Manual:Interface/SSTP
Summary
Standards: SSTP specification
Package: ppp
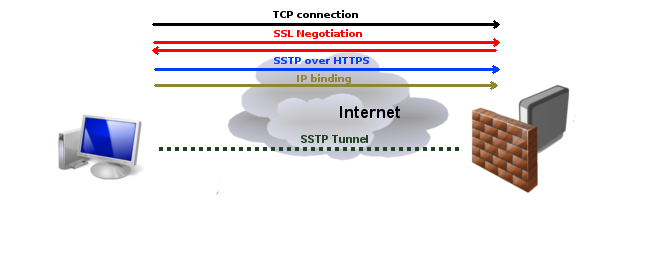
Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) is the way to transport PPP tunnel over SSL 3.0 channel. The use of SSL over TCP port 443 allows SSTP to pass through virtually all firewalls and proxy servers.
SSTP connection mechanism
- TCP connection is established from client to server (by default on port 443);
- SSL validates server certificate. If certificate is valid connection is established otherwise connection is torn down.
- The client sends SSTP control packets within the HTTPS session which establishes the SSTP state machine on both sides.
- PPP negotiation over SSTP. Client authenticates to the server and binds IP addresses to SSTP interface
- SSTP tunnel is now established and packet encapsulation can begin.
If both client and server are Mikrotik routers, then it is possible to establish SSTP tunnel without certificates and with any available authentication type. Otherwise to establish secure tunnels mschap authentication and client/server certificates from the same chain should be used. Read more>>

Note: Starting from v5.0beta2 SSTP does not require certificates to operate. This feature will work only between two MikroTik routers, as it is not according to standards.
Currently, SSTP clients exist only in Windows Vista, Windows 7 and RouterOS.

Note: While connecting to SSTP server, Windows does CRL (certificate revocation list) checking on server certificate which can introduce significant delay to complete connection or even prevent user from accessing sstp server at all if Windows is unable to access CRL distribution point! Custom generated CA which does not include CRLs can be used to minimize connection delays and certificate costs (signed certificates with known CA usually are not for free), but this custom CA must be imported into each Windows client individually. It is possible to disable CRL check in Windows registry, but it is supported only by Windows Server 2008 http://support.microsoft.com/kb/947054
Certificates
To set up secure SSTP tunnel, certificates are required. On the server authentication is done only by username and password, but on the client - server is authenticated using server certificate. It is also used by client to cryptographicly bind SSL and PPP authentication, meaning - the clients sends a special value over SSTP connection to server, this value is derived from the key data that is generated during PPP authentication and server certificate, this allows server to check if both channels are secure.
If sstp clients are Windows PCs then only way to set up secure SSTP tunnel when using self-signed certificate is by importing "server" certificate on SSTP server and on windows PC add CA certificate in trusted root.

Note: If your server certificate is issued by CA which is known by Windows, then Windows client will work witout any additional certificates.
Similar configuration on RouterOS client would be, importing CA certificate and enabling verify-server-certificate option. In this scenario Man-in-the-Middle attacks are not possible.
Between two Mikrotik routers it is also possible to set up insecure tunnel by not using certificates at all. In this case data going through SSTP tunnel is using anonymous DH and Man-in-the-Middle attacks are easily accomplished. This scenario is not compatible with Windows clients.
It is also possible to make secure SSTP tunnel by adding additional authorization with client certificate. Configuration requirements are:
- certificates on both server and client
- verification options enabled on server and client
This scenario is also not possible with Windows clients, because there is no way to set up client certificate on Windows.
Certificate error messages
When ssl handshake fails, you will see one of the following certificate errors:
- certificate is not yet valid - notBefore date is after the current time.
- certificate has expired - notAfter date is before the current time.
- invalid certificate purpose - the supplied certificate cannot be used for the specified purpose.
- self signed certificate in chain - the certificate chain could be built up using the untrusted certificates but the root could not be found locally.
- unable to get issuer certificate locally - CA certificate is not imported locally.
- server's IP address does not match certificate - server address verification is enabled, but address provided in certificate does not match servers address.
