Manual:CRS1xx/2xx series switches examples: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
added interVLAN routing example |
|||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
===Port Based VLAN=== | ===VLAN=== | ||
====Port Based VLAN==== | |||
[[File:Port-Based.png|center|frame|alt=Alt text|Port Based VLAN]] | [[File:Port-Based.png|center|frame|alt=Alt text|Port Based VLAN]] | ||
| Line 44: | Line 46: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
===Protocol Based VLAN=== | ====Protocol Based VLAN==== | ||
[[File:Protocol-Based.png|center|frame|alt=Alt text|Protocol Based VLAN]] | [[File:Protocol-Based.png|center|frame|alt=Alt text|Protocol Based VLAN]] | ||
| Line 85: | Line 87: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
===MAC Based VLAN=== | ====MAC Based VLAN==== | ||
[[File:MAC-Based.png|center|frame|alt=Alt text|MAC Based VLAN]] | [[File:MAC-Based.png|center|frame|alt=Alt text|MAC Based VLAN]] | ||
| Line 119: | Line 121: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
===Management IP Configuration=== | ====Management IP Configuration==== | ||
* Add VLAN 99 interface and assign IP address to it. Since the master-port receives all the traffic coming from switch-cpu port, VLAN has to be configured on master-port, in this case "ether2" port. | * Add VLAN 99 interface and assign IP address to it. Since the master-port receives all the traffic coming from switch-cpu port, VLAN has to be configured on master-port, in this case "ether2" port. | ||
| Line 128: | Line 130: | ||
/ip address | /ip address | ||
add address=192.168.88.1/24 interface=vlan99 network=192.168.88.0 | add address=192.168.88.1/24 interface=vlan99 network=192.168.88.0 | ||
</pre> | |||
====InterVLAN Routing with unknown VLAN filtering==== | |||
[[File:InterVLAN-Routing.png|center|frame|alt=Alt text|InterVLAN Routing]] | |||
InterVLAN routing configuration consists of two main parts – VLAN tagging in switch-chip and routing in RouterOS. This configuration can be used in many applications by combining it with DHCP server, Hotspot, PPP and other features for each VLAN. Additionally this example covers blocking of unwanted other VLAN traffic on ports. | |||
* Create a group of switched ports. | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface ethernet | |||
set ether6 master-port=ether2 | |||
set ether7 master-port=ether2 | |||
set ether8 master-port=ether2 | |||
</pre> | |||
* Set VLAN tagging on CPU port for all VLANs to make packets tagged before they are routed and add ingress VLAN translation rules to ensure correct VLAN id assignment is done on access ports. | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface ethernet switch egress-vlan-tag | |||
add tagged-ports=switch1-cpu vlan-id=200 | |||
add tagged-ports=switch1-cpu vlan-id=300 | |||
add tagged-ports=switch1-cpu vlan-id=400 | |||
/interface ethernet switch ingress-vlan-translation | |||
add ports=ether6 new-customer-vid=200 sa-learning=yes | |||
add ports=ether7 new-customer-vid=300 sa-learning=yes | |||
add ports=ether8 new-customer-vid=400 sa-learning=yes | |||
</pre> | |||
* For routing add VLAN interfaces on master-port because it connects with CPU port and add IP addresses to created VLAN interfaces. In this example three 192.168.x.1 addresses are added to vlan200, vlan300 and vlan400 interfaces. | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface vlan | |||
add name=vlan200 interface=ether2 vlan-id=200 | |||
add name=vlan300 interface=ether2 vlan-id=300 | |||
add name=vlan400 interface=ether2 vlan-id=400 | |||
/ip address | |||
add address=192.168.20.1/24 interface=vlan200 network=192.168.20.0 | |||
add address=192.168.30.1/24 interface=vlan300 network=192.168.30.0 | |||
add address=192.168.40.1/24 interface=vlan400 network=192.168.40.0 | |||
</pre> | |||
* VLAN membership is defined by the VLAN table. Adding entries with VLAN id and ports makes that VLAN traffic valid on those ports. After valid VLAN configuration unknown/invalid VLAN forwarding can be disabled in global switch settings. | |||
<pre> | |||
/interface ethernet switch vlan | |||
add ports=switch1-cpu,ether6 vlan-id=200 learn=yes | |||
add ports=switch1-cpu,ether7 vlan-id=300 learn=yes | |||
add ports=switch1-cpu,ether8 vlan-id=400 learn=yes | |||
/interface ethernet switch | |||
set forward-unknown-vlan=no | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Revision as of 07:59, 14 April 2014
Summary
Basic switch-chip configuration examples for Cloud Router Switch.
