Manual:CRS1xx/2xx series switches
Summary
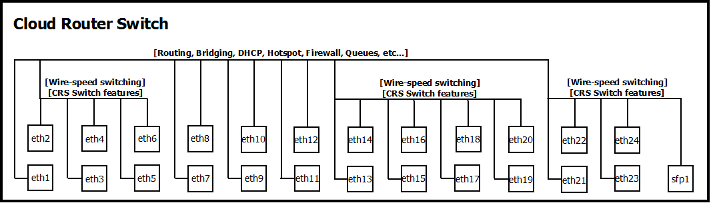
The Cloud Router Switch series are highly integrated switches with high performance MIPS CPU and feature-rich packet processor. The CRS switches can be designed into various Ethernet applications including unmanaged switch, Layer 2 managed switch, carrier switch and wireless/wired unified packet processing.
Abbreviations and Explanations
CVID - Customer VLAN id: inner VLAN tag id of the IEEE 802.1ad frame
SVID - Service VLAN id: outer VLAN tag id of the IEEE 802.1ad frame
IVL - Independent VLAN learning - learning/lookup is based on both MAC addresses and VLAN IDs.
SVL - Shared VLAN learning - learning/lookup is based on MAC addresses - not on VLAN IDs.
TPID - Tag Protocol Identifier
PCP - Priority Code Point: a 3-bit field which refers to the IEEE 802.1p priority
DEI - Drop Eligible Indicator
DSCP - Differentiated services Code Point
Drop precedence - internal CRS switch QoS attribute used for packet enqueuing or dropping.
Port Switching
Similarly to other RouterBoards, port switching on CRS allows wire-speed traffic forwarding among a group of ports, like the ports were a regular Ethernet switch. This feature is configurable by setting a "master-port" property to one or more ports in /interface ethernet menu. The "master-port" will be the port through which the RouterOS will communicate to all ports in the group. Interfaces which have the "master-port" specified become isolated - no traffic can be received and no traffic can be sent out directly from RouterOS.
Here is a general diagram of RouterBoard with a five port switch chip:

A packet that is received by one of the ports always passes through the switch logic first. Switch logic decides to which ports the packet should be going to. Passing packet "up" or giving it to RouterOS is also called sending it to switch chip's “CPU” port. It means at that point switch forwards the packet to CPU port the packet starts to get processed by RouterOS as incoming packet of the “master-port”. If the packet does not have to go to “CPU” port, it is handled entirely by switch logic, does not require any CPU resources and happen at wire-speed.
Additionally, CRS series switches support multiple “master-port” configurations and have no port selection limitations for a port group which makes possible many various switched port combinations with all CRS switch interfaces.
For example, consider a CRS125 switch with 24 Ethernet interfaces and 1 SFP interface:
[admin@MikroTik] > interface ethernet print Flags: X - disabled, R - running, S - slave # NAME MTU MAC-ADDRESS ARP MASTER-PORT SWITCH 0 R ether1 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:2F enabled none switch1 1 ether2 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:30 enabled none switch1 2 ether3 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:31 enabled none switch1 3 ether4 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:32 enabled none switch1 4 R ether5 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:33 enabled none switch1 5 R ether6 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:34 enabled none switch1 6 ether7 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:35 enabled none switch1 7 ether8 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:36 enabled none switch1 ... 22 ether23 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:45 enabled none switch1 23 R ether24 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:46 enabled none switch1 24 sfp1 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:47 enabled none switch1
And there are configured 3 switch groups: 1) ether2, ether3, ether4, ether5, ether6; 2) ether13, ether14, ether15, ether16, ether17, ether18, ether19, ether20; 3) ether21, ether22, ether23, ether24, sfp1.
Ports ether1, ether7-ether12 are not switched in this example, they remain as independent router ports.