Hostname verification
Starting from v5.6 when server ceritificate verification is enabled on sstp client, additionally IP addresses found in certificate's subjectAltName and then issuer CN will be compared to the real address. DNS names are ignored. v5.7 adds new parameter verify-server-address-from-certificate to disable/enable hostname verification.
SSTP Client
Sub-menu: /interface sstp-client
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| add-default-route (yes | no; Default: no) | Whether to add SSTP remote address as a default route. |
| authentication (mschap2 | mschap1 | chap | pap; Default: mschap2, mschap1, chap, pap) | Allowed authentication methods. |
| certificate (string | none; Default: none) | |
| comment (string; Default: ) | Descriptive name of an item |
| connect-to (IP:Port; Default: 0.0.0.0:443) | Remote address and port of SSTP server. |
| dial-on-demand (yes | no; Default: no) | |
| disabled (yes | no; Default: yes) | Whether interface is disabled or not. By default it is disabled. |
| keepalive-timeout (integer | disabled; Default: 60) | |
| max-mru (integer; Default: 1500) | Maximum Receive Unit. Max packet size that SSTP interface will be able to receive without packet fragmentation. |
| max-mtu (integer; Default: 1500) | Maximum Transmission Unit. Max packet size that SSTP interface will be able to send without packet fragmentation. |
| mrru (disabled | integer; Default: disabled) | Maximum packet size that can be received on the link. If a packet is bigger than tunnel MTU, it will be split into multiple packets, allowing full size IP or Ethernet packets to be sent over the tunnel. Read more >> |
| name (string; Default: ) | Descriptive name of the interface. |
| password (string; Default: "") | Password used for authentication. |
| profile (name; Default: default-encryption) | Used PPP profile. |
| proxy (IP:Port; Default: 0.0.0.0:443) | Address and port of HTTP proxy server. |
| user (string; Default: ) | User name used for authentication. |
| verify-server-certificate (yes | no; Default: no) | If set to yes, then client checks whether certificate belongs to the same certificate chain as server's certificate. To make it work CA certificate must be imported. |
| verify-server-address-from-certificate (yes | no; Default: yes) | If set to yes, server's IP address will be compared to one set in certificate. Read More >> |
Quick example
This example demonstrates how to set up SSTP client with username "sstp-test", password "123" and server 10.1.101.1
[admin@MikroTik] /interface sstp-client>add user=sstp-test password=123 \
\... connect-to=10.1.101.1 disabled=no
[admin@MikroTik] /interface sstp-client> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 R name="sstp-out1" max-mtu=1500 max-mru=1500 mrru=disabled connect-to=10.1.101.1:443
user="sstp-test" password="123" proxy=0.0.0.0:443 profile=default
certificate=none keepalive-timeout=60 add-default-route=no dial-on-demand=no
authentication=pap,chap,mschap1,mschap2
SSTP Server
Sub-menu: /interface sstp-server
This sub-menu shows interfaces for each connected SSTP clients.
An interface is created for each tunnel established to the given server. There are two types of interfaces in PPTP server's configuration
- Static interfaces are added administratively if there is a need to reference the particular interface name (in firewall rules or elsewhere) created for the particular user.
- Dynamic interfaces are added to this list automatically whenever a user is connected and its username does not match any existing static entry (or in case the entry is active already, as there can not be two separate tunnel interfaces referenced by the same name).
Dynamic interfaces appear when a user connects and disappear once the user disconnects, so it is impossible to reference the tunnel created for that use in router configuration (for example, in firewall), so if you need a persistent rules for that user, create a static entry for him/her. Otherwise it is safe to use dynamic configuration.

Note: in both cases PPP users must be configured properly - static entries do not replace PPP configuration.
