Manual:Interface/HWMPplus: Difference between revisions
New page: ''Prerequisites for this article: you understand what WDS is and why to use it'' == Overview == HWMP+ is a MikroTik specific layer-2 routing protocol for wireless mesh networks. It is ba... |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 98: | Line 98: | ||
Use '''wds-default-cost''' and '''wds-cost-range''' wireless interface parameters for controlling the metric that is used in the routing protocol. The WDS cost will be used as '''path-cost''' for ports dynamically added to the mesh interface. | Use '''wds-default-cost''' and '''wds-cost-range''' wireless interface parameters for controlling the metric that is used in the routing protocol. The WDS cost will be used as '''path-cost''' for ports dynamically added to the mesh interface. | ||
== Example | == Example == | ||
[[Image:mesh_ex1.jpg]] | |||
This example uses static WDS links that are dynamically added as mesh ports when they become active. Two different frequencies are used: one for AP interconnections, and one for client connections to APs, so the AP must have at least two wireless interfaces. | This example uses static WDS links that are dynamically added as mesh ports when they become active. Two different frequencies are used: one for AP interconnections, and one for client connections to APs, so the AP must have at least two wireless interfaces. | ||
Repeat this configuration on all APs: | Repeat this configuration on all APs: | ||
/interface mesh add disabled=no | /interface mesh add disabled=no | ||
| |||
/interface mesh port add interface=wlan1 mesh=mesh1 | /interface mesh port add interface=wlan1 mesh=mesh1 | ||
| |||
/interface mesh port add interface=wlan2 mesh=mesh1 | /interface mesh port add interface=wlan2 mesh=mesh1 | ||
| |||
# interface used for AP interconnections | # interface used for AP interconnections | ||
/interface wireless set wlan1 disabled=no ssid=mesh frequency=2437 band=2.4ghz-b/g mode=ap-bridge wds-mode=static-mesh wds-default-bridge=mesh1 | /interface wireless set wlan1 disabled=no ssid=mesh frequency=2437 band=2.4ghz-b/g mode=ap-bridge \ | ||
wds-mode=static-mesh wds-default-bridge=mesh1 | |||
| |||
# interface used for client connections | # interface used for client connections | ||
/interface wireless set wlan2 disabled=no ssid=mesh-clients frequency=5180 band=5ghz mode=ap-bridge | /interface wireless set wlan2 disabled=no ssid=mesh-clients frequency=5180 band=5ghz mode=ap-bridge | ||
| |||
# a static WDS interface for each AP you want to connect to | # a static WDS interface for each AP you want to connect to | ||
/interface wireless wds add disabled=no master-interface=wlan1 name=<descriptive name of remote end> wds-address=<MAC address of remote end> | /interface wireless wds add disabled=no master-interface=wlan1 name=<descriptive name of remote end> \ | ||
wds-address=<MAC address of remote end> | |||
Note that here WDS interface is added manually, because static WDS mode is used. If you are using '''wds-mode'''=dynamic-mesh, all WDS interfaces will be created automatically. | |||
In real world setups you also should take care of securing the wireless connections, using '''/interface wireless security-profile'''. For simplicity that configuration it's not shown here. | In real world setups you also should take care of securing the wireless connections, using '''/interface wireless security-profile'''. For simplicity that configuration it's not shown here. | ||
| Line 132: | Line 135: | ||
hwmp-preq-reply-and-forward=yes hwmp-prep-lifetime=5m hwmp-rann-interval=10s | hwmp-preq-reply-and-forward=yes hwmp-prep-lifetime=5m hwmp-rann-interval=10s | ||
hwmp-rann-propagation-delay=1s hwmp-rann-lifetime=22s | hwmp-rann-propagation-delay=1s hwmp-rann-lifetime=22s | ||
| |||
[admin@A] > interface mesh port p detail | [admin@A] > interface mesh port p detail | ||
Flags: X - disabled, I - inactive, D - dynamic | Flags: X - disabled, I - inactive, D - dynamic | ||
| Line 138: | Line 142: | ||
2 D interface=router_B mesh=mesh1 path-cost=105 hello-interval=10s port-type=auto port-type-used=WDS | 2 D interface=router_B mesh=mesh1 path-cost=105 hello-interval=10s port-type=auto port-type-used=WDS | ||
3 D interface=router_D mesh=mesh1 path-cost=76 hello-interval=10s port-type=auto port-type-used=WDS | 3 D interface=router_D mesh=mesh1 path-cost=76 hello-interval=10s port-type=auto port-type-used=WDS | ||