[admin@MikroTik] /interface ethernet> set ether3,ether4,ether5,ether6 master-port=ether2 [admin@MikroTik] /interface ethernet> set ether14,ether15,ether16,ether17,ether18,ether19,ether20 master-port=ether13 [admin@MikroTik] /interface ethernet> set ether22,ether23,ether24,sfp1 master-port=ether21 [admin@MikroTik] /interface ethernet> print Flags: X - disabled, R - running, S - slave # NAME MTU MAC-ADDRESS ARP MASTER-PORT SWITCH 0 R ether1 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:2F enabled none switch1 1 R ether2 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:30 enabled none switch1 2 S ether3 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:31 enabled ether2 switch1 3 S ether4 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:32 enabled ether2 switch1 4 RS ether5 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:33 enabled ether2 switch1 5 RS ether6 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:34 enabled ether2 switch1 6 ether7 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:35 enabled none switch1 7 ether8 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:36 enabled none switch1 8 ether9 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:37 enabled none switch1 9 ether10 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:38 enabled none switch1 10 ether11 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:39 enabled none switch1 11 ether12 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:3A enabled none switch1 12 R ether13 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:3B enabled none switch1 13 S ether14 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:3C enabled ether13 switch1 14 S ether15 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:3D enabled ether13 switch1 15 RS ether16 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:3E enabled ether13 switch1 16 S ether17 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:3F enabled ether13 switch1 17 S ether18 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:40 enabled ether13 switch1 18 S ether19 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:41 enabled ether13 switch1 19 S ether20 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:42 enabled ether13 switch1 20 R ether21 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:43 enabled none switch1 21 S ether22 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:44 enabled ether21 switch1 22 S ether23 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:45 enabled ether21 switch1 23 RS ether24 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:46 enabled ether21 switch1 24 S sfp1 1500 D4:CA:6D:F9:FE:47 enabled ether21 switch1
Now ether2 is the “master-port” of the group 1, ether13 – of the group 2 and ether21 – of the group 3.
Note: Previously a link was detected only on interfaces with a physical connection, but now since the ether2, ether13 and ether21 have connection to CPU, the running flag is propagated to them, as well.
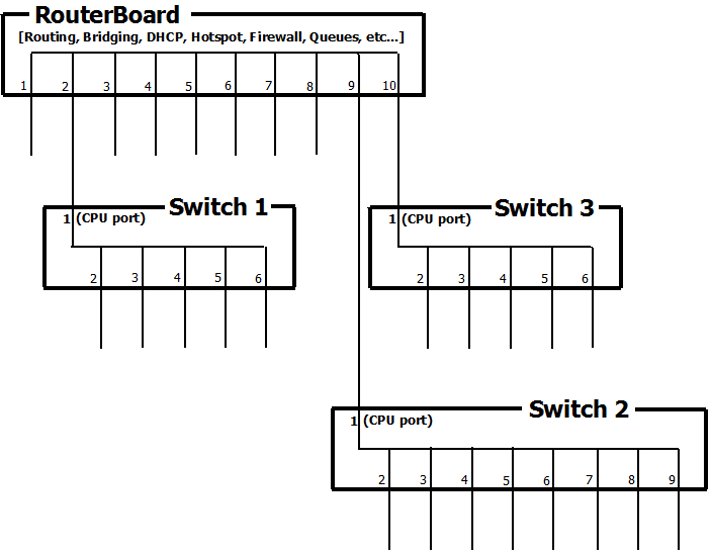
In essence this configuration is the same as if you had a RouterBoard with 10 Ethernet interfaces and 3 switches:
Global Switch Configuration
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
CRS switch chip is configurable from the /interface ethernet switch
console menu.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| bridge-type (customer-vid-used-as-lookup-vid | service-vid-used-as-lookup-vid; Default: customer-vid-used-as-lookup-vid) | Bridge type defines which VLAN tag is used as Lookup-VID. Lookup-VID serves as the VLAN key for all VLAN-based lookup. |
| bypass-ingress-port-policing-for (protocols; Default: none) | Protocols which are excluded from Ingress Port Policing. (arp, dhcpv4, dhcpv6, eapol, igmp, mld, nd, pppoe-discovery, ripv1) |
| bypass-l2-security-check-filter-for (protocols; Default: none) | Protocols which are excluded from Policy rule security check. (arp, dhcpv4, dhcpv6, eapol, igmp, mld, nd, pppoe-discovery, ripv1) |
| bypass-vlan-ingress-filter-for (protocols; Default: none) | Protocols which are excluded from Ingress VLAN filtering. These
protocols are not dropped if they have invalid VLAN. (arp, dhcpv4, dhcpv6, eapol, igmp, mld, nd, pppoe-discovery, ripv1) |
| drop-if-invalid-or-src-port- -not-member-of-vlan-on-ports (ports; Default: none) |
Ports which drop invalid and other port VLAN id frames. |
