAN 200, VLAN 300 and VLAN 400 tagging on ports according to diagram. The tagged-ports option allow multiple values to support tagging on many ports.
/interface ethernet switch egress-vlan-tag add tagged-ports=ether2,ether7,ether8 vlan-id=200 add tagged-ports=ether2,ether6,ether8 vlan-id=300 add tagged-ports=ether2,ether6,ether7 vlan-id=400
- VLAN membership definitions in the VLAN table are required for proper isolation. Adding entries with VLAN id and ports makes that VLAN traffic valid on those ports.
/interface ethernet switch vlan add ports=ether2,ether6,ether7,ether8 vlan-id=200 learn=yes add ports=ether2,ether6,ether7,ether8 vlan-id=300 learn=yes add ports=ether2,ether6,ether7,ether8 vlan-id=400 learn=yes
- Unknown VLANs should be disabled after valid VLAN membership configuration.
/interface ethernet switch set drop-if-invalid-or-src-port-not-member-of-vlan-on-ports=ether2,ether6,ether7,ether8
Protocol Based VLAN
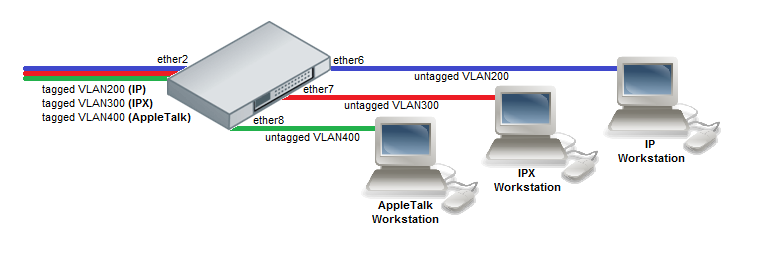
- Create a group of switched ports.
/interface ethernet set ether6 master-port=ether2 set ether7 master-port=ether2 set ether8 master-port=ether2
- Set VLAN for IP and ARP protocols
/interface ethernet switch protocol-based-vlan add port=ether2 protocol=arp set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=0 add port=ether6 protocol=arp set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=200 add port=ether2 protocol=ip set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=0 add port=ether6 protocol=ip set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=200
- Set VLAN for IPX protocol
/interface ethernet switch protocol-based-vlan add port=ether2 protocol=ipx set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=0 add port=ether7 protocol=ipx set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=300
- Set VLAN for AppleTalk AARP and AppleTalk DDP protocols
/interface ethernet switch protocol-based-vlan add port=ether2 protocol=0x80F3 set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=0 add port=ether8 protocol=0x80F3 set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=400 add port=ether2 protocol=0x809B set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=0 add port=ether8 protocol=0x809B set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=400
MAC Based VLAN
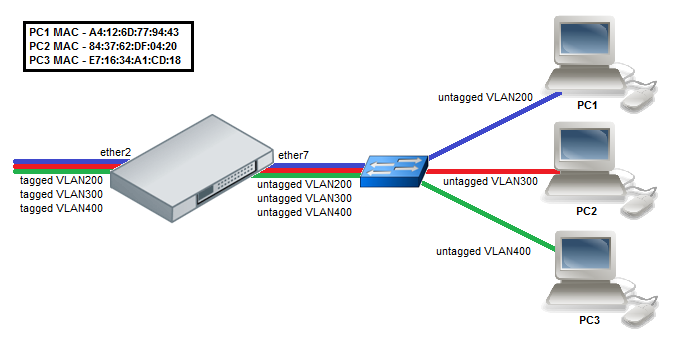
- Create a group of switched ports.
/interface ethernet set ether7 master-port=ether2
- Enable MAC based VLAN translation on access port.
/interface ethernet switch port set ether7 allow-fdb-based-vlan-translate=yes
- Add MAC-to-VLAN mapping entries in MAC based VLAN table.
/interface ethernet switch mac-based-vlan add src-mac=A4:12:6D:77:94:43 new-customer-vid=200 add src-mac=84:37:62:DF:04:20 new-customer-vid=300 add src-mac=E7:16:34:A1:CD:18 new-customer-vid=400
- Add VLAN 200, VLAN 300 and VLAN 400 tagging on ether2 port to create it as VLAN trunk port.
