Manual:IPv6/DHCP Client: Difference between revisions
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
{{Mr-arg-table | {{Mr-arg-table | ||
|arg=request | |arg=request | ||
|type=prefix | |type=prefix, address | ||
|desc=Whether to add default IPv6 route after client connects. | |desc=Whether to add default IPv6 route after client connects. | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 12:45, 13 May 2016
Summary
DHCP-client in RouterOS is capable of being a DHCPv6-client and DHCP-PD client. So it is able to get a prefix from DHCP-PD server as well as DHCPv6 stateful address from DHCPv6 server.
Quick setup example
This simple example demonstrates how to enable dhcp client to receive IPv6 prefix and add it to the pool.
/ipv6 dhcp-client add request=prefix pool-name=test-ipv6 pool-prefix-length=64 interface=ether13
Detailed print should show status of the client and we can verify if prefix is received
[admin@x86-test] /ipv6 dhcp-client> print detail
Flags: D - dynamic, X - disabled, I - invalid
0 interface=bypass pool-name="test-ipv6" pool-prefix-length=64 status=bound
prefix=2001:db8:7501:ff04::/62 expires-after=2d23h11m53s request=prefix
Notice that server gave us prefix 2a02:610:7501:ff04::/62 . And it should be also added to ipv6 pools
[admin@MikroTik] /ipv6 pool> print Flags: D - dynamic # NAME PREFIX REQUEST PREFIX-LENGTH 0 D test-ipv6 2001:db8:7501:ff04::/62 prefix 64
It works! Now you can use this pool, for example, for pppoe clients.
Properties
Sub-menu: /ipv6 dhcp-client
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| add-default-route (yes | no; Default: no) | Whether to add default IPv6 route after client connects. |
| request (prefix, address; Default: {{{default}}}) | Whether to add default IPv6 route after client connects. |
| comment (string; Default: ) | Short description of the client |
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | |
| interface (string; Default: ) | Interface on which DHCPv6 client will be running. |
| pool-name (string; Default: ) | Name of the IPv6 pool in which received IPv6 prefix will be added |
| pool-prefix-length (string; Default: ) | Prefix length parameter that will be set for IPv6 pool in which received IPv6 prefix is added. Prefix length must be greater than the length of received prefix, otherwise prefix-length will be set to received prefix length + 8 bits. |
Status
Command /ipv6 dhcp-client print detail will show current status of dhcp client and read-only properties listed in table below:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| duid (string) | Auto generated DUID that is sent to the server. DUID is generated using one of the MAC addresses available on the router. |
| dynamic (yes | no) | |
| expires-after (time) | Time when the IPv6 prefix expires (specified by the DHCPv6 server). |
| invalid (yes | no) | Shows whether configuration is invalid. |
| prefix (IPv6 prefix) | Shows received IPv6 prefix from DHCPv6-PD server |
| status (stopped | searching | requesting... | bound | renewing | rebinding | error | stopping) | Shows the status of DHCPv6 Client:
|
To determine what IAID will be used, convert internal ID of an interface on which DHCP client is running from hex to decimal.
For example, DHCP client is running on interface pppoe-out1. To get internal ID use following command
[admin@t36] /interface> :put [find name="pppoe-out1"] *15
Now convert hex value 15 to decimal and you get IAID=21
Menu specific commands
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| release (numbers) | Release current binding and restart DHCPv6 client |
| renew (numbers) | Renew current leases. If the renew operation was not successful, client tries to reinitialize lease (i.e. it starts lease request procedure (rebind) as if it had not received an IP address yet) |
Application Examples
Use received prefix for local RA
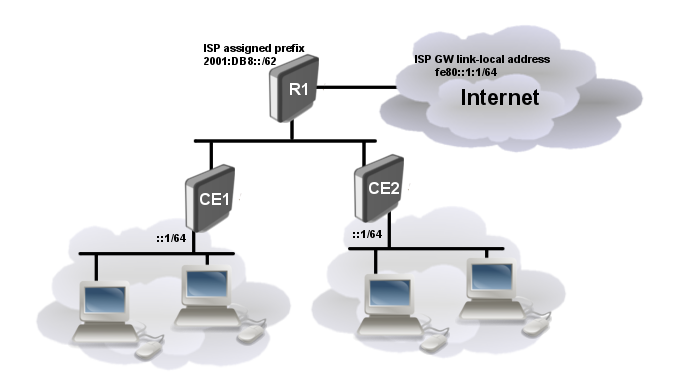
Consider following setup:
- ISP is routing prefix 2001:DB8::/62 to the router R1
- Router R1 runs DHCPv6 server to delegate /64 prefixes to the customer routers CE1 CE2
- DHCP client on routers CE1 and CE2 receives delegated /64 prefix from the DHCP server (R1).
- Client routers uses received prefix to set up RA on the local interface
Configuration
R1
/ipv6 route add gateway=fe80::1:1%to-ISP /ipv6 pool add name=myPool prefix=2001:db8::/62 prefix-length=64 /ipv6 dhcp-server add address-pool=myPool disabled=no interface=to-CE-routers lease-time=3m name=server1
CE1
/ipv6 dhcp-client add interface=to-R1 pool-name=my-ipv6 /ipv6 address add address=::1/64 from-pool=my-ipv6 interface=to-clients advertise=yes
CE2
/ipv6 dhcp-client add interface=to-R1 pool-name=my-ipv6 /ipv6 address add address=::1/64 from-pool=my-ipv6 interface=to-clients advertise=yes
Check the status
After configuration is complete we can verify that each CE router received its own prefix
On server:
[admin@R1] /ipv6 dhcp-server binding> print Flags: X - disabled, D - dynamic # ADDRESS DUID IAID SERVER STATUS 1 D 2001:db8:1::/64 0019d1393536 566 server1 bound 2 D 2001:db8:2::/64 0019d1393535 565 server1 bound
On client:
[admin@CE1] /ipv6 dhcp-client> print Flags: D - dynamic, X - disabled, I - invalid # INTERFACE STATUS PREFIX 0 to-R1 bound 2001:db8:1::/64 [admin@CE1] /ipv6 dhcp-client> /ipv6 pool print Flags: D - dynamic # NAME PREFIX PREFIX-LENGTH 0 D my-ipv6 2001:db8:1::/64 64
We can also see that IPv6 address was automatically added from the prefix pool:
[admin@CE1] /ipv6 address> print Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic, G - global, L - link-local # ADDRESS FROM-POOL INTERFACE ADVERTISE 0 G 2001:db8:1::1/64 to-clients yes ..
And pool usage shows that 'Address' is allocating the pool
[admin@CE1] /ipv6 pool used> print POOL PREFIX OWNER INFO my-ipv6 2001:db8:1::/64 Address to-clients
[ Top | Back to Content ]