Manual:Initial Configuration: Difference between revisions
initial user guide for starting users. simplified. |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
Both screens are similar you can check that by selecting user name, afterwards clicking ''OK'' or ''Cancel'' you will be brought back to initial screen of user management. | Both screens are similar you can check that by selecting user name, afterwards clicking ''OK'' or ''Cancel'' you will be brought back to initial screen of user management. | ||
[[File:ediit_create_user.png]] | |||
In user ''edit''/''Add new'' screen you can alter existing user or create new. Field marked with ''2.'' is the user name, field ''1.'' will open password screen. | |||
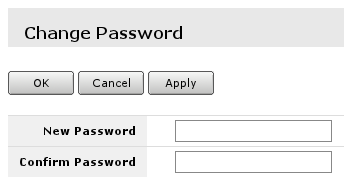
[[File:change_password_user_edit.png]] | |||
Where old password for the user can be changed or added for new user. | |||
====Configure access to internet==== | |||
If initial configuration did not work (your ISP is not providing DHCP server for automatic configuration) then you will have to have details from your ISP for static configuration of the router. These settings should include | |||
*IP address you can use | |||
*Network mask for the IP address | |||
*Default gateway address | |||
Less important settings regarding router configuration: | |||
*DNS address for name resolution | |||
*NTP server address for time automatic configuration | |||
*Your previous MAC address of the interface facing ISP | |||
======DHCP Client====== | |||
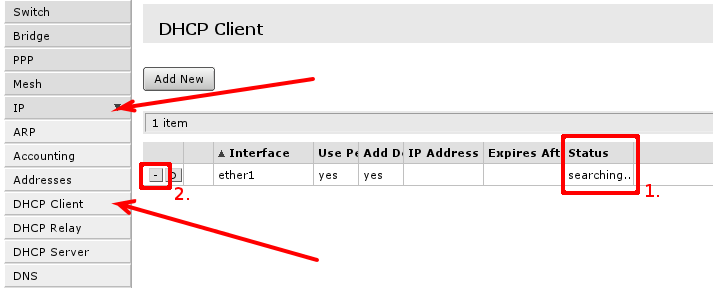
Default configuration is set up using DHCP-Client on interface facing your ISP or wide area network (WAN). It has to be disabled if your ISP is not providing this service in the network. Open 'IP -> DHCP Client' and inspect field ''1.'' to see status of DHCP Client, if it is in state as displayed in screenshot, means your ISP is not providing you with automatic configuration and you can use button in selection ''2.'' to remove DHCP-Client configured on the interface. | |||
[[File:DHCP_client.png]] | |||
======Static IP Address====== | |||
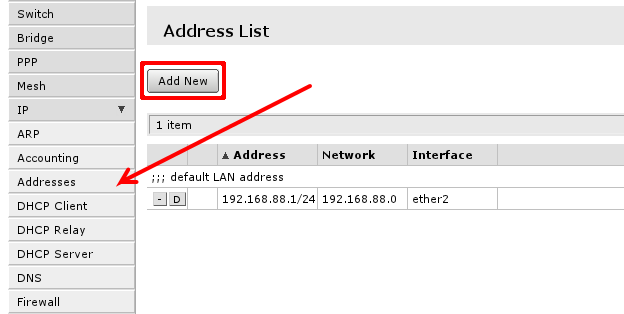
To manage IP addresses of the router open 'IP -> Address' | |||
[[File:add_new_address.png]] | |||
You will have one address here - address of your local area network (LAN) ''192.168.88.1'' one you are connected to router. Select ''Add new'' to add new static IP address to your router's configuration. | |||
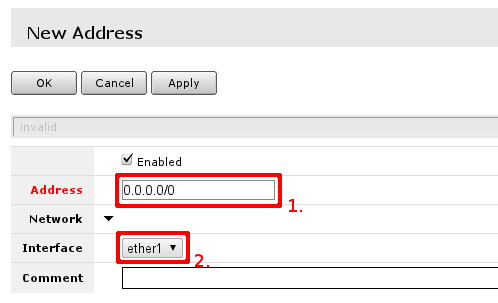
[[File:adding_new_address.png]] | |||
You have to fill only fields that are marked. Field ''1.'' should contain ''IP address'' provided by your ISP and ''network mask'. Allowed notation examples: | |||
*172.16.88.67/24 | |||
*172.16.88.67/255.255.255.0 | |||
both of these notations mean the same, if your ISP gave you address in one notation, or in the other, use one provided and router will do the rest of calculation. | |||
Other field of interest is ''interface'' this address is going to be assigned. This should be interface your ISP is connected to, if you followed this guide - interface contains name - ''ether1'' | |||
{{Note | While you type in the address, webfig will calculate if address you have typed is acceptable, if it is not label of the field will turn red, otherwise it will be blue}} | |||
{{Note| It is good practice to add comments on the items to give some additional information for the future, but that is not required}} | |||
======Configuring NAT====== | |||
Since you are using local and global networks, you have to set up network masquerade, so that your LAN is hidden behind IP address provided by your ISP. That should be so, since your ISP does not know what LAN addresses you are going to use and your LAN will not be routed from global network. | |||
Revision as of 12:10, 28 September 2011
Summary
What to do when you have new MikroTik router and you need configuration different from default what routers are provided with?
Connecting wires
Router initial configuration is set up in the way that should work in most of the cases and it is described on the box you received your router in. It is good idea to connect wires in the way it is described on that box:
- Connect ethernet wire from your internet service provider (ISP) to port ether1, rest of the ports on the router are for local area network (LAN). At this moment, your router is protected by default firewall configuration so you should not worry about that.
