Manual:IP/Firewall/NAT: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<div class=manual> | <div class=manual> | ||
{{Warning|This manual is moved to https://help.mikrotik.com/docs/display/ROS/Firewall}} | |||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
Revision as of 11:02, 3 June 2020

Warning: This manual is moved to https://help.mikrotik.com/docs/display/ROS/Firewall
Summary
Sub-menu: /ip firewall nat
Network Address Translation is an Internet standard that allows hosts on local area networks to use one set of IP addresses for internal communications and another set of IP addresses for external communications. A LAN that uses NAT is referred as natted network. For NAT to function, there should be a NAT gateway in each natted network. The NAT gateway (NAT router) performs IP address rewriting on the way a packet travel from/to LAN.
There are two types of NAT:
- source NAT or srcnat. This type of NAT is performed on packets that are originated from a natted network. A NAT router replaces the private source address of an IP packet with a new public IP address as it travels through the router. A reverse operation is applied to the reply packets travelling in the other direction.
- destination NAT or dstnat. This type of NAT is performed on packets that are destined to the natted network. It is most comonly used to make hosts on a private network to be acceesible from the Internet. A NAT router performing dstnat replaces the destination IP address of an IP packet as it travel through the router towards a private network.
Hosts behind a NAT-enabled router do not have true end-to-end connectivity. Therefore some Internet protocols might not work in scenarios with NAT. Services that require the initiation of TCP connection from outside the private network or stateless protocols such as UDP, can be disrupted. Moreover, some protocols are inherently incompatible with NAT, a bold example is AH protocol from the IPsec suite.
To overcome these limitations RouterOS includes a number of so-called NAT helpers, that enable NAT traversal for various protocols.
Masquerade
Firewall NAT action=masquerade is unique subversion of action=srcnat, it was designed for specific use in situations when public IP can randomly change, for example DHCP-server changes it, or PPPoE tunnel after disconnect gets different IP, in short - when public IP is dynamic.
Every time interface disconnects and/or its IP address changes, router will clear all masqueraded connection tracking entries that send packet out that interface, this way improving system recovery time after public ip address change.
Unfortunately this can lead to some issues when action=masquerade is used in setups with unstable connections/links that get routed over different link when primary is down. In such scenario following things can happen:
- on disconnect, all related connection tracking entries are purged;
- next packet from every purged (previously masqueraded) connection will come into firewall as
connection-state=new, and, if primary interface is not back, packet will be routed out via alternative route (if you have any) thus creating new connection; - primary link comes back, routing is restored over primary link, so packets that belong to existing connections are sent over primary interface without being masqueraded leaking local IPs to a public network.
You can workaround this by creating blackhole route as alternative to route that might disappear on disconnect).
When action=srcnat is used instead, connection tracking entries remain and connections can simply resume.
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| action (action name; Default: accept) | Action to take if packet is matched by the rule:
|
| address-list (string; Default: ) | Name of the address list to be used. Applicable if action is add-dst-to-address-list or add-src-to-address-list |
| address-list-timeout (none-dynamic | none-static | time; Default: none-dynamic) | Time interval after which the address will be removed from the address list specified by address-list parameter. Used in conjunction with add-dst-to-address-list or add-src-to-address-list actions
|
| chain (name; Default: ) | Specifies to which chain rule will be added. If the input does not match the name of an already defined chain, a new chain will be created. |
| comment (string; Default: ) | Descriptive comment for the rule. |
| connection-bytes (integer-integer; Default: ) | Matches packets only if a given amount of bytes has been transfered through the particular connection. 0 - means infinity, for example connection-bytes=2000000-0 means that the rule matches if more than 2MB has been transfered through the relevant connection |
| connection-limit (integer,netmaks; Default: ) | Matches connections per address or address block after given value is reached. |
| connection-mark (no-mark | string; Default: ) | Matches packets marked via mangle facility with particular connection mark. If no-mark is set, rule will match any unmarked connection. |
| connection-rate (Integer 0..4294967295; Default: ) | Connection Rate is a firewall matcher that allow to capture traffic based on present speed of the connection. Read more>> |
| connection-type (ftp | h323 | irc | pptp | quake3 | sip | tftp; Default: ) | Matches packets from related connections based on information from their connection tracking helpers. A relevant connection helper must be enabled under /ip firewall service-port |
| content (string; Default: ) | Match packets that contain specified text |
| dscp (integer: 0..63; Default: ) | Matches DSCP IP header field. |
| dst-address (IP/netmask | IP range; Default: ) | Matches packets which destination is equal to specified IP or falls into specified IP range. |
| dst-address-list (name; Default: ) | Matches destination address of a packet against user-defined address list |
| dst-address-type (unicast | local | broadcast | multicast; Default: ) | Matches destination address type:
|
| dst-limit (integer[/time],integer,dst-address | dst-port | src-address[/time]; Default: ) | Matches packets until a given pps limit is exceeded. As opposed to the limit matcher, every destination IP address / destination port has it's own limit. Parameters are written in following format: count[/time],burst,mode[/expire].