/interface ethernet switch egress-vlan-tag add tagged-ports=ether2 vlan-id=200 add tagged-ports=ether2 vlan-id=300 add tagged-ports=ether2 vlan-id=400
InterVLAN Routing
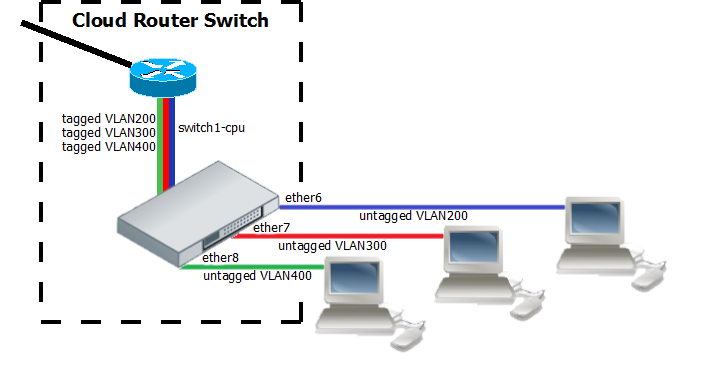
InterVLAN routing configuration consists of two main parts – VLAN tagging in switch-chip and routing in RouterOS. This configuration can be used in many applications by combining it with DHCP server, Hotspot, PPP and other features for each VLAN. Additionally this example covers blocking of unwanted other VLAN traffic on ports.
- Create a group of switched ports.
/interface ethernet set ether6 master-port=ether2 set ether7 master-port=ether2 set ether8 master-port=ether2
- Set VLAN tagging on CPU port for all VLANs to make packets tagged before they are routed and add ingress VLAN translation rules to ensure correct VLAN id assignment is done on access ports.
/interface ethernet switch egress-vlan-tag add tagged-ports=switch1-cpu vlan-id=200 add tagged-ports=switch1-cpu vlan-id=300 add tagged-ports=switch1-cpu vlan-id=400 /interface ethernet switch ingress-vlan-translation add ports=ether6 customer-vid=0 new-customer-vid=200 sa-learning=yes add ports=ether7 customer-vid=0 new-customer-vid=300 sa-learning=yes add ports=ether8 customer-vid=0 new-customer-vid=400 sa-learning=yes
- For routing add VLAN interfaces on master-port because it connects with CPU port and add IP addresses to created VLAN interfaces. In this example three 192.168.x.1 addresses are added to vlan200, vlan300 and vlan400 interfaces.
/interface vlan add name=vlan200 interface=ether2 vlan-id=200 add name=vlan300 interface=ether2 vlan-id=300 add name=vlan400 interface=ether2 vlan-id=400 /ip address add address=192.168.20.1/24 interface=vlan200 network=192.168.20.0 add address=192.168.30.1/24 interface=vlan300 network=192.168.30.0 add address=192.168.40.1/24 interface=vlan400 network=192.168.40.0
Unknown/Invalid VLAN filtering
VLAN membership is defined in the VLAN table. Adding entries with VLAN id and ports makes that VLAN traffic valid on those ports. After valid VLAN configuration unknown/invalid VLAN forwarding can be disabled in global switch settings. This VLAN filtering configuration example applies to InterVLAN Routing setup.
/interface ethernet switch vlan add ports=switch1-cpu,ether6 vlan-id=200 learn=yes add ports=switch1-cpu,ether7 vlan-id=300 learn=yes add ports=switch1-cpu,ether8 vlan-id=400 learn=yes
- Option 1: disable invalid VLAN forwarding on specific ports:
/interface ethernet switch set drop-if-invalid-or-src-port-not-member-of-vlan-on-ports=ether2,ether6,ether7,ether8
- Option 2: disable invalid VLAN forwarding on all ports:
/interface ethernet switch set forward-unknown-vlan=no
VLAN Tunneling (Q-in-Q)
This example covers typical VLAN tunneling use case where service provider devices add another VLAN tag for independent forwarding in the mean time allowing customers to use their own VLANs.

Note: This example contains only Service VLAN tagging part.
It is recommended to additionally set Unknown/Invalid VLAN filtering configuration on ports.
