Manual:Packet Flow: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
MikroTik RouterOS is designed to be easy to operate in various aspects of network configuration. Therefore creating limitation for individual IP or natting internal clients to a public address or Hotspot configuration can be done without the knowledge about how the packets are processed in the router - you just go to corresponding menu and create necessary configuration. | |||
However more complicated tasks, such as traffic prioritization, routing policies, where it is necessary to utilize more than one RouterOS facility, requires knowledge: How these facilities work together? What happens when and why? | |||
To address these questions we created a packet flow diagram. | |||
==Diagram== | ==Diagram== | ||
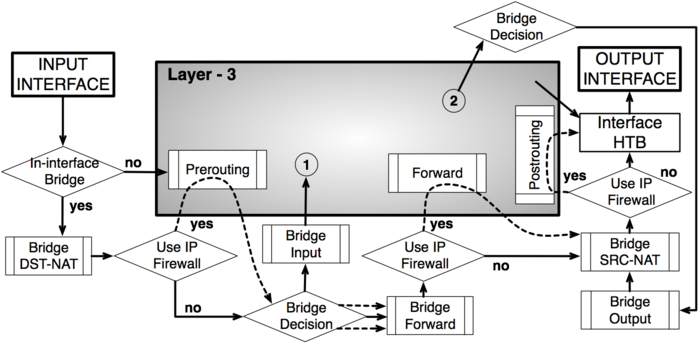
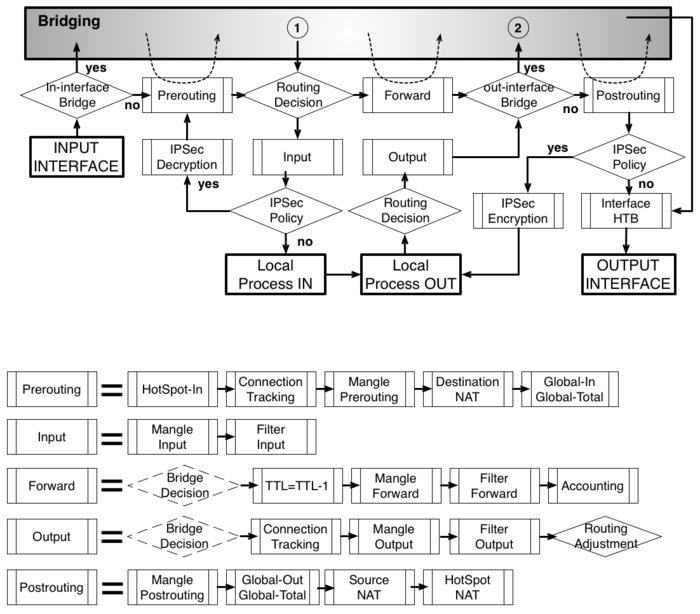
As it was impossible to get everything in one diagram, Packet flow diagram consist from 2 parts: | |||
* Bridging or Layer-2 (MAC) | |||
* Routing or Layer-3 (IP) | |||
[[Image:Bridge_final.png|Packet Flow in Layer-2|700px]] | [[Image:Bridge_final.png|Packet Flow in Layer-2|700px]] | ||
Revision as of 11:09, 27 November 2008
MikroTik RouterOS is designed to be easy to operate in various aspects of network configuration. Therefore creating limitation for individual IP or natting internal clients to a public address or Hotspot configuration can be done without the knowledge about how the packets are processed in the router - you just go to corresponding menu and create necessary configuration.
However more complicated tasks, such as traffic prioritization, routing policies, where it is necessary to utilize more than one RouterOS facility, requires knowledge: How these facilities work together? What happens when and why?
To address these questions we created a packet flow diagram.
Diagram
As it was impossible to get everything in one diagram, Packet flow diagram consist from 2 parts:
- Bridging or Layer-2 (MAC)
- Routing or Layer-3 (IP)