|
| dst-port (integer[-integer]: 0..65535; Default: ) | List of destination port numbers or port number ranges |
| fragment (yes|no; Default: ) | Matches fragmented packets. First (starting) fragment does not count. If connection tracking is enabled there will be no fragments as system automatically assembles every packet |
| hotspot (auth | from-client | http | local-dst | to-client; Default: ) | Matches packets received from HotSpot clients against various HotSpot matchers.
|
| icmp-options (integer:integer; Default: ) | Matches ICMP type:code fileds |
| in-bridge-port (name; Default: ) | Actual interface the packet has entered the router, if incoming interface is bridge |
| in-interface (name; Default: ) | Interface the packet has entered the router |
| ingress-priority (integer: 0..63; Default: ) | Matches ingress priority of the packet. Priority may be derived from VLAN, WMM or MPLS EXP bit. Read more>> |
| ipsec-policy (in | out, ipsec | none; Default: ) | Matches the policy used by IpSec. Value is written in following format: direction, policy. Direction is Used to select whether to match the policy used for decapsulation or the policy that will be used for encapsulation.
For example, if router receives Ipsec encapsulated Gre packet, then rule |
| ipv4-options (any | loose-source-routing | no-record-route | no-router-alert | no-source-routing | no-timestamp | none | record-route | router-alert | strict-source-routing | timestamp; Default: ) | Matches IPv4 header options.
|
| jump-target (name; Default: ) | Name of the target chain to jump to. Applicable only if action=jump |
| layer7-protocol (name; Default: ) | Layer7 filter name defined in layer7 protocol menu. |
| limit (integer,time,integer; Default: ) | Matches packets until a given pps limit is exceeded. Parameters are written in following format: count[/time],burst.
|
| log-prefix (string; Default: ) | Adds specified text at the beginning of every log message. Applicable if action=log |
| nth (integer,integer; Default: ) | Matches every nth packet. Read more >> |
| out-bridge-port (name; Default: ) | Actual interface the packet is leaving the router, if outgoing interface is bridge |
| out-interface (; Default: ) | Interface the packet is leaving the router |
| packet-mark (no-mark | string; Default: ) | Matches packets marked via mangle facility with particular packet mark. If no-mark is set, rule will match any unmarked packet. |
| packet-size (integer[-integer]:0..65535; Default: ) | Matches packets of specified size or size range in bytes. |
| per-connection-classifier (ValuesToHash:Denominator/Remainder; Default: ) | PCC matcher allows to divide traffic into equal streams with ability to keep packets with specific set of options in one particular stream. Read more >> |
| port (integer[-integer]: 0..65535; Default: ) | Matches if any (source or destination) port matches the specified list of ports or port ranges. Applicable only if protocol is TCP or UDP |
| protocol (name or protocol ID; Default: tcp) | Matches particular IP protocol specified by protocol name or number |
| psd (integer,time,integer,integer; Default: ) | Attempts to detect TCP and UDP scans. Parameters are in following format WeightThreshold, DelayThreshold, LowPortWeight, HighPortWeight
|
| random (integer: 1..99; Default: ) | Matches packets randomly with given probability. |
| routing-mark (string; Default: ) | Matches packets marked by mangle facility with particular routing mark |
| same-not-by-dst (yes | no; Default: ) | Specifies whether to take into account or not destination IP address when selecting a new source IP address. Applicable if action=same |
| src-address (Ip/Netmaks, Ip range; Default: ) | Matches packets which source is equal to specified IP or falls into specified IP range. |