Server configuration
Sub-menu: /interface sstp-server server
Properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| authentication (pap | chap | mschap1 | mschap2; Default: pap,chap,mschap1,mschap2) | Authentication methods that server will accept. |
| certificate (name | none; Default: none) | Name of the certificate that SSTP server will use. |
| default-profile (name; Default: default) | |
| enabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Defines whether SSTP server is enabled or not. |
| keepalive-timeout (integer | disabled; Default: 60) | Defines the time period (in seconds) after which the router is starting to send keepalive packets every second. If no traffic and no keepalive responses has came for that period of time (i.e. 2 * keepalive-timeout), not responding client is proclaimed disconnected |
| max-mru (integer; Default: 1500) | Maximum Receive Unit. Max packet size that SSTP interface will be able to receive without packet fragmentation. |
| max-mtu (integer; Default: 1500) | Maximum Transmission Unit. Max packet size that SSTP interface will be able to send without packet fragmentation. |
| mrru (disabled | integer; Default: disabled) | Maximum packet size that can be received on the link. If a packet is bigger than tunnel MTU, it will be split into multiple packets, allowing full size IP or Ethernet packets to be sent over the tunnel. Read more >> |
| verify-client-certificate (yes | no; Default: no) | If set to yes, then server checks whether client's certificate belongs to the same certificate chain. |
[admin@MikroTik] /interface sstp-server server> set certificate=server
[admin@MikroTik] /interface sstp-server server> set enabled=yes
[admin@MikroTik] /interface sstp-server server> print
enabled: yes
port: 443
max-mtu: 1500
max-mru: 1500
mrru: disabled
keepalive-timeout: 60
default-profile: default
certificate: server
verify-client-certificate: no
authentication: pap,chap,mschap1,mschap2
[admin@MikroTik] /interface sstp-server server>

Warning: It is very important that date on the router is in the range of certificate's date of expiration . To overcome any certificate verification problems, enable NTP date synchronization on both server and client.
Monitoring
Monitor command can be used to monitor status of the tunnel on both client and server.
[admin@dzeltenais_burkaans] /interface sstp-server> monitor 0
status: "connected"
uptime: 17m47s
idle-time: 17m47s
user: "sstp-test"
caller-id: "10.1.101.18:43886"
mtu: 1500
Read-only properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| status () | Current SSTP status. Value other than "connected" indicates that there are some problems estabising tunnel. |
| uptime (time) | Elapsed time since tunnel was established. |
| idle-time (time) | Elapsed time since last activity on the tunnel. |
| user (string) | Username used to establish the tunnel. |
| mtu (integer) | Negotiated and used MTU |
| caller-id (IP:ID) |
Application Examples
Connecting Remote Client
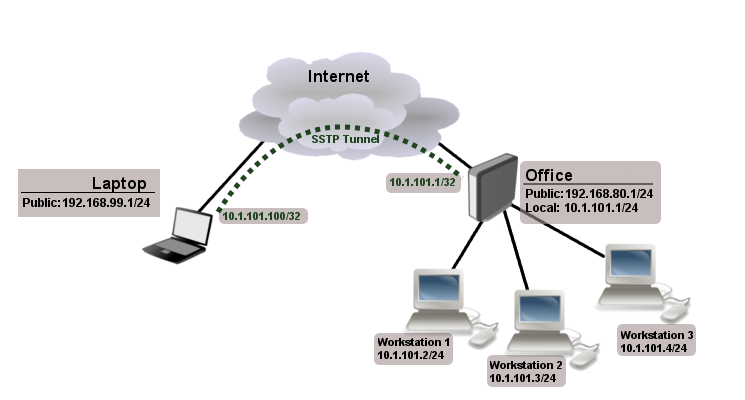
The following example shows how to connect a computer to a remote office network over secure SSTP encrypted tunnel giving that computer an IP address from the same network as the remote office has (without need of bridging over EoIP tunnels)
Consider following setup
Office router is connected to internet through ether1. Workstations are connected to ether2. Laptop is connected to the internet and can reach Office router's public IP (in our example it is 192.168.80.1).
Before you begin to configure SSTP you need to create server certificate and import it to router instructions here.
Now it is time to create a user
[admin@RemoteOffice] /ppp secret> add name=Laptop service=sstp password=123
local-address=10.1.101.1 remote-address=10.1.101.100
[admin@RemoteOffice] /ppp secret> print detail
Flags: X - disabled
0 name="Laptop" service=sstp caller-id="" password="123" profile=default
local-address=10.1.101.1 remote-address=10.1.101.100 routes==""
[admin@RemoteOffice] /ppp secret>
Notice that SSTP local address is the same as routers address on local interface and remote address is form the same range as local network (10.1.101.0/24).