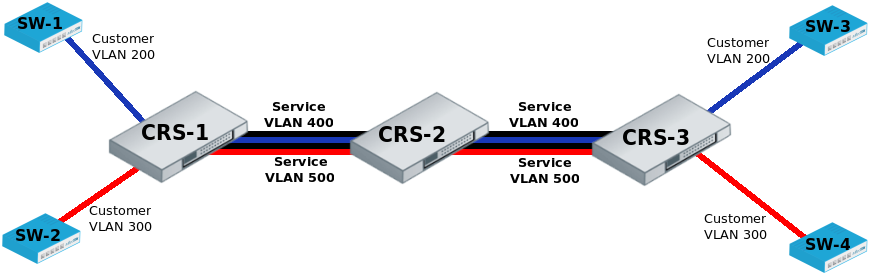
CRS-1:The first switch on the edge of service provider network has to properly indentify traffic from customer VLAN id on port and assign new service VLAN id with ingress VLAN translation rules.
VLAN trunk port configuration for service provider VLAN tags is in the same egress-vlan-tag table.
The main difference from basic Port Based VLAN configuration is that CRS switch-chip has to be set to do forwarding according to service (outer) VLAN id instead of customer (inner) VLAN id.
/interface ethernet set [ find default-name=ether2 ] master-port=ether1 set [ find default-name=ether9 ] master-port=ether1 /interface ethernet switch ingress-vlan-translation add customer-vid=200 new-service-vid=400 ports=ether1 sa-learning=yes add customer-vid=300 new-service-vid=500 ports=ether2 sa-learning=yes /interface ethernet switch egress-vlan-tag add tagged-ports=ether9 vlan-id=400 add tagged-ports=ether9 vlan-id=500 /interface ethernet switch set bridge-type=service-vid-used-as-lookup-vid
CRS-2: The second switch in the service provider network require only switched ports using master-port and bridge-type configured to do forwarding according to service (outer) VLAN id instead of customer (inner) VLAN id.
/interface ethernet set [ find default-name=ether10 ] master-port=ether9 /interface ethernet switch set bridge-type=service-vid-used-as-lookup-vid
CRS-3: The third switch has similar configuration to CRS-1:
- Ports in a switch group using master-port;
- Ingress VLAN translation rules to define new service VLAN assingments on ports;
- tagged-ports for service provider VLAN trunks;
- CRS switch-chip set to use service VLAN id in switching lookup.
/interface ethernet set [ find default-name=ether4 ] master-port=ether3 set [ find default-name=ether10 ] master-port=ether3 /interface ethernet switch ingress-vlan-translation add customer-vid=200 new-service-vid=400 ports=ether3 sa-learning=yes add customer-vid=300 new-service-vid=500 ports=ether4 sa-learning=yes /interface ethernet switch egress-vlan-tag add tagged-ports=ether10 vlan-id=400 add tagged-ports=ether10 vlan-id=500 /interface ethernet switch set bridge-type=service-vid-used-as-lookup-vid
Mirroring
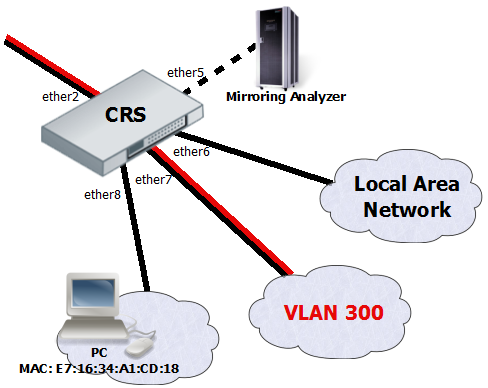
The Cloud Router Switches support three types of mirroring. Port based mirroring can be applied to any of switch-chip ports, VLAN based mirroring works for all specified VLANs regardless switch-chip ports and MAC based mirroring copies traffic sent or received from specific device reachable from the port configured in Unicast Forwarding Database.
Port Based Mirroring
The first configuration sets ether5 port as a mirror0 analyzer port for both ingress and egress mirroring, mirrored traffic will be sent to this port. Port based ingress and egress mirroring is enabled from ether6 port.
/interface ethernet switch set ingress-mirror0=ether5 egress-mirror0=ether5 /interface ethernet switch port set ether6 ingress-mirror-to=mirror0 egress-mirror-to=mirror0
VLAN Based Mirroring
The second example requires ports to be switched in a group. Mirroring configuration sets ether5 port as a mirror0 analyzer port and sets mirror0 port to be used when mirroring from VLAN occurs. VLAN table entry enables mirroring only for VLAN 300 traffic between ether2 and ether7 ports.