| src-address-list (name; Default: ) | Matches source address of a packet against user-defined address list |
| src-address-type (unicast | local | broadcast | multicast; Default: ) |
Matches source address type:
|
| src-port (integer[-integer]: 0..65535; Default: ) | List of source ports and ranges of source ports. Applicable only if protocol is TCP or UDP. |
| src-mac-address (MAC address; Default: ) | Matches source MAC address of the packet |
| tcp-mss (integer[-integer]: 0..65535; Default: ) | Matches TCP MSS value of an IP packet |
| time (time-time,sat | fri | thu | wed | tue | mon | sun; Default: ) | Allows to create filter based on the packets' arrival time and date or, for locally generated packets, departure time and date |
| to-addresses (IP address[-IP address]; Default: 0.0.0.0) | Replace original address with specified one. Applicable if action is dst-nat, netmap, same, src-nat |
| to-ports (integer[-integer]: 0..65535; Default: ) | Replace original port with specified one. Applicable if action is dst-nat, redirect, masquerade, netmap, same, src-nat |
| ttl (integer: 0..255; Default: ) | Matches packets TTL value |
Stats
/ip firewall nat print stats will show additional read-only properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| bytes (integer) | Total amount of bytes matched by the rule |
| packets (integer) | Total amount of packets matched by the rule |
By default print is equivalent to print static and shows only static rules.
[admin@dzeltenais_burkaans] /ip firewall mangle> print stats Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic # CHAIN ACTION BYTES PACKETS 0 prerouting mark-routing 17478158 127631 1 prerouting mark-routing 782505 4506
To print also dynamic rules use print all.
[admin@dzeltenais_burkaans] /ip firewall mangle> print all stats Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic # CHAIN ACTION BYTES PACKETS 0 prerouting mark-routing 17478158 127631 1 prerouting mark-routing 782505 4506 2 D forward change-mss 0 0 3 D forward change-mss 0 0 4 D forward change-mss 0 0 5 D forward change-mss 129372 2031
Or to print only dynamic rules use print dynamic
[admin@dzeltenais_burkaans] /ip firewall mangle> print stats dynamic Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic # CHAIN ACTION BYTES PACKETS 0 D forward change-mss 0 0 1 D forward change-mss 0 0 2 D forward change-mss 0 0 3 D forward change-mss 132444 2079
Menu specific commands
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| reset-counters (id) | Reset statistics counters for specified firewall rules. |
| reset-counters-all () | Reset statistics counters for all firewall rules. |
Basic examples
Source NAT
Masquerade
If you want to "hide" the private LAN 192.168.0.0/24 "behind" one address 10.5.8.109 given to you by the ISP, you should use the source network address translation (masquerading) feature of the MikroTik router. The masquerading will change the source IP address and port of the packets originated from the network 192.168.0.0/24 to the address 10.5.8.109 of the router when the packet is routed through it.
To use masquerading, a source NAT rule with action 'masquerade' should be added to the firewall configuration:
/ip firewall nat add chain=srcnat action=masquerade out-interface=Public
All outgoing connections from the network 192.168.0.0/24 will have source address 10.5.8.109 of the router and source port above 1024. No access from the Internet will be possible to the Local addresses. If you want to allow connections to the server on the local network, you should use destination Network Address Translation (NAT).
Source nat to specific address
If you have multiple public IP addresses, source nat can be changed to specific IP, for example, one local subnet can be hidden behind first IP and second local subnet is masqueraded behind second IP.