Next step is to enable sstp server and sstp client on the laptop.
[admin@RemoteOffice] /interface sstp-server server> set certificate=server
[admin@RemoteOffice] /interface sstp-server server> set enabled=yes
[admin@RemoteOffice] /interface sstp-server server> set authentication=mschap2
[admin@RemoteOffice] /interface sstp-server server> print
enabled: yes
port: 443
max-mtu: 1500
max-mru: 1500
mrru: disabled
keepalive-timeout: 60
default-profile: default
certificate: server
verify-client-certificate: no
authentication: mschap2
[admin@RemoteOffice] /interface sstp-server server>
Notice that authentication is set to mschap. These are the only authentication options that are valid to establish secure tunnel.
SSTP client from the laptop should connect to routers public IP which in our example is 192.168.80.1.
Please, consult the respective manual on how to set up a SSTP client with the software You are using. If you set up SSTP client on Windows and self-signed certificates are used, then CA certificate should be added to trusted root.

Note: Currently SSTP is supported on Windows 2008, Windows Vista and Vista SP1. Other OS will not be able to connect to SSTP server
To verify if sstp client is connected
[admin@RemoteOffice] /interface sstp-server> print
Flags: X - disabled, D - dynamic, R - running
# NAME USER MTU CLIENT-ADDRESS UPTIME ENCODING
0 DR <sstp-... Laptop 1500 10.1.101.18:43886 1h47s
[admin@RemoteOffice] /interface sstp-server>monitor 0
status: "connected"
uptime: 1h45s
idle-time: 1h45s
user: "Laptop"
caller-id: "192.168.99.1:43886"
mtu: 1500
At this point (when SSTP client is successfully connected) if you will try to ping any workstation form the laptop, ping will time out, because Laptop is unable to get ARPs from workstations. Solution is to set up proxy-arp on local interface
[admin@RemoteOffice] /interface ethernet> set ether2 arp=proxy-arp [admin@RemoteOffice] /interface ethernet> print Flags: X - disabled, R - running # NAME MTU MAC-ADDRESS ARP 0 R ether1 1500 00:30:4F:0B:7B:C1 enabled 1 R ether2 1500 00:30:4F:06:62:12 proxy-arp [admin@RemoteOffice] interface ethernet>
After proxy-arp is enabled client can successfully reach all workstations in local network behind the router.
Site-to-Site SSTP
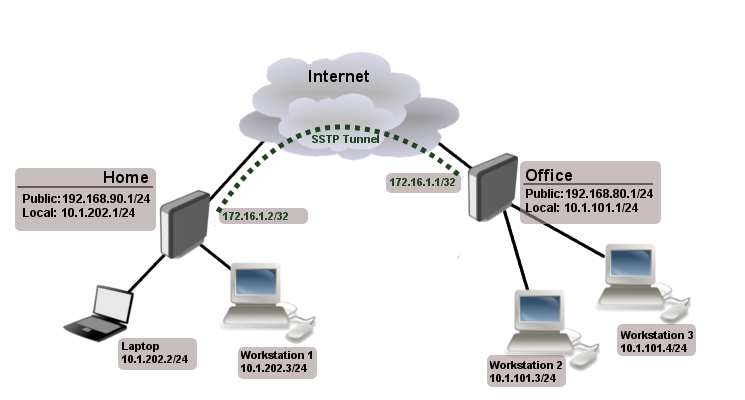
The following is an example of connecting two Intranets using SSTP tunnel over the Internet.
Consider following setup
Office and Home routers are connected to internet through ether1, workstations and laptops are connected to ether2. In this example both local networks are routed through sstp client, thus they are not in the same broadcast domain. To overcome this problem as any other ppp tunnel SSTP also supports BCP which allows to bridge SSTP tunnel with local interface.