The FDB (Forwarding Database) at the moment contains information only about local MAC addresses, non-mesh nodes reachable through local interface, and direct mesh neighbors: | |||
[admin@A] /interface mesh> fdb print | [admin@A] /interface mesh> fdb print | ||
| Line 147: | Line 153: | ||
A mesh1 direct 00:0C:42:0C:7A:2B wlan2 2m56s | A mesh1 direct 00:0C:42:0C:7A:2B wlan2 2m56s | ||
A mesh1 local 00:0C:42:0C:B5:A4 2m56s | A mesh1 local 00:0C:42:0C:B5:A4 2m56s | ||
| |||
[admin@A] /interface mesh> fdb print detail | [admin@A] /interface mesh> fdb print detail | ||
Flags: A - active, R - root | Flags: A - active, R - root | ||
| Line 167: | Line 174: | ||
4 packets transmitted, 4 packets received, 0% packet loss | 4 packets transmitted, 4 packets received, 0% packet loss | ||
round-trip min/avg/max = 39/60.2/108 ms | round-trip min/avg/max = 39/60.2/108 ms | ||
Router A had to discover path to Router C first, hence the slightly larger time for the first ping. | |||
Also test that ARP resolving works and so does IP level ping: | Also test that ARP resolving works and so does IP level ping: | ||
| Line 183: | Line 192: | ||
=== Problematic example 1: Ethernet switch inside a mesh === | === Problematic example 1: Ethernet switch inside a mesh === | ||
[[Image:mesh_bad_ex1.jpg]] | |||
A will not be able to communicate reliably with C. The problem manifests itself when D is the designated router for Ethernet; if B takes this role, everything is OK. | Router A will not be able to communicate reliably with router C. The problem manifests itself when D is the designated router for Ethernet; if B takes this role, everything is OK. The main cause of the problem is MAC address learning on Ethernet switch. | ||
Consider what happens when router A wants to send something to C. We suppose router A either knowns or floods data to all interfaces. Either way, data arrives at switch. The switch, not knowing anything about destination's MAC address, forwards to data both to B and D. | Consider what happens when router A wants to send something to C. We suppose router A either knowns or floods data to all interfaces. Either way, data arrives at switch. The switch, not knowing anything about destination's MAC address, forwards to data both to B and D. | ||
What happens now: | What happens now: | ||
# B receives the packet on a mesh interface. Since the MAC address is not local for B, and B knows that he is not the designated router for | # B receives the packet on a mesh interface. Since the MAC address is not local for B, and B knows that he is not the designated router for the Ethernet network, he simply ignores the packet. | ||
# D receives the packet on a mesh interface. Since the MAC address is not local for B, and D is the designated router for | # D receives the packet on a mesh interface. Since the MAC address is not local for B, and D is the designated router for the Ethernet network, he initiates path discovery process to C. | ||
After path discovery is completed, D has information that C is reachable over B. Now D encapsulates the packet and forwards back to | After path discovery is completed, D has information that C is reachable over B. Now D encapsulates the packet and forwards back to Ethernet network. The encapsulated packet forwarded by switch, received and forwarded by B, and received by C. So far everything is good. | ||
Now C is likely to respond to the packet. Since B already knows where A is, he will decapsulate and forward the packet. But now switch will learn that the MAC address of C is reachable through B! That means, next time when something arrives from A addressed to C, the switch will forward data ''only'' to B. (And B, of course, will silently ignore the packet). | Now C is likely to respond to the packet. Since B already knows where A is, he will decapsulate and forward the reply packet. But now switch will learn that the MAC address of C is reachable through B! That means, next time when something arrives from A addressed to C, the switch will forward data ''only'' to B. (And B, of course, will silently ignore the packet). | ||
In contrast, if B took up the role of designated router, everything would be OK, because traffic would not have to | In contrast, if B took up the role of designated router, everything would be OK, because traffic would not have to go through the Ethernet switch twice. | ||