/interface ethernet set ether7 master-port=ether2 /interface ethernet switch set ingress-mirror0=ether5 vlan-uses=mirror0 /interface ethernet switch vlan add ports=ether2,ether7 vlan-id=300 learn=yes ingress-mirror=yes
MAC Based Mirroring
The third configuration also requires ports to be switched in a group. Mirroring configuration sets ether5 port as a mirror0 analyzer port and sets mirror0 port to be used when mirroring from Unicast Forwarding database occurs. The entry from Unicast Forwarding database enables mirroring for packets with source or destination MAC address E7:16:34:A1:CD:18 from ether8 port.
/interface ethernet set ether8 master-port=ether2 /interface ethernet switch set ingress-mirror0=ether5 fdb-uses=mirror0 /interface ethernet switch unicast-fdb add port=ether8 mirror=yes svl=yes mac-address=E7:16:34:A1:CD:18
Trunking
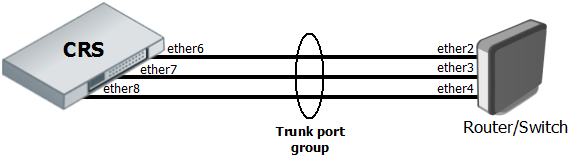
The Trunking in the Cloud Router Switches provides static link aggregation groups with hardware automatic failover and load balancing. IEEE802.3ad and IEEE802.1ax compatible Link Aggregation Control Protocol is not supported yet. Up to 8 Trunk groups are supported with up to 8 Trunk member ports per Trunk group.
- Configuration requires a group of switched ports and an entry in the Trunk table.
/interface ethernet set ether6 master-port=ether2 set ether7 master-port=ether2 set ether8 master-port=ether2 /interface ethernet switch trunk add name=trunk1 member-ports=ether6,ether7,ether8
- This example also shows proper bonding configuration in RouterOS on the other end.
/interface bonding add name=bonding1 slaves=ether2,ether3,ether4 mode=balance-xor transmit-hash-policy=layer-2-and-3 \ link-monitoring=mii mii-interval=100ms
Isolation
Port Level Isolation
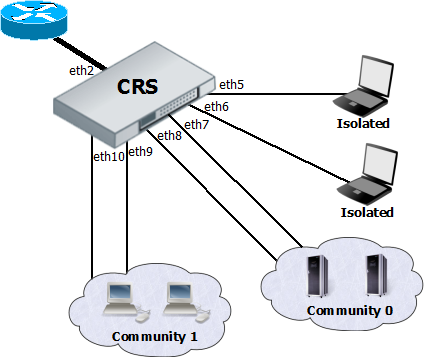
Port-level isolation is often used for Private VLAN, where:
- One or multiple uplink ports are shared among all users for accessing gateway or router.
- Port group Isolated Ports is for guest users. Communication is through the uplink ports only.
- Port group Community 0 is for department A. Communication is allowed between the group members and through uplink ports.
- Port group Community X is for department X. Communication is allowed between the group members and through uplink ports.
The Cloud Router Switches use port-level isolation profiles for Private VLAN implementation:
- Uplink ports – Port-level isolation profile 0
- Isolated ports – Port-level isolation profile 1
- Community 0 ports - Port-level isolation profile 2
- Community X (X <= 30) ports - Port-level isolation profile X
This example requires a group of switched ports. Assume that all ports used in this example are in one switch group configured with master-port setting.
/interface ethernet set ether6 master-port=ether2 set ether7 master-port=ether2 set ether8 master-port=ether2 set ether9 master-port=ether2 set ether10 master-port=ether2
The first part of port isolation configuration is setting the Uplink port – set port profile to 0 for ether2.
/interface ethernet switch port set ether2 isolation-leakage-profile-override=0
Then continue with setting isolation profile 1 to all isolated ports and adding the communication port for port isolation profile 1.
/interface ethernet switch port set ether5 isolation-leakage-profile-override=1 set ether6 isolation-leakage-profile-override=1 /interface ethernet switch port-isolation add port-profile=1 ports=ether2 type=dst
Configuration to set Community 0 and Community 1 ports is similar.
