Manual:Queues - Burst: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Theory== | ==Theory== | ||
To understand burst it is necessary to be aware of 5 concepts: | To understand burst it is necessary to be aware of 5 concepts: | ||
# burst-limit (NUMBER) : maximal upload/download data rate which can be reached while the burst is active | # '''burst-limit''' (NUMBER) : maximal upload/download data rate which can be reached while the burst is active | ||
# burst-time (TIME) : period of time, in seconds, over which the average data rate is calculated. (This is NOT the time of actual burst) | # '''burst-time''' (TIME) : period of time, in seconds, over which the average data rate is calculated. (This is NOT the time of actual burst) | ||
# burst-threshold (NUMBER) : when average data rate is below this value - burst is allowed, as soon as average data rate reach this value - burst is denied. (basically this is burst on/off switch). For optimal burst behavior this value should above limit-at value and below max-limit value | # '''burst-threshold''' (NUMBER) : when average data rate is below this value - burst is allowed, as soon as average data rate reach this value - burst is denied. (basically this is burst on/off switch). For optimal burst behavior this value should above limit-at value and below max-limit value | ||
# average-rate (read-only) : Every 1/16 part of the '''burst-time''', the router calculates the average data rate of each class over the last '''burst-time''' seconds. | # '''average-rate''' (read-only) : Every 1/16 part of the '''burst-time''', the router calculates the average data rate of each class over the last '''burst-time''' seconds. | ||
# actual-rate (read-only) : actual traffic transfer rate of the queue | # '''actual-rate''' (read-only) : actual traffic transfer rate of the queue | ||
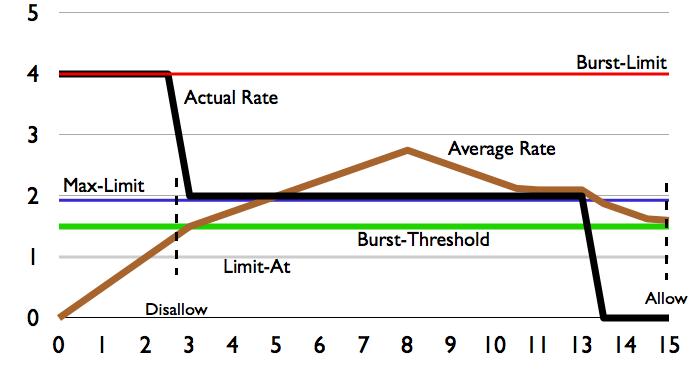
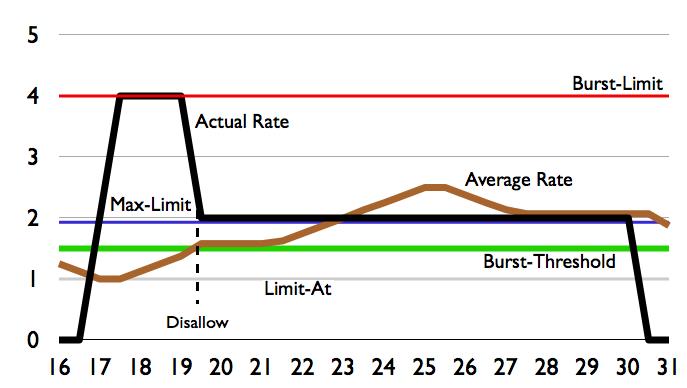
To simplify calculations for examples we will use limit-at=1M, max-limit=2M, burst-threshold=1500k, burst-limit=4M | |||
==Example Burst-time=8s== | |||
[[Image:Burst time.8.part1.JPG]] | [[Image:Burst time.8.part1.JPG]] | ||
| Line 16: | Line 22: | ||
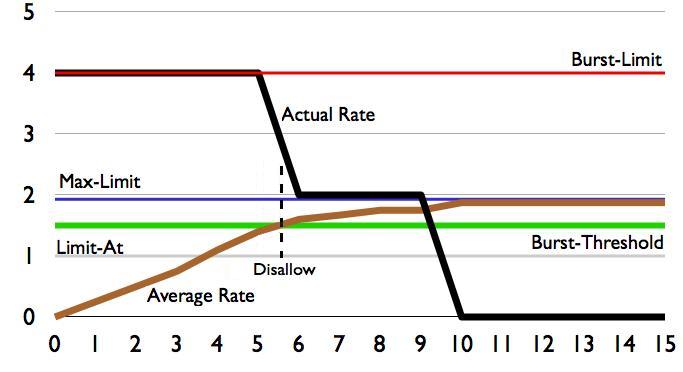
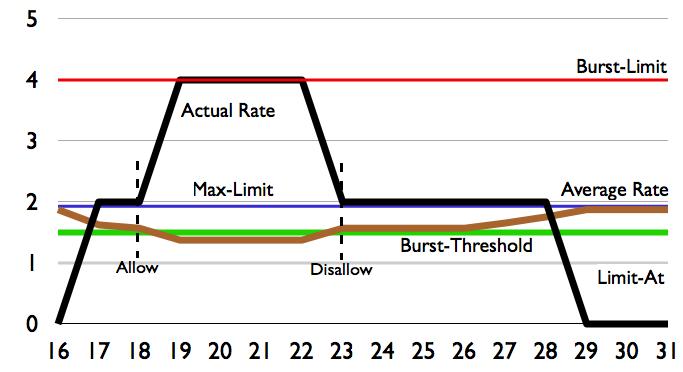
== | ==Example Burst-time=16s== | ||
[[Image:Burst time.16.part1.JPG]] | [[Image:Burst time.16.part1.JPG]] | ||
Revision as of 15:30, 13 October 2008
Theory
To understand burst it is necessary to be aware of 5 concepts:
- burst-limit (NUMBER) : maximal upload/download data rate which can be reached while the burst is active
- burst-time (TIME) : period of time, in seconds, over which the average data rate is calculated. (This is NOT the time of actual burst)
- burst-threshold (NUMBER) : when average data rate is below this value - burst is allowed, as soon as average data rate reach this value - burst is denied. (basically this is burst on/off switch). For optimal burst behavior this value should above limit-at value and below max-limit value
- average-rate (read-only) : Every 1/16 part of the burst-time, the router calculates the average data rate of each class over the last burst-time seconds.
- actual-rate (read-only) : actual traffic transfer rate of the queue
To simplify calculations for examples we will use limit-at=1M, max-limit=2M, burst-threshold=1500k, burst-limit=4M
Example Burst-time=8s