'''''Troubleshooting''''': either avoid such setup or disable MAC address learning on the switch. Note that it's not possible | '''''Troubleshooting''''': either avoid such setup or disable MAC address learning on the switch. Note that on many switches it's not possible. | ||
=== Problematic example 2: wireless modes === | === Problematic example 2: wireless modes === | ||
| Line 208: | Line 214: | ||
''Consider this setup (invalid)'': | ''Consider this setup (invalid)'': | ||
[[Image:mesh_bad_ex2.jpg]] | |||
It is not possible to bridge wlan1 and wlan2 on | It is not possible to bridge wlan1 and wlan2 on RouterB now. The reason for this is pretty obvious if you understand how WDS works. For WDS communications four address frames are used. This is because for wireless multihop forwarding you need to know both the addresses of intermediate hops, as well as the original sender and final receiver. In contrast, non-WDS 802.11 communication includes only three MAC addresses in a frame. That's why it's not possible to do multihop forwarding in station mode. | ||
'''''Troubleshooting''''': depends on what you want to achieve: | '''''Troubleshooting''''': depends on what you want to achieve: | ||
# If you want to | # If you want to RouterC as a repeater either for wireless or Ethernet traffic, configure WDS link between RouterB and RouterC, and run mesh routing protocol on all nodes. | ||
# In other cases configure wlan2 on | # In other cases configure wlan2 on RouterB in AP mode, and wlan on RouterC in station mode. | ||
Revision as of 11:35, 9 May 2008
Prerequisites for this article: you understand what WDS is and why to use it
Overview
HWMP+ is a MikroTik specific layer-2 routing protocol for wireless mesh networks. It is based on Hybrid Wireless Mesh Protocol (HWMP) from IEEE 802.11s draft standard. It can be used instead of (Rapid) Spanning Tree protocols in mesh setups to ensure loop-free optimal routing.
The HWMP+ protocol however is not compatible with HWMP from the proposed IEEE 802.11s standard.
Note that the distribution system you use for your network need not to be Wireless Distribution System (WDS). HWMP+ mesh routing supports not only WDS interfaces, but also Ethernet interfaces inside the mesh. So you can use simple Ethernet based distribution system, or you can combine both WDS and Ethernet links!
Configuration
/interface mesh
Configure mesh interface.
admin-mac (MAC address, default: 00:00:00:00:00:00) -- administratively assigned MAC address, used when auto-mac setting is disabled
arp (disabled | enabled | proxy-arp | reply-only; default: enabled) - address resolution protocol setting
auto-mac (boolean, default: no) -- if disabled, then value from admin-mac will be used as the MAC address of the mesh interface; else address of some port will be used if ports are present
hwmp-default-hoplimit (integer: 1..255) -- maximum hop count for generated routing protocol packets; after a HWMP+ packet is forwarded "hoplimit" times, it is dropped
hwmp-prep-lifetime (time, default: 5m) -- lifetime for routes created from received PREP or PREQ messages
hwmp-preq-destination-only (boolean, default: yes) -- whether only destination can respond to HWMP+ PREQ message
hwmp-preq-reply-and-forward (boolean, default: yes) -- whether intermediate nodes should forward HWMP+ PREQ message after responding to it. Useful only when hwmp-preq-destination-only is disabled
hwmp-preq-retries (integer, default: 2) -- how much times to retry route discovery to a specific MAC address before the address is considered unreachable
hwmp-preq-waiting-time (time, default: 4s) -- how long to wait for a response to the first PREQ message. Note that for subsequent PREQs the waiting time is increased exponentially
hwmp-rann-interval (time, default: 10s) -- how often to send out HWMP+ RANN messages
hwmp-rann-lifetime (time, default: 1s) -- lifetime for routes created from received RANN messages
hwmp-rann-propagation-delay (number, default: 50) -- how long to wait before propagating a RANN message. Value in centiseconds (100cs = 1sec)
mesh-portal (boolean, default: no) -- whether this interface is a portal in the mesh network
mtu (number, default: 1500) -- maximum transmit units
name (string) -- interface name
reoptimize-paths (boolean, default: no) -- whether to send out periodic PREQ messages asking for known MAC addresses. Turing on this setting is useful if network topology is often changing. Note that if no reply is received to a reoptimization PREQ, the existing path is kept anyway (until it timeouts itself)
/interface mesh port
Configure mesh interface ports.