| drop-if-no-vlan-assignment-on-ports (ports; Default: none) | Ports which drop frames if no MAC-based, Protocol-based VLAN assignment or Ingress VLAN Translation is applied. |
| egress-mirror-ratio (1/32768..1/1; Default: 1/1) | Proportion of egress mirrored packets compared to all packets. |
| egress-mirror0 (port | trunk,format; Default: none,modified) | The first egress mirroring analyzer port or trunk and mirroring format:
|
| egress-mirror1 (port | trunk,format; Default: none,modified) | The second egress mirroring analyzer port or trunk and mirroring format:
|
| fdb-uses (mirror0 | mirror1; Default: mirror0) | Analyzer port used for FDB-based mirroring. |
| forward-unknown-vlan (yes | no; Default: yes) | Whether to allow forwarding VLANs which are not members of VLAN table. |
| ingress-mirror-ratio (1/32768..1/1; Default: 1/1) | Proportion of ingress mirrored packets compared to all packets. |
| ingress-mirror0 (port | trunk,format; Default: none,modified) | The first ingress mirroring analyzer port or trunk and mirroring format:
|
| ingress-mirror1 (port | trunk,format; Default: none,modified) | The second ingress mirroring analyzer port or trunk and mirroring format:
|
| mac-level-isolation (yes | no; Default: yes) | Enables or disables MAC level isolation. |
| mirror-egress-if-ingress-mirrored (yes | no; Default: no) | When packet is applied to both ingress and egress mirroring, if this
setting is disabled, only ingress mirroring is performed on the packet; if this setting is enabled both mirroring types are applied. |
| mirror-tx-on-mirror-port (yes | no; Default: no) | |
| mirrored-packet-drop-precedence (drop | green | red | yellow; Default: green) | Remarked drop precedence in mirrored packets. This QoS attribute is used for mirrored packet enqueuing or dropping. |
| mirrored-packet-qos-priority (0..7; Default: 0) | Remarked priority in mirrored packets. |
| multicast-lookup-mode
(dst-ip-and-vid-for-ipv4 | dst-mac-and-vid-always; Default: dst-ip-and-vid-for-ipv4) |
Lookup mode for IPv4 multicast bridging.
|
| name (string value; Default: switch1) | Name of the switch. |
| override-existing-when-ufdb-full (yes | no; Default: no) | Enable or disable to override existing entry which has the lowest aging value when UFDB is full. |
| unicast-fdb-timeout (time interval; Default: 5m) | Timeout for Unicast FDB entries. |
| unknown-vlan-lookup-mode (ivl | svl; Default: svl) | Lookup and learning mode for packets with invalid VLAN. |
| use-cvid-in-one2one-vlan-lookup (yes | no; Default: yes) | Whether to use customer VLAN id for 1:1 VLAN switching lookup. |
| use-svid-in-one2one-vlan-lookup (yes | no; Default: no) | Whether to use service VLAN id for 1:1 VLAN switching lookup. |
| vlan-uses (mirror0 | mirror1; Default: mirror0) | Analyzer port used for VLAN-based mirroring. |
Port Configuration
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
port
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| action-on-restricted-unknown-sa (copy-to-cpu | drop | forward | redirect-to-cpu; Default: forward) | Forwarding action for packets with restricted unknown source MAC address. |
| action-on-static-station-move (copy-to-cpu | drop | forward | redirect-to-cpu; Default: forward) | Forwarding action for packets with normal static station move. |
| allow-multicast-loopback (yes | no; Default: no) | Multicast loopback on port. When enabled, it permits sending back when
source port and destination port are the same for registered multicast or broadcast packets. |
| allow-unicast-loopback (yes | no; Default: no) | Unicast loopback on port. When enabled, it permits sending back when
source port and destination port are the same one for known unicast packets. |
| default-customer-pcp (0..7; Default: 0) | Default customer priority of the port. |
| default-service-pcp (0..7; Default: 0) | Default service priority of the port. |
| drop-counter-config (; Default: none) | |
| drop-when-ufdb-entry-sa-drop (yes | no; Default: no) | Enable or disable to drop packets when UFDB entry has action "src-drop". |
| dynamic-mac-move-is-restricted-unknown-sa (yes | no; Default: no) | |
| egress-customer-tpid (0..10000; Default: 0x8100) | |
| egress-mirror-to (mirror0 | mirror1; Default: mirror0) | Analyzer port for port-based egress mirroring. |
| egress-mirroring (yes | no; Default: no) | Enable or disable egress mirroring on the port. |
| egress-pcp-propagation (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables egress PCP propagation.