VLAN
Port Based VLAN
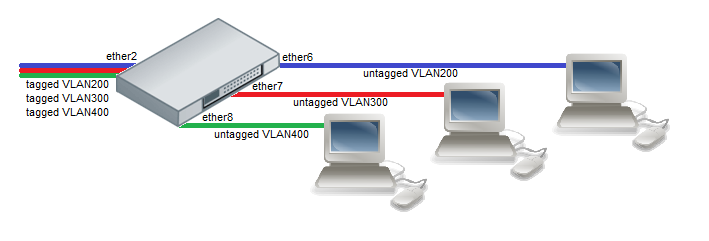
- Create a group of switched ports and configure switch for IEEE 802.1Q bridging.
/interface ethernet set ether6 master-port=ether2 set ether7 master-port=ether2 set ether8 master-port=ether2 /interface ethernet switch set bridge-type=customer-vlan-bridge
- Tag ingress traffic coming from each of the access ports by assigning new VLAN ids for untagged (VLAN id 0) frames.
/interface ethernet switch ingress-vlan-translation add port=ether6 customer-vid=0 new-customer-vid=200 sa-learning=yes add port=ether7 customer-vid=0 new-customer-vid=300 sa-learning=yes add port=ether8 customer-vid=0 new-customer-vid=400 sa-learning=yes
- Untag egress traffic on access ports by replacing current VLAN ids with VLAN id 0.
/interface ethernet switch egress-vlan-translation add port=ether6 customer-vid=200 new-customer-vid=0 add port=ether7 customer-vid=300 new-customer-vid=0 add port=ether8 customer-vid=400 new-customer-vid=0
Protocol Based VLAN
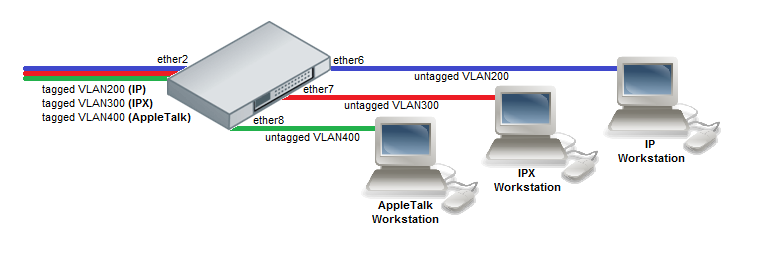
- Create a group of switched ports.
/interface ethernet set ether6 master-port=ether2 set ether7 master-port=ether2 set ether8 master-port=ether2
- Set VLAN for IP and ARP protocols
/interface ethernet switch protocol-based-vlan add port=ether2 protocol=arp set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=0 add port=ether6 protocol=arp set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=200 add port=ether2 protocol=ip set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=0 add port=ether6 protocol=ip set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=200
- Set VLAN for IPX protocol
/interface ethernet switch protocol-based-vlan add port=ether2 protocol=ipx set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=0 add port=ether7 protocol=ipx set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=300
- Set VLAN for AppleTalk AARP and AppleTalk DDP protocols
/interface ethernet switch protocol-based-vlan add port=ether2 protocol=0x80F3 set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=0 add port=ether8 protocol=0x80F3 set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=400 add port=ether2 protocol=0x809B set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=0 add port=ether8 protocol=0x809B set-customer-vid-for=all new-customer-vid=400
MAC Based VLAN
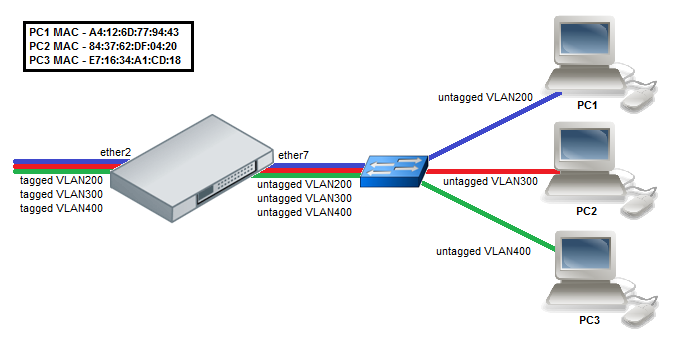
- Create a group of switched ports.