hello-interval (time, default: 10s) -- maximum interval between sending out HWMP+ Hello messages. Used only for Ethernet type ports
interface (interface name) -- interface name, which is to be included in a mesh
mesh (interface name) -- mesh interface this port belongs to
path-cost (integer: 0..65535; default: 10) -- path cost to the interface, used by routing protocol to determine the 'best' path
port-type (WDS | auto | ethernet | wireless) -- port type to use
- auto - port type is determined automatically based on the underlying interface's type
- WDS - a Wireless Distribution System interface, kind of point-to-point wireless link. Remote MAC address is known from wireless connection data
- ethernet - Remote MAC addresses are learned either from HWMP+ Hello messages or from source MAC addresses in received or forwarded traffic
- wireless - Remote MAC addresses are known from wireless connection data
port-type-used (read-only, wireless | WDS | ethernet-mesh | ethernet-bridge | ethernet-mixed) -- port type and state actually used
/interface mesh fdb
Read-only status of the mesh interface Forwarding Database (FDB).
mac-address (MAC address) -- MAC address corresponding for this FDB entry
seqnum (integer) -- sequence number used in routing protocol to avoid loops
type (local | outsider | direct | mesh | neighbor | larval | unknown) -- type of this FDB entry
- local -- MAC address belongs to the local router itself
- outsider -- MAC address belongs to a device external to the mesh network
- direct -- MAC address belongs to a wireless client on an interface that is in the mesh network
- mesh -- MAC address belongs to a device reachable over the mesh network; it can be either internal or external to the mesh network
- neighbor -- MAC address belongs to a mesh router that is direct neighbor to this router
- larval -- MAC address belongs to an unknown device that is reachable over the mesh network
- unknown -- MAC address belongs to an unknown device
mesh (interface name) -- the mesh interface this FDB entry belongs to
on-interface (interface name) -- mesh port used for traffic forwarding, kind of a next-hop value
lifetime (time) -- time remaining to live if this entry is not used for traffic forwarding
age (time) -- age of this FDB entry
metric (integer) -- metric value used by routing protocol to determine the 'best' path
Additional wireless configuration
Use wds-default-cost and wds-cost-range wireless interface parameters for controlling the metric that is used in the routing protocol. The WDS cost will be used as path-cost for ports dynamically added to the mesh interface.
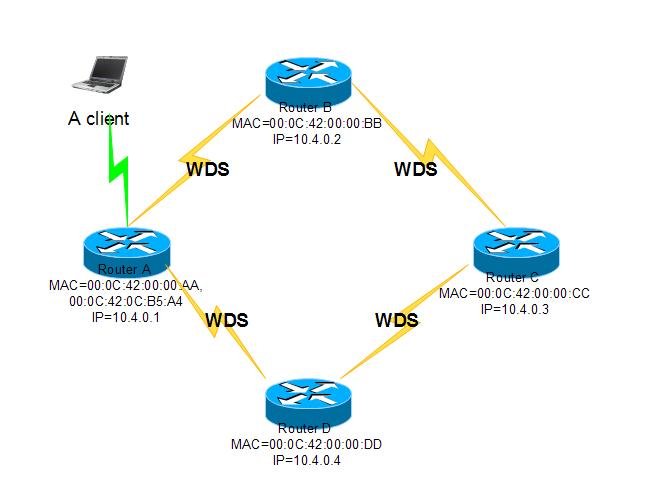
Example
This example uses static WDS links that are dynamically added as mesh ports when they become active. Two different frequencies are used: one for AP interconnections, and one for client connections to APs, so the AP must have at least two wireless interfaces.
