Manual:Simple BGP Multihoming: Difference between revisions
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
===Network Advertisements and Routing Filters=== | ===Network Advertisements and Routing Filters=== | ||
Now we can start to advertise our networks and filter out all other unnecessary advertisements. | |||
First step is to advertise our networks | |||
<pre> | |||
/routing bgp network | |||
add network=10.1.1.0/24 synchronize=no | |||
add network=10.1.2.0/24 synchronize=no | |||
</pre> | |||
Next step is to specify which routing filter chains will be used | |||
<pre> | |||
/routing bgp peer | |||
set isp1 in-filter=isp1-in out-filter=isp1-out | |||
set isp2 in-filter=isp2-in out-filter=isp2-out | |||
</pre> | |||
''in-filter'' is for incoming (received) prefixes, ''out-filter'' is for advertised prefixes. | |||
After chains are specified we can accept our networks and drop everything else as we are not '''transit provider''' | |||
{{cont}} | {{cont}} | ||
Revision as of 17:11, 1 November 2010
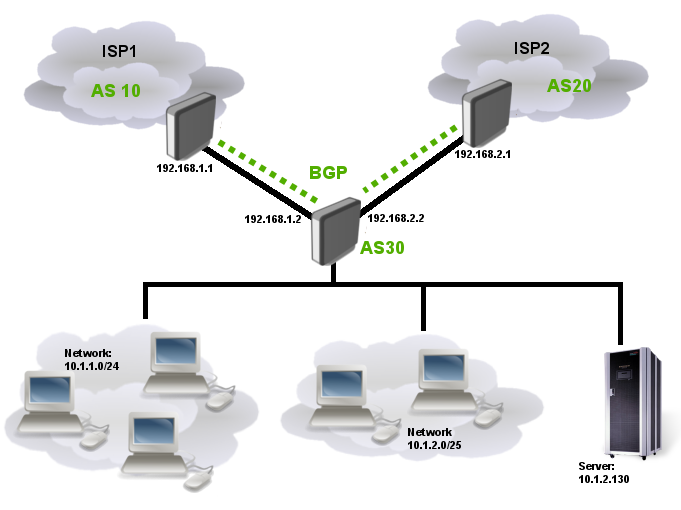
Setup
Ilustration below shows simple multihomed BGP setup. This setup can be used for load sharing between ISPs or one ISP as main and other ISP as backup link.
Lets say that local Internet registry assigned to us two /24 networks: 10.1.1.0/24 and 10.1.2.0/24 and our AS is 30 (Private AS cannot be used in such setups). First network entirely is used for workstations in our corporate network. Part of the other network is also used for workstation and another part is reserved for server. At this point our company has only one server with address 10.1.2.130
The goal is advertise our assigned networks to BGP peers and use only one provider as main link, ISP2 link is for backup only.

Note: This example does not show how to provide connectivity between core router, local networks and servers
BGP Peering
Consider that IP connectivity between ISPs edge routers and Our Core router is already set up and working properly. So we can start to establish BGP peering to both ISPs.
#set our AS number /routing bgp instance set default as=30 #add BGP peers /routing bgp peer add name=toISP1 remote-address=192.168.1.1 remote-as=10 add name=toISP2 remote-address=192.168.2.1 remote-as=20
If everything is set up properly, peer should have E (established) flag and router should receive bunch of BGP routes from both ISPs
[admin@RB1100test] /routing bgp peer> print Flags: X - disabled, E - established # INSTANCE REMOTE-ADDRESS REMOTE-AS 0 E default 192.168.1.1 10 1 E default 192.168.1.2 20
Network Advertisements and Routing Filters
Now we can start to advertise our networks and filter out all other unnecessary advertisements.
First step is to advertise our networks
/routing bgp network add network=10.1.1.0/24 synchronize=no add network=10.1.2.0/24 synchronize=no
Next step is to specify which routing filter chains will be used
/routing bgp peer set isp1 in-filter=isp1-in out-filter=isp1-out set isp2 in-filter=isp2-in out-filter=isp2-out
in-filter is for incoming (received) prefixes, out-filter is for advertised prefixes.
After chains are specified we can accept our networks and drop everything else as we are not transit provider
[ Top | Back to Content ]