Manual:Interface/Dot1x: Difference between revisions
| Line 124: | Line 124: | ||
|default=1m | |default=1m | ||
|desc=Total time available for EAP authentication. | |desc=Total time available for EAP authentication. | ||
}} | |||
{{Mr-arg-table | |||
|arg=auth-types | |||
|type=dot1x {{!}} mac-auth | |||
|default=dot1x | |||
|desc=Used authentication type on a server interface. Both options can be selected at the same time. | |||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 14:05, 21 January 2020
Summary
Sub-menu: /interface dot1x
Dot1x is implementation of IEEE 802.1X standard in RouterOS. Main purpose is to provide port-based network access control using EAP over LAN also known as EAPOL. 802.1X consists of a supplicant, an authenticator and an authentication server (RADIUS server). Currently both authenticator and supplicant sides are supported in RouterOS. Supported EAP methods for supplicant are EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS, EAP-MSCHAPv2 and PEAPv0/EAP-MSCHAPv2.
Client
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| anon-identity (string; Default: ) | Identity for outer layer EAP authentication. Used only with eap-ttls and eap-peap methods. If not set, value from identity parameter will be used for outer layer EAP authentication. |
| certificate (string; Default: ) | Name of a certificate listed in System/Certificates. Necessary when eap-tls method is used. |
| comment (string; Default: ) | Short description of the entry. |
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Whether client is enabled or not. |
| eap-methods (eap-tls | eap-ttls | eap-peap | eap-mschapv2; Default: ) | Ordered list of EAP methods used for authentication. |
| identity (string; Default: ) | Supplicant identity used for EAP authentication. |
| interface (string; Default: ) | Name of the interface the client will run on. |
| password (string; Default: ) | Cleartext password for supplicant. |
Read only properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| status (authenticated | authenticating | disabled) | Possible statuses:
|
Server
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| accounting (yes | no; Default: yes) | Whether to send RADIUS accounting requests to authentication server. |
| auth-timeout (time; Default: 1m) | Total time available for EAP authentication. |
| auth-types (dot1x | mac-auth; Default: dot1x) | Used authentication type on a server interface. Both options can be selected at the same time. |
| comment (string; Default: ) | Short description of the entry. |
| interim-update (time; Default: 0s) | Interval between scheduled RADIUS Interim-Update messages. |
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Whether server config is enabled or not. |
| interface (string; Default: ) | Name of the interface or interface list the server will run on. |
| retrans-timeout (time; Default: 30s) | Time interval between message retransmissions if no response is received from supplicant. |
Active
Currently authenticated clients are listed in this menu.
Read only properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| client-mac (mac-address) | MAC Address of the supplicant. |
| interface (string) | Name of the interface. |
| session-id (string) | Unique session identifier. |
| username (string) | Identity of the supplicant. |
| vlan-id (string) | Untagged VLAN ID that is assigned to the interface. VLAN ID filtering must be enabled on bridge. |
State
Statuses of all active dot1x server interfaces are listed in this menu.
Read only properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| interface (string) | Name of the interface. |
| status (string) | Possible interface statuses:
|
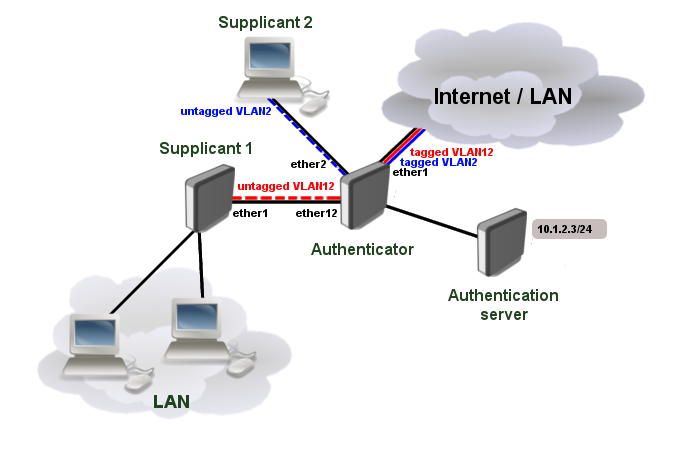
Application Example
RouterOS Authenticator configuration
Start off by adding a new RADIUS client. The authentication server (RADIUS) does not necessary have to be in the same LAN as authenticator, but it must be reachable from the authenticator, so any firewall limitations must be considered.