First step is to create a user
[admin@RemoteOffice] /ppp secret> add name=Home service=sstp password=123
local-address=172.16.1.1 remote-address=172.16.1.2 routes="10.1.202.0/24 172.16.1.2 1"
[admin@RemoteOffice] ppp secret> print detail
Flags: X - disabled
0 name="Home" service=sstp caller-id="" password="123" profile=default
local-address=172.16.1.1 remote-address=172.16.1.2 routes=="10.1.101.0/24 172.16.1.1 1"
[admin@RemoteOffice] /ppp secret>
Notice that we set up SSTP to add route whenever client connects. If this option is not set, then you will need static routing configuration on the server to route traffic between sites through SSTP tunnel.
Now we need to upload and import CA and server/client certificates. Assume that files are already uploaded use following commands:
admin@RemoteOffice] /certificate> import file-name=ca.crt passphrase: admin@RemoteOffice] /certificate> import file-name=server.crt passphrase: **** admin@RemoteOffice] /certificate> import file-name=server.key passphrase: ****
Set up proper names:
admin@RemoteOffice] /certificate>set 0 name=CA
admin@RemoteOffice] /certificate>set 1 name=server
admin@RemoteOffice] /certificate> print
Flags: K - decrypted-private-key, Q - private-key, R - rsa, D - dsa
0 D name="CA" subject=C=LV,ST=RI,L=Riga,O=MT,CN=MT CA,emailAddress=xx@mt.lv
issuer=C=LV,ST=RI,L=Riga,O=MT,CN=MT CA,emailAddress=xx@mt.lv
serial-number="DF626FA846090BCC" email=xx@mt.lv invalid-before=jun/25/2008 07:23:50
invalid-after=jun/23/2018 07:23:50 ca=yes
1 KR name="server" subject=C=LV,ST=RI,L=Riga,O=MT,CN=server,emailAddress=xx@mt.lv
issuer=C=LV,ST=RI,L=Riga,O=MT,CN=MT CA,emailAddress=xx@mt.lv serial-number="01"
email=xx@mt.lv invalid-before=jun/25/2008 07:24:33 invalid-after=jun/23/2018 07:24:33
ca=yes
Do the same on client side, but instead of server's certificate import client's certificate.
Next step is to enable SSTP server on the office router and configure SSTP client on the Home router.
[admin@RemoteOffice] /interface sstp-server server> set certificate=server
[admin@RemoteOffice] /interface sstp-server server> set enabled=yes
[admin@RemoteOffice] /interface sstp-server server> set verify-client-certificate=yes
[admin@RemoteOffice] /interface sstp-server server> print
enabled: yes
port: 443
max-mtu: 1500
max-mru: 1500
mrru: disabled
keepalive-timeout: 60
default-profile: default
certificate: server
verify-client-certificate: yes
authentication: pap,chap,mschap1,mschap2
[admin@Home] /interface sstp-client> add user=Home password=123 connect-to=192.168.80.1 disabled=no
certificate=client verify-server-certificate=yes
[admin@Home] /interface sstp-client> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 R name="sstp-out1" max-mtu=1500 max-mru=1500 mrru=disabled connect-to=192.168.80.1:443
user="Home" password="123" proxy=0.0.0.0:443 profile=default certificate=client
keepalive-timeout=60 add-default-route=no dial-on-demand=no
authentication=pap,chap,mschap1,mschap2 verify-server-certificate=yes
[admin@Home] /interface sstp-client>
Now we need to add static route on Home router to reach local network behind Office router
[admin@Home] /ip route> add dst-address=10.1.101.0/24 gateway=172.16.1.1
After tunnel is established you should be able to ping remote network.
Troubleshooting
- After Windows 7 upgrade SSTP is unable to connect (windows error 631) ?
- MS Patch KB2585542 changes cypher to RC4 which was not supported on RouterOS. Starting from v5.13. From now on RC4 is the preferred cipher and AES will be used only if peer does not advertise RC4.
Read More
- Creating Certificates
- BCP (Bridge Control Protocol)
- http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731352(WS.10).aspx
- Free trusted Class1 certificates online
[ Top | Back to Content ]