|
| egress-sampling (yes | no; Default: no) | |
| egress-service-tpid (0..10000; Default: 0x88A8) | |
| egress-vlan-lookup (according-to-bridge-type |
according-to-egress-vlan-type; Default: according-to-egress-vlan-type) |
Egress VLAN table (VLAN Tagging) lookup:
|
| egress-vlan-mode (tagged | unmodified | untagged; Default: unmodified) | Egress VLAN tagging action on the port. |
| egress-vlan-type (edge-port | network-port; Default: edge-port) | Port type for Egress VLAN lookup. |
| filter-priority-tagged-frame (yes | no; Default: no) | Whether to filter tagged frames with priority on the port. |
| filter-tagged-frame (yes | no; Default: no) | Whether to filter tagged frames on the port. |
| filter-untagged-frame (yes | no; Default: no) | Whether to filter untagged frames on the port. |
| ingress-customer-tpid (0..10000; Default: 0x8100) | |
| ingress-mirror-to (mirror0 | mirror1; Default: mirror0) | Analyzer port for port-based ingress mirroring. |
| ingress-mirroring (yes | no; Default: no) | Enable or disable ingress mirroring on the port. |
| ingress-mirroring-according-to-vlan (yes | no; Default: no) | |
| ingress-sampling (yes | no; Default: no) | |
| ingress-sampling-mode
(all-frames-excluding-filtered | all-frames-without-mac-error; Default: all-frames-without-mac-error) |
|
| ingress-sampling-ratio (1/32768..1/1; Default: 1/1) | |
| ingress-service-tpid (0..10000; Default: 0x88A8) | |
| ingress-vlan-type (edge-port | network-port; Default: edge-port) | |
| isolation-profile (0..31; Default: 30) |
|
| learn (yes | no; Default: ) | Enable or disable MAC address learning on the port. |
| learn-limit (1..1023; Default: ) | Number of allowed MAC address limit of the port. |
| learn-restricted-unknown-sa (yes | no; Default: yes) | Enable to learn restricted unknown source MAC. Source MAC is classified
as Restricted Unknown if any one of the following conditions are met:
|
| mac-based-customer-vlan-for (all-frames | none |
tagged-frame-only | untagged-and-priority-tagged-frame-only; Default: none) |
Frame type for which applies MAC-based customer VLAN translation. |
| mac-based-service-vlan-for (all-frames | none |
tagged-frame-only | untagged-and-priority-tagged-frame-only; Default: none) |
Frame type for which applies MAC-based service VLAN translation. |
| mac-based-vlan-translate (yes | no; Default: no) | Enable or disable MAC-based VLAN translation on the port. |
| mac-vlan-type (edge-port | network-port; Default: edge-port) | Port type for MAC based VLAN translation. |
| pcp-propagation-for-initial-pcp (yes | no; Default: no) | |
| per-queue-scheduling (strict-priority | wrr-group0 | wrr-group1; Default: ) | |
| priority-to-queue (; Default: 0-15:0,1:1,2:2,3:3) | |
| qos-change-dei (yes | no; Default: no) | Whether to change DEI on the port. |
| qos-change-dscp (yes | no; Default: no) | Whether to change DSCP on the port. |
| qos-change-pcp (yes | no; Default: no) | Whether to change PCP on the port. |
| qos-dscp-to-dscp-mapping (yes | no; Default: no) | Enable or disable DSCP mapping on the port. |
| qos-pcp-dei-map-dei (; Default: 0-15:0) | |
| qos-pcp-dei-map-drop-precedence (; Default: 0-15:green) | |
| qos-pcp-dei-map-dscp (; Default: 0-15:0) | |
| qos-pcp-dei-map-pcp (; Default: 0-15:0) | |
| qos-pcp-dei-map-priority (yes | no; Default: 0-15:0) | |
| qos-scheme-precedence (da-based | dscp-based |
pcp-based | protocol-based | sa-based | vlan-based; Default: pcp-based) |
|
| secure-static-mac-move-is-restricted-unknown-sa (yes | no; Default: no) |
Ingress/Egress VLAN Translation
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
ingress-vlan-translation
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
egress-vlan-translation
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| customer-dei (0..1; Default: none) | Matching DEI of the customer tag. |
| customer-pcp (0..7; Default: none) | Matching PCP of the customer tag. |
| customer-vid (0..4095; Default: none) | Matching VLAN id of the customer tag. |
| customer-vlan-format (any | priority-tagged-or-tagged | tagged | untagged-or-tagged; Default:any) | Type of frames with customer tag for which VLAN translation rule is valid. |
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables VLAN translation entry. |
| new-customer-vid (0..4095; Default: none) | The new customer VLAN id which replaces matching customer VLAN id. |
| new-service-vid (0..4095; Default: none) | The new service VLAN id which replaces matching service VLAN id. |
| pcp-propagation (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables PCP propagation.