Repeat this configuration on all APs:
/interface mesh add disabled=no /interface mesh port add interface=wlan1 mesh=mesh1 /interface mesh port add interface=wlan2 mesh=mesh1 # interface used for AP interconnections /interface wireless set wlan1 disabled=no ssid=mesh frequency=2437 band=2.4ghz-b/g mode=ap-bridge \ wds-mode=static-mesh wds-default-bridge=mesh1 # interface used for client connections /interface wireless set wlan2 disabled=no ssid=mesh-clients frequency=5180 band=5ghz mode=ap-bridge # a static WDS interface for each AP you want to connect to /interface wireless wds add disabled=no master-interface=wlan1 name=<descriptive name of remote end> \ wds-address=<MAC address of remote end>
Note that here WDS interface is added manually, because static WDS mode is used. If you are using wds-mode=dynamic-mesh, all WDS interfaces will be created automatically.
In real world setups you also should take care of securing the wireless connections, using /interface wireless security-profile. For simplicity that configuration it's not shown here.
Results on router A (there is one client is connected to wlan2):
[admin@A] > /interface mesh pr
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 R name="mesh1" mtu=1500 arp=enabled mac-address=00:0C:42:0C:B5:A4 auto-mac=yes
admin-mac=00:00:00:00:00:00 mesh-portal=no hwmp-default-hoplimit=32
hwmp-preq-waiting-time=4s hwmp-preq-retries=2 hwmp-preq-destination-only=yes
hwmp-preq-reply-and-forward=yes hwmp-prep-lifetime=5m hwmp-rann-interval=10s
hwmp-rann-propagation-delay=1s hwmp-rann-lifetime=22s
[admin@A] > interface mesh port p detail
Flags: X - disabled, I - inactive, D - dynamic
0 interface=wlan1 mesh=mesh1 path-cost=10 hello-interval=10s port-type=auto port-type-used=wireless
1 interface=wlan2 mesh=mesh1 path-cost=10 hello-interval=10s port-type=auto port-type-used=wireless
2 D interface=router_B mesh=mesh1 path-cost=105 hello-interval=10s port-type=auto port-type-used=WDS
3 D interface=router_D mesh=mesh1 path-cost=76 hello-interval=10s port-type=auto port-type-used=WDS
The FDB (Forwarding Database) at the moment contains information only about local MAC addresses, non-mesh nodes reachable through local interface, and direct mesh neighbors:
[admin@A] /interface mesh> fdb print
Flags: A - active, R - root
MESH TYPE MAC-ADDRESS ON-INTERFACE LIFETIME AGE
A mesh1 local 00:0C:42:00:00:AA 3m17s
A mesh1 neighbor 00:0C:42:00:00:BB router_B 1m2s
A mesh1 neighbor 00:0C:42:00:00:DD router_D 3m16s
A mesh1 direct 00:0C:42:0C:7A:2B wlan2 2m56s
A mesh1 local 00:0C:42:0C:B5:A4 2m56s
[admin@A] /interface mesh> fdb print detail
Flags: A - active, R - root
A mac-address=00:0C:42:00:00:AA type=local age=3m21s mesh=mesh1 metric=0
seqnum=4294967196
A mac-address=00:0C:42:00:00:BB type=neighbor on-interface=router_B age=1m6s
mesh=mesh1 metric=132 seqnum=4294967196
A mac-address=00:0C:42:00:00:DD type=neighbor on-interface=router_D age=3m20s
mesh=mesh1 metric=79 seqnum=4294967196
A mac-address=00:0C:42:0C:7A:2B type=direct on-interface=wlan2 age=3m mesh=mesh1
metric=10 seqnum=0
A mac-address=00:0C:42:0C:B5:A4 type=local age=3m mesh=mesh1 metric=0 seqnum=0
Test that ping works:
[admin@A] > /ping 00:0C:42:00:00:CC 00:0C:42:00:00:CC 64 byte ping time=108 ms 00:0C:42:00:00:CC 64 byte ping time=51 ms 00:0C:42:00:00:CC 64 byte ping time=39 ms 00:0C:42:00:00:CC 64 byte ping time=43 ms 4 packets transmitted, 4 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 39/60.2/108 ms
Router A had to discover path to Router C first, hence the slightly larger time for the first ping.
