IKEv2 EAP between NordVPN and RouterOS: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
==Choosing what | ==Choosing what to send over the tunnel== | ||
If we look at the generated dynamic [[M:IP/IPsec#Policies | policies]], we see that only traffic with a specific (received by [[M:IP/IPsec#Mode_configs | mode config]]) source address will be sent through the tunnel. But a router in most cases will need to route a specific device or network through the tunnel. In such case we can use source NAT to change the source address of packets to match the mode config address. Since the mode config address is dynamic, it is impossible to create static source NAT rule. In RouterOS it is possible to generate dynamic source NAT rules for mode config clients. | If we look at the generated dynamic [[M:IP/IPsec#Policies | policies]], we see that only traffic with a specific (received by [[M:IP/IPsec#Mode_configs | mode config]]) source address will be sent through the tunnel. But a router in most cases will need to route a specific device or network through the tunnel. In such case we can use source NAT to change the source address of packets to match the mode config address. Since the mode config address is dynamic, it is impossible to create static source NAT rule. In RouterOS it is possible to generate dynamic source NAT rules for mode config clients. | ||
| Line 124: | Line 124: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
When it is done, a | When it is done, a NAT rule is generated with the dynamic address provided by the server: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
After that, it is possible to apply this <var>connection-mark</var> to any traffic using [[M:IP/Firewall/Mangle | Mangle firewall]]. In this example, access to mikrotik.com is granted over the tunnel. | After that, it is possible to apply this <var>connection-mark</var> to any traffic using [[M:IP/Firewall/Mangle | Mangle firewall]]. In this example, access to mikrotik.com and 8.8.8.8 is granted over the tunnel. | ||
Create a new address list: | Create a new address list: | ||
| Line 140: | Line 140: | ||
/ip firewall address-list | /ip firewall address-list | ||
add address=mikrotik.com list=VPN | add address=mikrotik.com list=VPN | ||
add address=8.8.8.8 list=VPN | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Apply <var>connection-mark</var> to traffic | Apply <var>connection-mark</var> to traffic matching the created address list: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
Latest revision as of 09:30, 16 July 2019
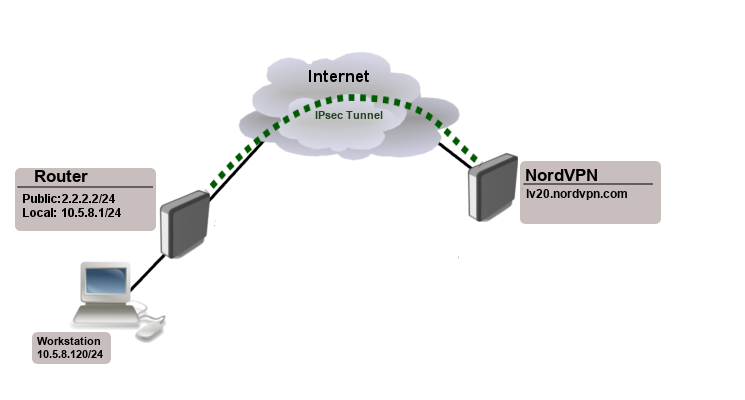
Starting from RouterOS v6.45, it is possible to establish IKEv2 secured tunnel to NordVPN servers using EAP authentication. This manual page explains how to configure it.
Installing the root CA
Start off by downloading and importing the NordVPN root CA certificate.
/tool fetch url="https://downloads.nordvpn.com/certificates/root.der" /certificate import file-name=root.der
There should now be the trusted NordVPN Root CA certificate in System/Certificates menu.
[admin@MikroTik] > /certificate print where name~"root.der" Flags: K - private-key, L - crl, C - smart-card-key, A - authority, I - issued, R - revoked, E - expired, T - trusted # NAME COMMON-NAME SUBJECT-ALT-NAME FINGERPRINT 0 T root.der_0 NordVPN Root CA 8b5a495db498a6c2c8c...
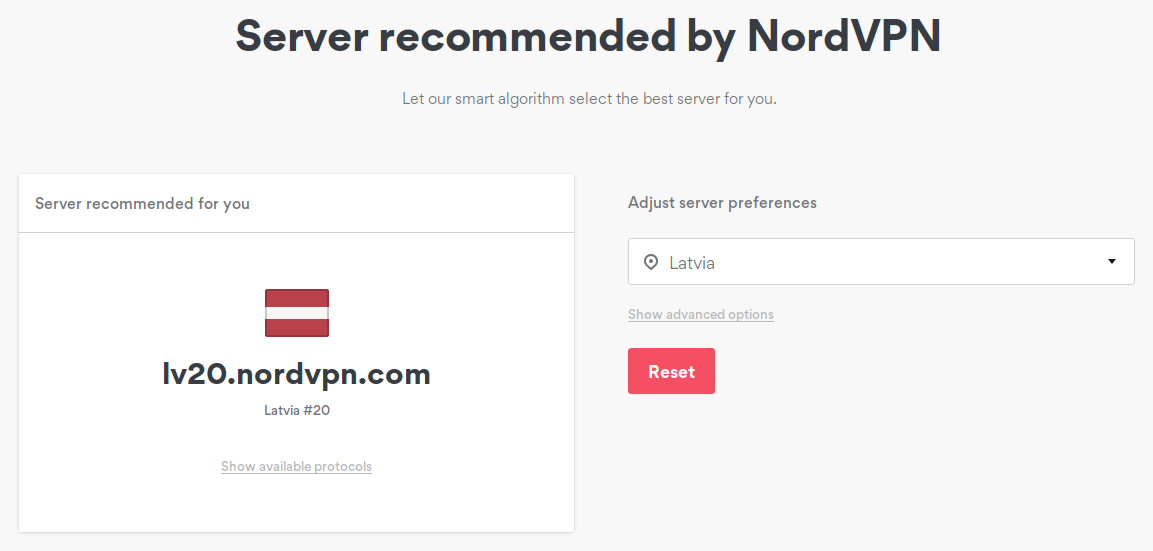
Finding out the server's hostname
Navigate to https://nordvpn.com/servers/tools/ and find out the recommended server's hostname. In this case it is lv20.nordvpn.com.
Setting up the IPsec tunnel
It is advised to create a separate Phase 1 profile and Phase 2 proposal configurations to not interfere with any existing or future IPsec configuration.
/ip ipsec profile add name=NordVPN /ip ipsec proposal add name=NordVPN pfs-group=none
While it is possible to use the default policy template for policy generation, it is better to create a new policy group and template to separate this configuration from any other IPsec configuration.
/ip ipsec policy group add name=NordVPN /ip ipsec policy add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 group=NordVPN proposal=NordVPN src-address=0.0.0.0/0 template=yes
Create a new mode config entry with responder=no that will request configuration parameters from the server.
/ip ipsec mode-config add name=NordVPN responder=no
Lastly, create peer and identity configurations. Specify your NordVPN credentials in username and password parameters.
/ip ipsec peer add address=lv20.nordvpn.com exchange-mode=ike2 name=NordVPN profile=NordVPN /ip ipsec identity add auth-method=eap certificate="" eap-methods=eap-mschapv2 generate-policy=port-strict mode-config=NordVPN peer=NordVPN policy-template-group=NordVPN username=support@mikrotik.com password=secret
Verify that the connection is successfully established.
/ip ipsec active-peers print installed-sa print
Choosing what to send over the tunnel
If we look at the generated dynamic policies, we see that only traffic with a specific (received by mode config) source address will be sent through the tunnel. But a router in most cases will need to route a specific device or network through the tunnel. In such case we can use source NAT to change the source address of packets to match the mode config address. Since the mode config address is dynamic, it is impossible to create static source NAT rule. In RouterOS it is possible to generate dynamic source NAT rules for mode config clients.
Option 1: Sending all traffic over the tunnel
In this example, we have a local network 10.5.8.0/24 behind the router and we want all traffic from this network to be sent over the tunnel. First of all, we have to make a new IP/Firewall/Address list which consists of our local network.
/ip firewall address-list add address=10.5.8.0/24 list=local
It is also possible to specify only single hosts from which all traffic will be sent over the tunnel. Example:
/ip firewall address-list add address=10.5.8.120 list=local add address=10.5.8.23 list=local
When it is done, we can assign newly created IP/Firewall/Address list to mode config configuration.
/ip ipsec mode-config set [ find name=NordVPN ] src-address-list=local
Verify correct source NAT rule is dynamically generated when the tunnel is established.
[admin@MikroTik] > /ip firewall nat print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic
0 D ;;; ipsec mode-config
chain=srcnat action=src-nat to-addresses=192.168.77.254 src-address-list=local dst-address-list=!local