|
| ports (ports) | Matching switch ports for VLAN translation rule. |
| protocol (protocols; Default: none) | Matching Ethernet protocol. (only for Ingress VLAN Translation) |
| sa-learning (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables source MAC learning after VLAN translation. (only for Ingress VLAN Translation) |
| service-dei (0..1; Default: none) | Matching DEI of the service tag. |
| service-pcp (0..7; Default: none) | Matching PCP of the service tag. |
| service-vid (0..4095; Default: none) | Matching VLAN id of the service tag. |
| service-vlan-format (any | priority-tagged-or-tagged | tagged | untagged-or-tagged; Default:any) | Type of frames with service tag for which VLAN translation rule is valid. |
Protocol Based VLAN
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
protocol-based-vlan
Protocol Based VLAN table is used to assign VID and QoS attributes to related protocol packet per port.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables Protocol Based VLAN entry. |
| frame-type (ethernet | llc | rfc-1042; Default: ethernet) | Encapsulation type of the matching frames. |
| new-customer-vid (0..4095; Default: 0) | The new customer VLAN id which replaces original customer VLAN id for specified protocol. |
| new-service-vid (0..4095; Default: 0) | The new service VLAN id which replaces original service VLAN id for specified protocol. |
| ports (ports) | Matching switch ports for Protocol based VLAN rule. |
| protocol (protocol; Default: 0) | Matching protocol for Protocol based VLAN rule. |
| qos-group (none; Default: none) | Defined QoS group from QoS group menu. |
| set-customer-vid-for (all | none | tagged | untagged-or-priority-tagged; Default: all) | Customer VLAN id assignment command for different packet type. |
| set-qos-for (all | none | tagged | untagged-or-priority-tagged; Default: none) | Frame type for which QoS assignment command applies. |
| set-service-vid-for (all | none | tagged | untagged-or-priority-tagged; Default: all) | Service VLAN id assignment command for different packet type. |
MAC Based VLAN
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
mac-based-vlan
MAC Based VLAN table is used to assign VLAN based on source MAC.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables MAC Based VLAN entry. |
| new-customer-vid (0..4095; Default: 0) | The new customer VLAN id which replaces original service VLAN id for matched packets. |
| new-service-vid (0..4095; Default: 0) | The new service VLAN id which replaces original service VLAN id for matched packets. |
| src-mac-address (MAC address) | Matching source MAC address for MAC based VLAN rule. |
VLAN Table
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
vlan
The VLAN table supports 4096 VLAN entries for storing VLAN member information as well as other VLAN information such as QoS, isolation, forced VLAN, learning, and mirroring.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Indicate whether the VLAN entry is disabled. Only enabled entry is applied to lookup process and forwarding decision. |
| flood (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables forced VLAN flooding per VLAN. If the feature is
enabled, the result of destination MAC lookup in the UFDB or MFDB is ignored, and the packet is forced to flood in the VLAN. |
| ingress-mirror (yes | no; Default: no) | Enable the ingress mirror per VLAN to support the VLAN-based mirror function. |
| learn (yes | no; Default: yes) | Enables or disables source MAC learning for VLAN. |
| ports (ports) | Member ports of the VLAN. |
| qos-group (none; Default: none) | Defined QoS group from QoS group menu. |
| svl (yes | no; Default: no) | FDB lookup mode for lookup in UFDB and MFDB.