/radius add address=10.1.2.3 secret=radiussecret service=dot1x

Note: if RADIUS communication is done over public network, it is advised to use RadSec for RADIUS communication. More information: RADIUS Client
Add new dot1x server instances.
/interface dot1x server add interface=ether2 interim-update=30s comment=accounted add interface=ether12 accounting=no comment=notaccounted
Port based VLAN ID assignment
It is possible to assign an authenticated interface to a specific VLAN ID using bridge VLAN filtering. This can be done using RADIUS Tunnel-Type, Tunnel-Medium-Type and Tunnel-Private-Group-ID attributes. Note that only devices with hardware offloaded VLAN filtering will be able to do this in switch chip. See Bridge Hardware Offloading.
First of all, make sure the interface is added to a bridge which has VLAN filtering enabled.
/interface bridge add name=bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes /interface bridge port add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether1 add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether2 add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether12
It is necessary to add static VLAN configuration for tagged VLAN traffic to be sent over ether1 interface.
/interface bridge vlan add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether1 vlan-ids=2 add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether1 vlan-ids=12
With enabled RADIUS debug logs it is possible to see complete RADIUS message packets with all attributes. In our example, Tunnel attributes are received in Access-Accept message from RADIUS server:
09:51:45 radius,debug,packet received Access-Accept with id 64 from 10.1.2.3:1812 09:51:45 radius,debug,packet Tunnel-Type = 13 09:51:45 radius,debug,packet Tunnel-Medium-Type = 6 09:51:45 radius,debug,packet Tunnel-Private-Group-ID = "12" (..) 09:51:45 radius,debug,packet User-Name = "dot1x-user"
The VLAN ID is now present in active session list and untagged ports are added to previously created static VLAN configuration.
/interface dot1x server active print 0 interface=ether12 username="dot1x-user" user-mac=00:0C:42:EB:71:F6 session-id="86b00006" vlan=12
/interface bridge vlan print detail Flags: X - disabled, D - dynamic 0 D bridge=bridge1 vlan-ids=1 tagged="" untagged="" current-tagged="" current-untagged=bridge1,ether3 1 bridge=bridge1 vlan-ids=2 tagged=ether1 untagged="" current-tagged=ether1 current-untagged=ether2 2 bridge=bridge1 vlan-ids=12 tagged=ether1 untagged="" current-tagged=ether1 current-untagged=ether12
Dynamic switch rule configuration
In some network configurations, additional access rules are needed for a particular supplicant to restrict or allow certain network services. This can be done using a Mikrotik-Switching-Filter attribute, please see the RADIUS vendor dictionary. When a client is successfully authenticated by an authentication server, the server can pass back the Mikrotik-Switching-Filter attribute. Based on the received information, the authenticator will create dynamic access rules on a switch port where the client resides. These rules will be active as long as the client session is active and the interface is running. There are certain order and restrictions regarding correct switch rule implementation:
- The mac-protocol, dst-address, dst-port and protocol conditional parameters are supported. Only hexadecimal or decimal representation can be used for mac-protocol and protocol parameters
- The src-mac-address, switch and ports conditional parametrs are automatically set for each rule
- Each rule should end with an action property, supported values are either drop or allow
- Multiple rules are supported for a single supplicant and they must be separated by a comma ","
Below are some examples of Mikrotik-Switching-Filter attributes and dynamic switch rules they create:
# Drop ARP frames (EtherType: 0x0806 or 2054)
Mikrotik-Switching-Filter = "mac-protocol 2054 action drop"
[admin@MikroTik] /interface ethernet switch rule print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic
0 D ;;; dot1x dynamic
switch=switch1 ports=ether1 src-mac-address=CC:2D:E0:11:22:33/FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF mac-protocol=arp copy-to-cpu=no redirect-to-cpu=no mirror=no new-dst-ports=""
# Allow UDP (IP protocol: 0x11 or 17) destination port 100 and drop all other packets
Mikrotik-Switching-Filter = "protocol 17 dst-port 100 action allow, action drop"
[admin@MikroTik] /interface ethernet switch rule print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic
0 D ;;; dot1x dynamic
switch=switch1 ports=ether1 src-mac-address=CC:2D:E0:11:22:33/FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF protocol=udp dst-port=100 copy-to-cpu=no redirect-to-cpu=no mirror=no
1 D ;;; dot1x dynamic
switch=switch1 ports=ether1 src-mac-address=CC:2D:E0:11:22:33/FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF copy-to-cpu=no redirect-to-cpu=no mirror=no new-dst-ports=""
In our example, Supplicant2 on ether2 is only allowed to access the 192.168.50.0/24 network with UDP destination port 50, all other traffic should be dropped. First, make sure that hardware offloading is working on bridge ports, otherwise switch rules might not work properly.