/ip firewall nat add chain=srcnat src-address=192.168.1.0/24 action=src-nat to-addresses=1.1.1.1 out-interface=Public add chain=srcnat src-address=192.168.2.0/24 action=src-nat to-addresses=1.1.1.2 out-interface=Public
Destination NAT
Forward all traffic to internal host
If you want to link Public IP 10.5.8.200 address to Local one 192.168.0.109, you should use destination address translation feature of the MikroTik router. Also if you want allow Local server to initiate connections to outside with given Public IP you should use source address translation, too.
Add Public IP to Public interface:
/ip address add address=10.5.8.200/32 interface=Public
Add rule allowing access to the internal server from external networks:
/ip firewall nat add chain=dstnat dst-address=10.5.8.200 action=dst-nat \ to-addresses=192.168.0.109
Add rule allowing the internal server to initate connections to the outer networks having its source address translated to 10.5.8.200:
/ip firewall nat add chain=srcnat src-address=192.168.0.109 action=src-nat \ to-addresses=10.5.8.200
Port mapping/forwarding
If you would like to direct requests for a certain port to an internal machine (sometimes called opening a port, port mapping), you can do it like this:
/ip firewall nat add chain=dstnat dst-port=1234 action=dst-nat protocol=tcp to-address=192.168.1.1 to-port=1234
This rule translates to: when an incoming connection requests TCP port 1234, use the DST-NAT action and redirect it to local address 192.168.1.1 and the port 1234
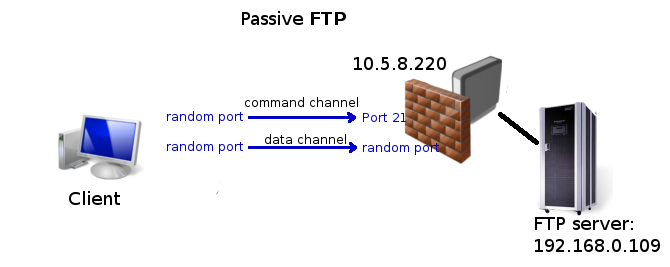
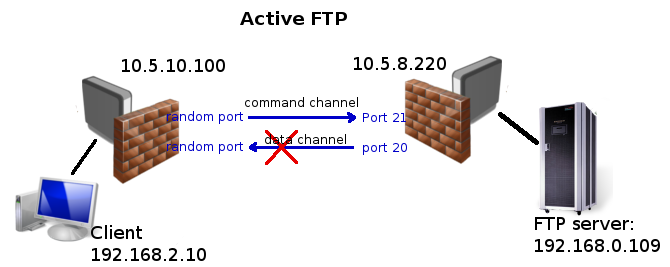
Port forwarding to internal FTP server
As you can see from illustration above FTP uses more than one connection, but only command channel should be forwarded by Destination nat. Data channel is considered as related connection and should be accepted with "accept related" rule if you have strict firewall. Note that for related connections to be properly detected FTP helper has to be enabled.
/ip firewall nat add chain=dstnat dst-address=10.5.8.200 dst-port=21 protocol=tcp action=dst-nat to-addresses=192.168.0.109
/ip firewall filter add chain=forward connection-state=established,related action=accept
Note that active FTP might not work if client is behind dumb firewall or NATed router, because data channel is initiated by the server and cannot directly access the client.
If client is behind Mikrotik router, then make sure that FTP helper is enabled
[admin@3C22-atombumba] /ip firewall service-port> print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid
# NAME PORTS
0 ftp 21
1 tftp 69
2 irc 6667
3 h323
4 sip 5060
5061
5 pptp
1:1 mapping
If you want to link Public IP subnet 11.11.11.0/24 to local one 2.2.2.0/24, you should use destination address translation and source address translation features with action=netmap.