Connecting to router
Router initial configuration have DHCP client on WAN interface (ether1), rest of the ports are set as your local network with DHCP server configured for automatic configuration of devices that support that in your network. In that phase you have to set your computer to accept DHCP settings and connect to router port other than ether1 (please check routerboard.com for what port is what, or check front panel of the router).
Logging into the router
Router will have address 192.168.88.1 that you can open in your browser. When you do that you will be introduced with initial RouterOS page where you have to choose option WebFig.
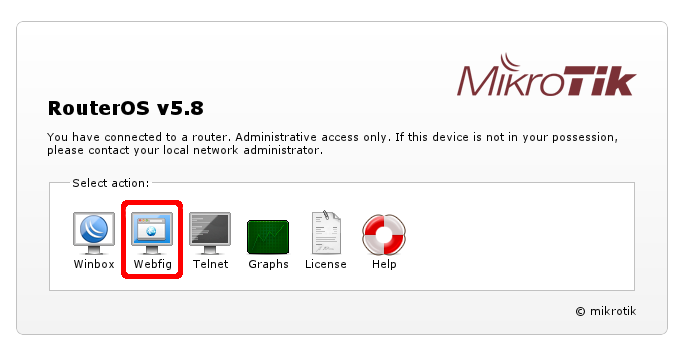
You will be prompted with login screen into WebFig RouterOS configuration interface.
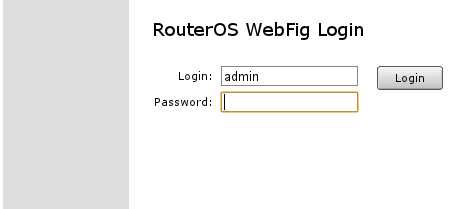
You have to fill in login name with admin and use blank password as it is already. After that you can login into the router.
Router user accounts
It is good idea to set up password for your default user admin and create new user for your use.
To do this, you have to go to 'System-> Users'
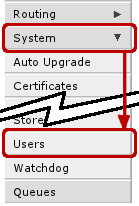
Afterwards click on Users menu:
You will see this screen, where you can manage users of the router.
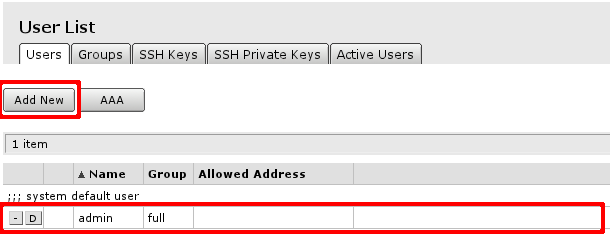
- By clicking on account name, in this case admin will open edit screen for the user
- Add new will open new user creation screen
Both screens are similar you can check that by selecting user name, afterwards clicking OK or Cancel you will be brought back to initial screen of user management.
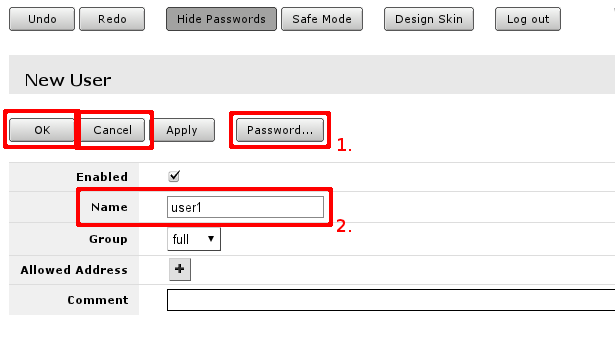
In user edit/Add new screen you can alter existing user or create new. Field marked with 2. is the user name, field 1. will open password screen.
Where old password for the user can be changed or added for new user.
Configure access to internet
If initial configuration did not work (your ISP is not providing DHCP server for automatic configuration) then you will have to have details from your ISP for static configuration of the router. These settings should include
- IP address you can use
- Network mask for the IP address
- Default gateway address
Less important settings regarding router configuration:
- DNS address for name resolution
- NTP server address for time automatic configuration
- Your previous MAC address of the interface facing ISP
DHCP Client
Default configuration is set up using DHCP-Client on interface facing your ISP or wide area network (WAN). It has to be disabled if your ISP is not providing this service in the network. Open 'IP -> DHCP Client' and inspect field 1. to see status of DHCP Client, if it is in state as displayed in screenshot, means your ISP is not providing you with automatic configuration and you can use button in selection 2. to remove DHCP-Client configured on the interface.
Static IP Address
To manage IP addresses of the router open 'IP -> Address'
You will have one address here - address of your local area network (LAN) 192.168.88.1 one you are connected to router. Select Add new to add new static IP address to your router's configuration.
You have to fill only fields that are marked. Field 1. should contain IP address provided by your ISP and network mask'. Allowed notation examples:
- 172.16.88.67/24
- 172.16.88.67/255.255.255.0
both of these notations mean the same, if your ISP gave you address in one notation, or in the other, use one provided and router will do the rest of calculation.
Other field of interest is interface this address is going to be assigned. This should be interface your ISP is connected to, if you followed this guide - interface contains name - ether1

Note: While you type in the address, webfig will calculate if address you have typed is acceptable, if it is not label of the field will turn red, otherwise it will be blue

Note: It is good practice to add comments on the items to give some additional information for the future, but that is not required
Configuring NAT
Since you are using local and global networks, you have to set up network masquerade, so that your LAN is hidden behind IP address provided by your ISP. That should be so, since your ISP does not know what LAN addresses you are going to use and your LAN will not be routed from global network.