/interface ethernet set ether7 master-port=ether2
- Enable MAC based VLAN translation on access port.
/interface ethernet switch port set ether7 mac-based-vlan-translate=yes mac-based-customer-vlan=all-frames
- Add MAC-to-VLAN mapping entries in MAC based VLAN table.
/interface ethernet switch mac-based-vlan add src-mac=A4:12:6D:77:94:43 new-customer-vid=200 add src-mac=84:37:62:DF:04:20 new-customer-vid=300 add src-mac=E7:16:34:A1:CD:18 new-customer-vid=400
- Set VLAN id untagging for tagged frames coming from the trunk port.
/interface ethernet switch ingress-vlan-translation add port=ether2 customer-vlan-lookup-for=tagged new-customer-vid=0 sa-learning=yes
Management IP Configuration
- Add VLAN 99 interface and assign IP address to it. Since the master-port receives all the traffic coming from switch-cpu port, VLAN has to be configured on master-port, in this case "ether2" port.
/interface vlan add name=vlan99 vlan-id=99 interface=ether2 /ip address add address=192.168.88.1/24 interface=vlan99 network=192.168.88.0
InterVLAN Routing with unknown VLAN filtering
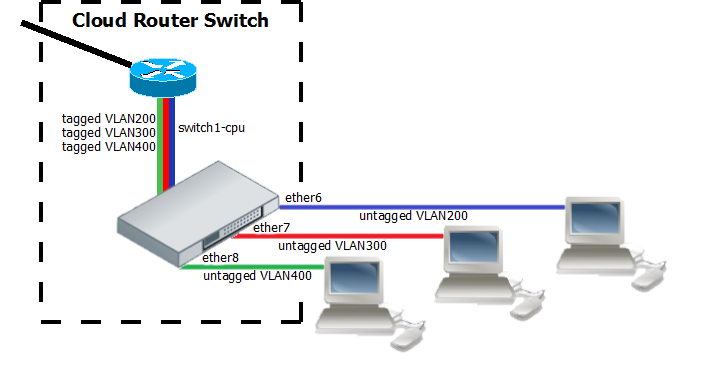
InterVLAN routing configuration consists of two main parts – VLAN tagging in switch-chip and routing in RouterOS. This configuration can be used in many applications by combining it with DHCP server, Hotspot, PPP and other features for each VLAN. Additionally this example covers blocking of unwanted other VLAN traffic on ports.
- Create a group of switched ports.
/interface ethernet set ether6 master-port=ether2 set ether7 master-port=ether2 set ether8 master-port=ether2
- Set VLAN tagging on CPU port for all VLANs to make packets tagged before they are routed and add ingress VLAN translation rules to ensure correct VLAN id assignment is done on access ports.
/interface ethernet switch egress-vlan-tag add tagged-ports=switch1-cpu vlan-id=200 add tagged-ports=switch1-cpu vlan-id=300 add tagged-ports=switch1-cpu vlan-id=400 /interface ethernet switch ingress-vlan-translation add ports=ether6 new-customer-vid=200 sa-learning=yes add ports=ether7 new-customer-vid=300 sa-learning=yes add ports=ether8 new-customer-vid=400 sa-learning=yes
- For routing add VLAN interfaces on master-port because it connects with CPU port and add IP addresses to created VLAN interfaces. In this example three 192.168.x.1 addresses are added to vlan200, vlan300 and vlan400 interfaces.
/interface vlan add name=vlan200 interface=ether2 vlan-id=200 add name=vlan300 interface=ether2 vlan-id=300 add name=vlan400 interface=ether2 vlan-id=400 /ip address add address=192.168.20.1/24 interface=vlan200 network=192.168.20.0 add address=192.168.30.1/24 interface=vlan300 network=192.168.30.0 add address=192.168.40.1/24 interface=vlan400 network=192.168.40.0
- VLAN membership is defined by the VLAN table. Adding entries with VLAN id and ports makes that VLAN traffic valid on those ports. After valid VLAN configuration unknown/invalid VLAN forwarding can be disabled in global switch settings.
/interface ethernet switch vlan add ports=switch1-cpu,ether6 vlan-id=200 learn=yes add ports=switch1-cpu,ether7 vlan-id=300 learn=yes add ports=switch1-cpu,ether8 vlan-id=400 learn=yes /interface ethernet switch set forward-unknown-vlan=no
[ Top | Back to Content ]