[admin@MikroTik] /interface bridge port print Flags: X - disabled, I - inactive, D - dynamic, H - hw-offload # INTERFACE BRIDGE HW PVID PRIORITY PATH-COST INTERNAL-PATH-COST HORIZON 0 H ether1 bridge1 yes 1 0x80 10 10 none 1 H ether2 bridge1 yes 1 0x80 10 10 none 2 H ether12 bridge1 yes 1 0x80 10 10 none
With enabled RADIUS debug logs it is possible to see complete RADIUS message packets with all attributes. In our example, Mikrotik-Switching-Filter attribute is received in Access-Accept message from Radius server:
02:35:38 radius,debug,packet received Access-Accept with id 121 from 10.1.2.3:1812 (..) 02:35:38 radius,debug,packet MT-Switching-Filter = "mac-protocol 2048 dst-address 192.168.50.0/24 dst-port 50 protocol 17 action allow,action drop"
The dynamic switch rules are now present under the switch menu:
[admin@MikroTik] > interface ethernet switch rule print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic
0 D ;;; dot1x dynamic
switch=switch1 ports=ether2 src-mac-address=CC:2D:E0:11:22:33/FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF mac-protocol=ip dst-address=192.168.50.0/24 protocol=udp dst-port=50 copy-to-cpu=no redirect-to-cpu=no mirror=no
1 D ;;; dot1x dynamic
switch=switch1 ports=ether2 src-mac-address=CC:2D:E0:11:22:33/FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF copy-to-cpu=no redirect-to-cpu=no mirror=no new-dst-ports=""

Note: Dynamic switch rules will only apply to RouterBoards with switch rule support - CRS3xx series switches, devices with QCA8337, Atheros8327 and Atheros8316 switch chips. CRS1xx/2xx series switches do no support this functionality. Take into consideration the maximum number of rules for each device, see CRS3xx table and basic switch chip table
RouterOS Supplicant configuration
CA certificates are required for eap-tls, eap-ttls and eap-peap authentication methods. Additionally a client certificate is required for eap-tls method. For this example we have already imported a P12 certificate bundle with self signed client and CA certificates. For more information how to import certificates in RouterOS, please visit System/Certificates.
/certificate print Flags: K - private-key, L - crl, C - smart-card-key, A - authority, I - issued, R - revoked, E - expired, T - trusted # NAME COMMON-NAME SUBJECT-ALT-NAME FINGERPRINT 0 K A T dot1x-client ez_dot1x-client IP:10.1.2.34 1 L A T dot1x CA ca
Simply add a new dot1x client instance that will initiate authentication process.
/interface dot1x client add anon-identity=anonymous client-certificate=dot1x-client eap-methods=eap-tls identity=dot1x-user interface=ether1 password=dot1xtest
If authentication was successful, the interface should have status authenticated.
/interface dot1x client print Flags: I - inactive, X - disabled 0 interface=ether1 eap-methods=eap-peap identity="dot1x-user" password="dot1xtest" anon-identity="anonymous" certificate=dot1x-client status="authenticated"
[ Top | Back to Content ]