|
| vlan-id (0..4095) | VLAN id of the VLAN member entry. |
1:1 VLAN Switching
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
one2one-vlan-switching
1:1 VLAN switching can be used to replace the regular L2 bridging for matched packets. When a packet hits an 1:1 VLAN switching table entry, the destination port information in the entry is assigned to the packet. The matched destination information in UFDB and MFDB entry no longer applies to the packet.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| customer-vid (0..4095; Default: 0) | Matching customer VLAN id for 1:1 VLAN switching. |
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables 1:1 VLAN switching table entry. |
| dst-port (port) | Destination port for matched 1:1 VLAN switching packets. |
| service-vid (0..4095; Default: 0) | Matching customer VLAN id for 1:1 VLAN switching. |
Egress VLAN Tag
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
egress-vlan-tag
Egress packets can be assigned different VLAN tag format. The VLAN tags can be removed, added, or remained as is when the packet is sent to the egress port (destination port). Each port has dedicated control on the egress VLAN tag format. The tag formats include:
- Untagged
- Tagged
- Unmodified
The Egress VLAN Tag table includes 4096 entries for VLAN tagging selection.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables Egress VLAN Tag table entry. |
| tagged-ports (ports) | Ports which are tagged in egress. |
| vlan-id (0..4095) | VLAN id which is tagged in egress. |
Unicast FDB
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
unicast-fdb
The unicast forwarding database supports up to 16318 MAC entries.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| action (action; Default: forward) | Action for UFDB entry:
|
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables Unicast FDB entry. |
| isolation-profile (community1 | community2 | isolated | promiscuous; Default: promiscuous) | MAC level isolation profile. |
| mac-address (MAC address) | The action command applies to the packet when the destination MAC or source MAC matches the entry. |
| mirror (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables mirroring based on source MAC or destination MAC. |
| port (port) | Matching port for the Unicast FDB entry. |
| qos-group (none; Default: none) | Defined QoS group from QoS group menu. |
| svl (yes | no; Default: no) | Unicast FDB learning mode:
|
| vlan-id (0..4095) | Unicast FDB lookup/learning VLAN id. |
Multicast FDB
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
multicast-fdb
CRS125 switch-chip supports up to 1024 entries in MFDB for multicast forwarding. For each multicast packet, destination MAC or destination IP lookup is performed in MFDB. MFDB entries are not automatically learnt and can only be configured.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| address (X.X.X.X | XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX) | Matching IP address or MAC address for multicast packets. |
| bypass-vlan-filter (yes | no; Default: no) | Allow to bypass VLAN filtering for matching multicast packets. |
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables Multicast FDB entry. |
| ports (ports) | Member ports for multicast traffic. |
| qos-group (none; Default: none) | Defined QoS group from QoS group menu. |
| svl (yes | no; Default: no) | Multicast FDB learning mode:
|
| vlan-id (0..4095; Default: 0) | Multicast FDB lookup VLAN id. If VLAN learning mode is IVL, VLAN id is lookup id, otherwise VLAN id = 0. |
Reserved FDB
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
reserved-fdb
Cloud Router Switch supports 256 RFDB entries. Each RFDB entry can store either Layer2 unicast or multicast MAC address with specific commands.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| action (copy-to-cpu | drop | forward | redirect-to-cpu; Default: forward) | Action for RFDB entry:
|
| bypass-ingress-port-policing (yes | no; Default: no) | Allow to bypass Ingress Port Policer for matching packets. |
| bypass-ingress-vlan-filter (yes | no; Default: no) | Allow to bypass VLAN filtering for matching packets. |
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables Reserved FDB entry. |
| mac-address (MAC address; Default: 00:00:00:00:00:00) | Matching MAC address for Reserved FDB entry. |
| qos-group (none; Default: none) | Defined QoS group from QoS group menu. |
Port Isolation/Leakage
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
port-isolation
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
port-leakage
The CRS switches support flexible multi-level isolation features, which can be used for user access control, traffic engineering and advanced security and network management. The isolation features provide an organized fabric structure allowing user to easily program and control the access by port, MAC address, VLAN, protocol, flow and frame type. The following isolation and leakage features are supported:
- Port-level isolation
- MAC-level isolation
- VLAN-level isolation
- Protocol-level isolation
- Flow-level isolation
- Free combination of the above
Port-level isolation supports different control schemes on source port and destination port. Each entry can be programmed with access control for either source port or destination port.