/ip firewall nat add chain=dstnat dst-address=11.11.11.0/24 \ action=netmap to-addresses=2.2.2.0/24 /ip firewall nat add chain=srcnat src-address=2.2.2.0/24 \ action=netmap to-addresses=11.11.11.0/24
Same can be written using different address notation, that still have to match with the described network
/ip firewall nat add chain=dstnat dst-address=11.11.11.0-11.11.11.255 \ action=netmap to-addresses=2.2.2.0-2.2.2.255 /ip firewall nat add chain=srcnat src-address=2.2.2.0-2.2.2.255 \ action=netmap to-addresses=11.11.11.0-11.11.11.255
Carrier-Grade NAT (CGNAT) or NAT444
To combat IPv4 address exhaustion, new RFC 6598 was deployed. The idea is to use shared 100.64.0.0/10 address space inside carrier's network and performing NAT on carrier's edge router to sigle public IP or public IP range.
Because of nature of such setup it is also called NAT444, as opposed to a NAT44 network for a 'normal' NAT environment, three different IPv4 address spaces are involved.
CGNAT configuration on RouterOS does not differ from any other regular source NAT configuration:
/ip firewall nat add chain=src-nat action=srcnat src-address=100.64.0.0/10 to-address=2.2.2.2 out-interface=<public_if>
Where:
- 2.2.2.2 - public IP address,
- public_if - interface on providers edge router connected to internet
The advantage of NAT444 is obvious, less public IPv4 addresses used. But this technique comes with mayor drawbacks:
- The service provider router performing CGNAT needs to maintain a state table for all the address translations: this requires a lot of memory and CPU resources.
- Console gaming problems. Some games fail when two subscribers using the same outside public IPv4 address try to connect to each other.
- Tracking of users for legal reasons means extra logging, as multiple households go behind one public address.
- Anything requiring incoming connections is broken. While this already was the case with regular NAT, end users could usually still set up port forwarding on their NAT router. CGNAT makes this impossible. This means no web servers can be hosted here, and IP Phones cannot receive incoming calls by default either.
- Some web servers only allow a maximum number of connections from the same public IP address, as a means to counter DoS attacks like SYN floods. Using CGNAT this limit is reached more often and some services may be of poor quality.
- 6to4 requires globally reachable addresses and will not work in networks that employ addresses with limited topological span.
More on things that can break can be read in this article [1]
Packets with Shared Address Space source or destination addresses MUST NOT be forwarded across Service Provider boundaries. Service Providers MUST filter such packets on ingress links. In RouterOS this can be easily done with firewall filters on edge routers:
/ip firewall filter add chain=input src-address=100.64.0.0/10 action=drop in-interface=<public_if> add chain=output dst-address=100.64.0.0/10 action=drop out-interface=<public_if> add chain=forward src-address=100.64.0.0/10 action=drop in-interface=<public_if> add chain=forward src-address=100.64.0.0/10 action=drop out-interface=<public_if> add chain=forward dst-address=100.64.0.0/10 action=drop out-interface=<public_if>
Service providers may be required to do logging of MAPed addresses, in large CGN deployed network that may be a problem.
Fortunately RFC 7422 suggests a way to manage CGN translations in such a way as to significantly reduce the amount of logging required while providing traceability for abuse response.
RFC states that instead of logging each connection, CGNs could deterministically map customer private addresses (received on the customer-facing interface of the CGN, a.k.a., internal side) to public addresses extended with port ranges.
In RouterOS described algorithm can be done with few script functions. Lets take an example:
| Inside IP | Outside IP/Port range |
| 100.64.1.1 | 2.2.2.2:2000-2099 |
| 100.64.1.2 | 2.2.2.2:2100-2199 |
| 100.64.1.3 | 2.2.2.2:2200-2299 |
| 100.64.1.4 | 2.2.2.2:2300-2399 |
| 100.64.1.5 | 2.2.2.2:2400-2499 |
| 100.64.1.6 | 2.2.2.2:2500-2599 |
Instead of writing NAT mappings by hand we could write a function which adds such rules automatically.
