CALEA: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
* '''pcap-file-stop-interval''' - maximal interval between creating new fileset, if size limit is not reached earlier | * '''pcap-file-stop-interval''' - maximal interval between creating new fileset, if size limit is not reached earlier | ||
* '''pcap-file-stop-size''' - maximal filesize, in KiB | * '''pcap-file-stop-size''' - maximal filesize, in KiB | ||
* '''pcap-file-hash-method''' - hashing algorithm ('''md5''' or ''' | * '''pcap-file-hash-method''' - hashing algorithm ('''md5''', '''sha1''' or '''sha256''') for the data file (saved once the data file is completed and closed); no file is created if set to '''none''' | ||
== Calea Server/Client Configuration Example == | == Calea Server/Client Configuration Example == | ||
Revision as of 10:43, 26 June 2007
Communications Assistance for Law Enforcement Act requires the routers to have ability to intercept and log network traffic. RouterOS now provides this facility by means of firewall rules. RouterOS can also function as a data retention server if the additional calea package is installed.
CALEA features included in RouterOS
Multiple subject/multiple destination packet interception and streaming in following formats:
- Call Content Connection (CCC) Interface according to PKT-SP-ES-DCI-I01-060914 (PacketCable 2.0 PacketCable Electronic Surveillance Delivery Function to Collection Function Interface Specification)
- Call Content Connection (CCC) Interface according to ANSI/SCTE 24-13 2006 (IPCalblecom Electronic Surveillance Standard) that is approved method for Communication Content delivery to LEA according to ATIS-1000013.2007 (Lawfully Authorized Electronic Surveillance For Internet Access and Services)
- TZSP format - for reception with 'Ethereal', tcpdump, trafr (sniffer stream reader for linux) - http://www.mikrotik.com/download.html
CALEA-server package
- accepts multiple CCC streams (identified by destination port/source address/case id)
- stores communication content according to "IP Network Access Intercept Requirements and Method"(FBI-WISPA draft) specified "full content" intercept requirements (without out-of-band events)
- stores communication content of multiple subjects/cases
- stores communication content in libpcap format
- new libpcap file based on different conditions (interval/size/packet count)
- generates hash for each pcap file (md5/sha1/sha256)
Intercepting Packet Flow
The IP Firewall filters now have two additional actions:
- sniff - generates a tzsp stream that can be directed to any Wireshark (Ethereal) server
- sniff-pc - generates a Packet Cable stream that can be directed to a MikroTik RouterOS system with the calea package installed
By selecting either action, the following options will be available:
- sniff-id (Packet Cable protocol only) - packet stream case ID, that can be used to differentiate between separate traffic sets (e.g., between different users; or between client traffic and server traffic)
- sniff-target - IP address of the data retention server
- sniff-target-port - UDP port that the data retention server is listening on
Data Retention Server
The calea package provides an additional tool menu - /tool calea, that allows to save certain incoming data streams to a file. The server will create separate files for each packet stream (one data file and one hash file, if configured). The files will not grow indefinitely, but rather util a certain limit, after which a new set of files will be created for that stream. The limit is specified in size and extent of time, whichever is reached first.
Add a rule with the following properties:
- case-id - case ID set by the intercepting router
- intercept-ip - IP address of the intercepting router (IP address to receive the stream from)
- intercept-port - UDP port to listen on (port to receive the stream on)
- action - storage format (only pcap for now)
- pcap-file-stop-interval - maximal interval between creating new fileset, if size limit is not reached earlier
- pcap-file-stop-size - maximal filesize, in KiB
- pcap-file-hash-method - hashing algorithm (md5, sha1 or sha256) for the data file (saved once the data file is completed and closed); no file is created if set to none
Calea Server/Client Configuration Example
Let's assume the particular network configuration, we need to intercept data from 192.168.0.10 Wireless Client and send it to the Calea Server located on Local Network:
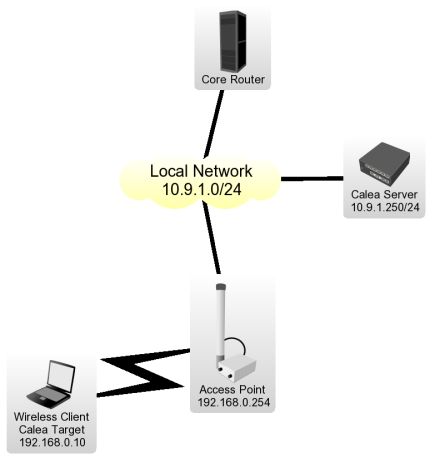
Client Configuration for the Intercept
Wireless Client is connected to Access Point, data interception has to be performed on Access Point for the particular network design.
- We have requirement to capture all data from the user Wireless Client with IP address of 192.168.0.10 We have to add two rules to make the interception,
ip firewall filter add action=sniff-pc chain=forward sniff-id=100 sniff-target=10.9.1.250 sniff-target-port=5555 src-address=192.168.0.10 ip firewall filter add action=sniff-pc chain=forward sniff-id=100 sniff-target=10.9.1.250 sniff-target-port=5555 dst-address=192.168.0.10
All traffic going trough the router for specified src/dst addresses is intercepted and sent to Calea Server (sniff-target) with sniff-id=100
- Calea package is not required for intercepting host.
Calea Server Configuration
- Calea package is required for server.
- One rule is required to accept the data from the Access Point to receive all intercepted traffic from the Access Point,
/tool calea add action=pcp intercept-port=5555 case-id=100 intercept-ip=192.168.0.254
Intercept-port and case-id should be equal on server and client side, intercept-ip is IP address of the intercepting router (Access Point).