Also test that ARP resolving works and so does IP level ping:
[admin@A] > /ping 10.4.0.3 10.4.0.3 64 byte ping: ttl=64 time=163 ms 10.4.0.3 64 byte ping: ttl=64 time=46 ms 10.4.0.3 64 byte ping: ttl=64 time=48 ms 3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 46/85.6/163 ms
Advanced topics
We all know that it's easy to make problematic layer-2 bridging or routing setups and hard to debug them. (Compared to layer-3 routing setups.) So there are a few bad configuration examples which could create problems for you. Avoid them!
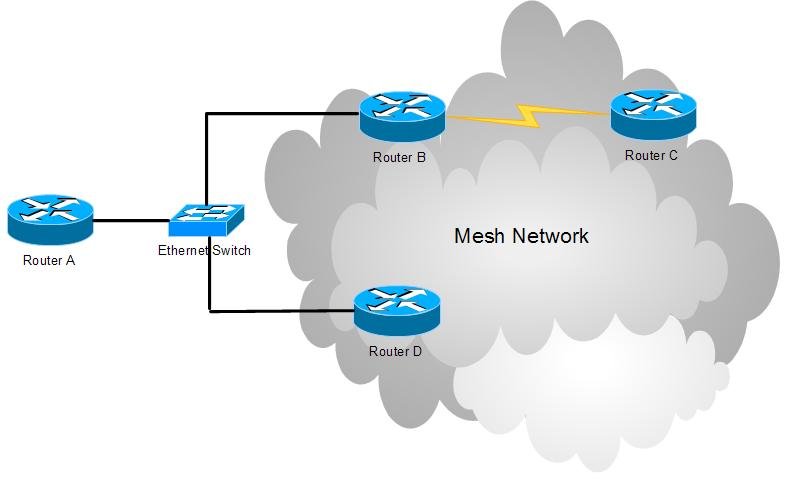
Problematic example 1: Ethernet switch inside a mesh
Router A will not be able to communicate reliably with router C. The problem manifests itself when D is the designated router for Ethernet; if B takes this role, everything is OK. The main cause of the problem is MAC address learning on Ethernet switch.
Consider what happens when router A wants to send something to C. We suppose router A either knowns or floods data to all interfaces. Either way, data arrives at switch. The switch, not knowing anything about destination's MAC address, forwards to data both to B and D.
What happens now:
- B receives the packet on a mesh interface. Since the MAC address is not local for B, and B knows that he is not the designated router for the Ethernet network, he simply ignores the packet.
- D receives the packet on a mesh interface. Since the MAC address is not local for B, and D is the designated router for the Ethernet network, he initiates path discovery process to C.
After path discovery is completed, D has information that C is reachable over B. Now D encapsulates the packet and forwards back to Ethernet network. The encapsulated packet forwarded by switch, received and forwarded by B, and received by C. So far everything is good.
Now C is likely to respond to the packet. Since B already knows where A is, he will decapsulate and forward the reply packet. But now switch will learn that the MAC address of C is reachable through B! That means, next time when something arrives from A addressed to C, the switch will forward data only to B. (And B, of course, will silently ignore the packet).
In contrast, if B took up the role of designated router, everything would be OK, because traffic would not have to go through the Ethernet switch twice.
Troubleshooting: either avoid such setup or disable MAC address learning on the switch. Note that on many switches it's not possible.
Problematic example 2: wireless modes
Consider this setup (invalid):
It is not possible to bridge wlan1 and wlan2 on RouterB now. The reason for this is pretty obvious if you understand how WDS works. For WDS communications four address frames are used. This is because for wireless multihop forwarding you need to know both the addresses of intermediate hops, as well as the original sender and final receiver. In contrast, non-WDS 802.11 communication includes only three MAC addresses in a frame. That's why it's not possible to do multihop forwarding in station mode.
Troubleshooting: depends on what you want to achieve:
- If you want to RouterC as a repeater either for wireless or Ethernet traffic, configure WDS link between RouterB and RouterC, and run mesh routing protocol on all nodes.
- In other cases configure wlan2 on RouterB in AP mode, and wlan on RouterC in station mode.