/interface ethernet switch port set ether7 isolation-leakage-profile-override=2 set ether8 isolation-leakage-profile-override=2 /interface ethernet switch port-isolation add port-profile=2 ports=ether2,ether7,ether8 type=dst
/interface ethernet switch port set ether9 isolation-leakage-profile-override=3 set ether10 isolation-leakage-profile-override=3 /interface ethernet switch port-isolation add port-profile=3 ports=ether2,ether9,ether10 type=dst
Protocol Level Isolation
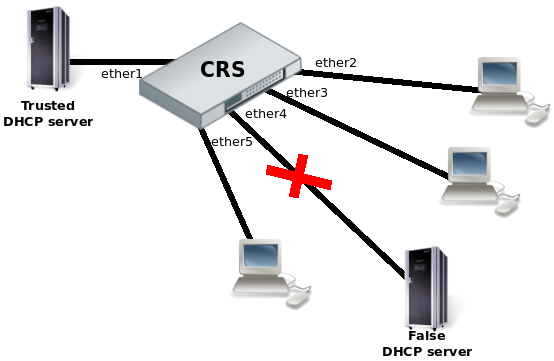
Protocol level isolation on CRS switches can be used to enchance network security. For example, restricting DHCP traffic between the users and allowing it only to trusted DHCP server port can prevent security risks like DHCP spoofing attack. The following example shows how to configure it on CRS.
- Choose a master port and enslave the ports you need to be within the same switch group.
/interface ethernet set [ find default-name=ether2 ] master-port=ether1 set [ find default-name=ether3 ] master-port=ether1 set [ find default-name=ether4 ] master-port=ether1 set [ find default-name=ether5 ] master-port=ether1
- Set the same Community port profile for all DHCP client ports. Community port profile numbers are from 2 to 30.
/interface ethernet switch port set ether2 isolation-leakage-profile-override=2 set ether3 isolation-leakage-profile-override=2 set ether4 isolation-leakage-profile-override=2 set ether5 isolation-leakage-profile-override=2
- And configure port isolation/leakage profile for selected Community (2) to allow DHCP traffic destined only to port where the trusted DHCP server is located. registration-status and traffic-type properties have to be set empty in order to apply restriction only for DHCP protocol.
/interface ethernet switch port-isolation add port-profile=2 protocol-type=dhcpv4 type=dst forwarding-type=bridged ports=ether1 \ registration-status="" traffic-type=""
Quality of Service (QoS)
QoS configuration schemes
MAC based traffic scheduling and shaping: [MAC address in UFDB] -> [QoS Group] -> [Priority] -> [Queue] -> [Shaper]
VLAN based traffic scheduling and shaping: [VLAN id in VLAN table] -> [QoS Group] -> [Priority] -> [Queue] -> [Shaper]
Protocol based traffic scheduling and shaping: [Protocol in Protocol VLAN table] -> [QoS Group] -> [Priority] -> [Queue] -> [Shaper]
PCP/DEI based traffic scheduling and shaping: [Switch port PCP/DEI mapping] -> [Priority] -> [Queue] -> [Shaper]
DSCP based traffic scheduling and shaping: [QoS DSCP mapping] -> [Priority] -> [Queue] -> [Shaper]
MAC based traffic scheduling using internal Priority
In Strict Priority scheduling mode, the highest priority queue is served first. The queue number represents the priority and the queue with highest queue number has the highest priority. Traffic is transmitted from highest priority queue until the queue is empty, and then moves to the next highest priority queue, and so on. If no congestion is present on the egress port, packet is transmitted as soon as it is received. If congestion occurs on the port where high priority traffics keep coming, the lower priority queues starve.
On all CRS switches the scheme where MAC based egress traffic scheduling is done according to internal Priority would be following: [MAC address] -> [QoS Group] -> [Priority] -> [Queue];
In this example host1 (E7:16:34:00:00:01) and host2 (E7:16:34:00:00:02) will have higher priority 1 and the rest of the hosts will have lower priority 0 for transmited traffic on port ether7.
Note that CRS has maximum 8 queues per port.
- Create a group of ports for switching.
/interface ethernet set [ find default-name=ether7 ] master-port=ether6 set [ find default-name=ether8 ] master-port=ether6
- Create QoS group for use in UFDB.
/interface ethernet switch qos-group add name=group1 priority=1
- Add UFDB entries to match specific MACs on ether7 and apply QoS group1
/interface ethernet switch unicast-fdb add mac-address=E7:16:34:00:00:01 port=ether7 qos-group=group1 svl=yes add mac-address=E7:16:34:00:00:02 port=ether7 qos-group=group1 svl=yes
- Configure ether7 port queues to work according Strict Priority and QoS scheme only for destination address.