- When the entry is programmed with source port access control, the entry is
applied to the ingress packets.
- When the entry is programmed with destination port access control, the entry
is applied to the egress packets.
Port leakage allows bypassing egress VLAN filtering on the port. Leaky port is allowed to access other ports for various applications such as security, network control and management. Note: When both isolation and leakage is applied to the same port, the port is isolated.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables port isolation/leakage entry. |
| flow-id (0..63; Default: none) | |
| forwarding-type (bridged; routed; Default: bridged,routed) | Matching traffic forwarding type on Cloud Router Switch. |
| mac-profile (community1 | community2 | isolated | promiscuous; Default: none) | Matching MAC isolation/leakage profile. |
| port-profile (0..31; Default: none) | Matching Port isolation/leakage profile. |
| ports (ports; Default: none) | Isolated/leaked ports. |
| protocol-type (arp; nd; dhcpv4; dhcpv6; ripv1; Default: arp,nd,dhcpv4,dhcpv6,ripv1) | Included protocols for isolation/leakage. |
| registration-status (known; unknown; Default: known,unknown) | Registration status for matching packets. Known are present in UFDB and MFDB, unknown are not. |
| traffic-type (unicast; multicast; broadcast; Default: unicast,multicast,broadcast) | Matching traffic type. |
| type (dst | src; Default: src) | Lookup type of the isolation/leakage entry:
|
| vlan-profile (community1 | community2 | isolated | promiscuous; Default: none) | Matching VLAN isolation/leakage profile. |
Shaper
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
shaper
Traffic shaping restricts the rate and burst size of the flow which is transmitted out from the interface. The shaper is implemented by a token bucket. If the packet exceeds the maximum rate or the burst size, which means no enough token for the packet, the packet is stored to buffer until there is enough token to transmit it.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| burst (integer; Default: 100k) | Maximum data rate which can be transmitted while the burst is allowed. |
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables traffic shaper entry. |
| meter-unit (bit | packet; Default: bit) | Measuring units for traffic shaper rate. |
| port (port) | Physical port for traffic shaper. |
| rate (integer; Default: 1M) | Maximum data rate limit. |
| target (port | queueX | wrr-groupX; Default: port) | Three levels of shapers are supported on each port (including CPU port):
|
QoS Group
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
qos-group
The global QoS group table is used for VLAN-based, Protocol-based and MAC-based QoS group assignment configuration.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| dei (0..1; Default: none) | The new value of DEI for the QoS group. |
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables protocol QoS group entry. |
| drop-precedence (drop | green | red | yellow; Default: green) | Drop precedence is internal QoS attribute used for packet enqueuing or dropping. |
| dscp (0..63; Default: none) | The new value of DSCP for the QoS group. |
| name (string value; Default: groupX) | Name of the QoS group. |
| pcp (0..7; Default: none) | The new value of PCP for the QoS group. |
| priority (0..15; Default: 0) | Internal priority is a local significance of priority for classifying traffics to different egress queues on a port. |
DSCP QoS Map
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
dscp-qos-map
The global DSCP to QOS mapping table is used for mapping from DSCP of the packet to new QoS attributes configured in the table.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| dei (0..1) | The new value of DEI for the DSCP to QOS mapping entry. |
| drop-precedence (drop | green | red | yellow) | The new value of Drop precedence for the DSCP to QOS mapping entry. |
| pcp (0..7) | The new value of PCP for the DSCP to QOS mapping entry. |
| priority (0..15) | The new value of internal priority for the DSCP to QOS mapping entry. |
DSCP To DSCP Map
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
dscp-to-dscp
The global DSCP to DSCP mapping table is used for mapping from the packet's original DSCP to new DSCP value configured in the table.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| new-dscp (0..63) | The new value of DSCP for the DSCP to DSCP mapping entry. |
Trunk
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
trunk
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Enables or disables port trunking entry. |
| member-ports (ports) | Member ports of the Trunk group. |
| name (string value; Default: trunkX) | Name of the Trunk group. |
[ Top | Back to Content ]