Warning: Make sure dynamic mode config address is not a part of local network.

Note: It is also possible to combine both options (1 and 2) to allow access to specific addresses only for specific local addresses/networks
Option 2: Accessing certain addresses over the tunnel
It is also possible to send only specific traffic over the tunnel by using the connection-mark parameter in Mangle firewall. It works similarly as Option 1 - a dynamic NAT rule is generated based on configured connection-mark parameter under mode config.
First of all, set the connection-mark under your mode config configuration.
/ip ipsec mode-config set [ find name=NordVPN ] connection-mark=NordVPN
When it is done, a NAT rule is generated with the dynamic address provided by the server:
[admin@MikroTik] > /ip firewall nat print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic
0 D ;;; ipsec mode-config
chain=srcnat action=src-nat to-addresses=192.168.77.254 connection-mark=NordVPN
After that, it is possible to apply this connection-mark to any traffic using Mangle firewall. In this example, access to mikrotik.com and 8.8.8.8 is granted over the tunnel.
Create a new address list:
/ip firewall address-list add address=mikrotik.com list=VPN add address=8.8.8.8 list=VPN
Apply connection-mark to traffic matching the created address list:
/ip firewall mangle add action=mark-connection chain=prerouting dst-address-list=VPN new-connection-mark=NordVPN passthrough=yes

Note: It is also possible to combine both options (1 and 2) to allow access to specific addresses only for specific local addresses/networks
[ Top | Back to Content ]