/interface ethernet switch port
set ether7 per-queue-scheduling="strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0,strict-prior\
ity:0,strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0" priority-to-queue=0:0,1:1 \
qos-scheme-precedence=da-based
MAC based traffic shaping using internal Priority
The scheme where MAC based traffic shaping is done according to internal Priority would be following: [MAC address] -> [QoS Group] -> [Priority] -> [Queue] -> [Shaper];
In this example unlimited traffic will have priority 0 and limited traffic will have priority 1 with the bandwidth limit 10Mbit.
Note that CRS has maximum 8 queues per port.
- Create a group of ports for switching.
/interface ethernet set [ find default-name=ether7 ] master-port=ether6 set [ find default-name=ether8 ] master-port=ether6
- Create QoS group for use in UFDB.
/interface ethernet switch qos-group add name=group1 priority=1
- Add UFDB entry to match specific MAC on ether8 and apply QoS group1
/interface ethernet switch unicast-fdb add mac-address=E7:16:34:A1:CD:18 port=ether8 qos-group=group1 svl=yes
- Configure ether8 port queues to work according Strict Priority and QoS scheme only for destination address.
/interface ethernet switch port
set ether8 per-queue-scheduling="strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0,strict-prior\
ity:0,strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0" priority-to-queue=0:0,1:1 \
qos-scheme-precedence=da-based
- Apply bandwidth limit for queue1 on ether8.
/interface ethernet switch shaper add port=ether8 rate=10M target=queue1
If CRS switch supports Access Control List, this configuration would be simplier.
/interface ethernet switch acl policer add name=policer1 yellow-burst=100k yellow-rate=10M /interface ethernet switch acl add mac-dst-address=E7:16:34:A1:CD:18 policer=policer1
VLAN based traffic scheduling + shaping using internal Priorities
Best practice is to assign lower internal QoS Priority for traffic limited by shaper to make it also less important in Strict Priority scheduler. (higher priority should be more important and unlimited)
In this example:
VLAN10 -> QoS group0 = traffic limited by shaper
VLAN20 -> QoS group1 = normal traffic
VLAN30 -> QoS group2 = prioritized traffic
- Create a group of ports for switching.
/interface ethernet set [ find default-name=ether7 ] master-port=ether6 set [ find default-name=ether8 ] master-port=ether6
- Create QoS groups for use in VLAN table.
/interface ethernet switch qos-group add name=group0 priority=0 add name=group1 priority=1 add name=group2 priority=2
- Add VLAN entries to apply QoS groups for certain VLANs.
/interface ethernet switch vlan add ports=ether7,ether8 qos-group=group0 vlan-id=10 add ports=ether7,ether8 qos-group=group1 vlan-id=20 add ports=ether7,ether8 qos-group=group2 vlan-id=30
- Configure ether7, ether8 port queues to work according Strict Priority and QoS scheme only for VLAN based QoS.
/interface ethernet switch port
set ether7 per-queue-scheduling="strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0,strict-prior\
ity:0,strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0" priority-to-queue=0:0,1:1,2:2 \
qos-scheme-precedence=vlan-based
set ether8 per-queue-scheduling="strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0,strict-prior\
ity:0,strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0,strict-priority:0" priority-to-queue=0:0,1:1,2:2 \
qos-scheme-precedence=vlan-based
- Apply bandwidth limit for queue0 on ether7, ether8.
/interface ethernet switch shaper add port=ether7 rate=10M target=queue0 add port=ether8 rate=10M target=queue0
Bandwidth Limiting
Both Ingress Port policer and Shaper provide bandwidth limiting features for CRS switches.
- Ingress Port Policer sets RX limit on port:
/interface ethernet switch ingress-port-policer add port=ether5 meter-unit=bit rate=10M
- Shaper sets TX limit on port:
/interface ethernet switch shaper add port=ether5 meter-unit=bit rate=10M
Traffic Storm Control
The same Ingress Port policer also can be used for the traffic storm control to prevent disruptions on Layer 2 ports caused by broadcast, multicast or unicast traffic storms.
- Broadcast storm control example on ether5 port with 500 packet limit per second:
/interface ethernet switch ingress-port-policer add port=ether5 rate=500 meter-unit=packet packet-types=broadcast
- Example with multiple packet types which includes ARP and ND protocols and unregistered multicast traffic. Unregistered multicast is traffic which is not defined in Multicast Forwarding database.
/interface ethernet switch ingress-port-policer add port=ether5 rate=5k meter-unit=packet packet-types=broadcast,arp-or-nd,unregistered-multicast
[ Top | Back to Content ]