:global sqrt do={
:for i from=0 to=$1 do={
:if (i * i > $1) do={ :return ($i - 1) }
}
}
:global addNatRules do={
/ip firewall nat add chain=srcnat action=jump jump-target=xxx \
src-address="$($srcStart)-$($srcStart + $count - 1)"
:local x [$sqrt $count]
:local y $x
:if ($x * $x = $count) do={ :set y ($x + 1) }
:for i from=0 to=$x do={
/ip firewall nat add chain=xxx action=jump jump-target="xxx-$($i)" \
src-address="$($srcStart + ($x * $i))-$($srcStart + ($x * ($i + 1) - 1))"
}
:for i from=0 to=($count - 1) do={
:local prange "$($portStart + ($i * $portsPerAddr))-$($portStart + (($i + 1) * $portsPerAddr) - 1)"
/ip firewall nat add chain="xxx-$($i / $x)" action=src-nat protocol=tcp src-address=($srcStart + $i) \
to-address=$toAddr to-ports=$prange
/ip firewall nat add chain="xxx-$($i / $x)" action=src-nat protocol=udp src-address=($srcStart + $i) \
to-address=$toAddr to-ports=$prange
}
}
After pasting above script in the terminal function "addNatRules" is available. If we take our example, we need to map 6 shared network addresses to be mapped to 2.2.2.2 and each address uses range of 100 ports starting from 2000. So we run our function:
$addNatRules count=6 srcStart=100.64.1.1 toAddr=2.2.2.2 portStart=2000 portsPerAddr=100
Now you should be able to get set of rules:
[admin@rack1_b18_450] /ip firewall nat> print Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic 0 chain=srcnat action=jump jump-target=xxx src-address=100.64.1.1-100.64.1.6 log=no log-prefix="" 1 chain=xxx action=jump jump-target=xxx-0 src-address=100.64.1.1-100.64.1.2 log=no log-prefix="" 2 chain=xxx action=jump jump-target=xxx-1 src-address=100.64.1.3-100.64.1.4 log=no log-prefix="" 3 chain=xxx action=jump jump-target=xxx-2 src-address=100.64.1.5-100.64.1.6 log=no log-prefix="" 4 chain=xxx-0 action=src-nat to-addresses=2.2.2.2 to-ports=2000-2099 protocol=tcp src-address=100.64.1.1 log=no log-prefix="" 5 chain=xxx-0 action=src-nat to-addresses=2.2.2.2 to-ports=2000-2099 protocol=udp src-address=100.64.1.1 log=no log-prefix="" 6 chain=xxx-0 action=src-nat to-addresses=2.2.2.2 to-ports=2100-2199 protocol=tcp src-address=100.64.1.2 log=no log-prefix="" 7 chain=xxx-0 action=src-nat to-addresses=2.2.2.2 to-ports=2100-2199 protocol=udp src-address=100.64.1.2 log=no log-prefix="" 8 chain=xxx-1 action=src-nat to-addresses=2.2.2.2 to-ports=2200-2299 protocol=tcp src-address=100.64.1.3 log=no log-prefix="" 9 chain=xxx-1 action=src-nat to-addresses=2.2.2.2 to-ports=2200-2299 protocol=udp src-address=100.64.1.3 log=no log-prefix="" 10 chain=xxx-1 action=src-nat to-addresses=2.2.2.2 to-ports=2300-2399 protocol=tcp src-address=100.64.1.4 log=no log-prefix="" 11 chain=xxx-1 action=src-nat to-addresses=2.2.2.2 to-ports=2300-2399 protocol=udp src-address=100.64.1.4 log=no log-prefix="" 12 chain=xxx-2 action=src-nat to-addresses=2.2.2.2 to-ports=2400-2499 protocol=tcp src-address=100.64.1.5 log=no log-prefix="" 13 chain=xxx-2 action=src-nat to-addresses=2.2.2.2 to-ports=2400-2499 protocol=udp src-address=100.64.1.5 log=no log-prefix="" 14 chain=xxx-2 action=src-nat to-addresses=2.2.2.2 to-ports=2500-2599 protocol=tcp src-address=100.64.1.6 log=no log-prefix="" 15 chain=xxx-2 action=src-nat to-addresses=2.2.2.2 to-ports=2500-2599 protocol=udp src-address=100.64.1.6 log=no log-prefix=""
[ Top | Back to Content ]