Manual:Interface/Bonding
Summary
Bonding is a technology that allows to aggregate multiple ethernet-like interfaces into a single virtual link, thus getting higher data rates and providing failover.
Specifications
- Packages required: system
- License required: Level1
- Submenu level:
/interface bonding
- Standards and Technologies: None
- Hardware usage: Not significant
Quick Setup Guide
Let us assume that we have 2 NICs in each router (Router1 and Router2) and want to get maximum data rate between 2 routers. To make this possible, follow these steps:
- Make sure that you do not have IP addresses on interfaces which will be enslaved for bonding interface!
- Add bonding interface on Router1:
[admin@Router1] interface bonding> add slaves=ether1,ether2
And on Router2:
[admin@Router2] interface bonding> add slaves=ether1,ether2
Add addresses to bonding interfaces:
[admin@Router1] ip address> add address=172.16.0.1/24 interface=bonding1 [admin@Router2] ip address> add address=172.16.0.2/24 interface=bonding1
Test the link from Router1:
[admin@Router1] interface bonding> /pi 172.16.0.2 172.16.0.2 ping timeout 172.16.0.2 ping timeout 172.16.0.2 ping timeout 172.16.0.2 64 byte ping: ttl=64 time=2 ms 172.16.0.2 64 byte ping: ttl=64 time=2 ms
Note that bonding interface needs a couple of seconds to get connectivity with its peer.
Link monitoring
It is critical that one of available link monitoring options are enabled. In example above if one of the bonded links fail, bonding driver will still continue to send packets over failed link which will lead to network degradation. Currently bonding in RouterOS supports two schemes for monitoring a link state of slave devices: MII and ARP monitoring. It is not possible to use both methods at a time due to restrictions in the bonding driver.
ARP Monitoring
ARP monitoring sends ARP queries and uses the response as an indication that the link is operational. This also gives assurance that traffic is actually flowing over the links. If balance-rr and balance-xor modes are set, then the switch should be configured to evenly distribute packets across all links. Otherwise all replies from the ARP targets will be received on the same link which could cause other links to fail. ARP monitoring is enabled by setting three properties link-monitoring, arp-ip-targets and arp-interval. Meaning of each option is described later in this article. It is possible to specify multiple ARP targets that can be useful in a High Availability setups. If only one target is set, the target itself may go down. Having an additional targets increases the reliability of the ARP monitoring.
Enable ARP monitoring
[admin@Router1] interface bonding> set 0 link-monitoring=arp arp-ip-targets=172.16.0.2 [admin@Router2] interface bonding> set 0 link-monitoring=arp arp-ip-targets=172.16.0.1
We will not change arp-interval value in our example, RouterOS sets arp-interval to 100ms by default.
Unplug one of the cables to test if link monitoring works correctly, you will notice some ping timeouts until arp monitoring detects link failure.
[admin@Router1] interface bonding> /pi 172.16.0.2 172.16.0.2 ping timeout 172.16.0.2 64 byte ping: ttl=64 time=2 ms 172.16.0.2 ping timeout 172.16.0.2 64 byte ping: ttl=64 time=2 ms 172.16.0.2 ping timeout 172.16.0.2 64 byte ping: ttl=64 time=2 ms 172.16.0.2 64 byte ping: ttl=64 time=2 ms 172.16.0.2 64 byte ping: ttl=64 time=2 ms
MII monitoring
MII monitoring monitors only the state of the local interface. In RouterOS it is possible to configure MII monitoring in two ways:
- MII Type 1 - device driver determines whether link is up or down. If device driver does not support this option then link will appear as always up.
- MII Type 2 - deprecated calling sequences within the kernel are used to determine if link is up. This method is less efficient but can be used on all devices. This mode should be set only if MII type 1 is not supported.
Main disadvantage is that MII monitoring can't tell if the link actually can pass the packets or not even if the link is detected as up.
MII monitoring is configured setting desired link-monitoring mode and mii-interval.
Enable MII Type2 monitoring:
[admin@Router1] interface bonding> set 0 link-monitoring=mii-type-2 [admin@Router2] interface bonding> set 0 link-monitoring=mii-type-2
We will leave mii-interval to it's default value (100ms)
When unplugging one of the cables, notice that failure was detected almost instantly compared to ARP link monitoring.
Bonding modes
802.3ad
802.3ad mode is an IEEE standard. It includes automatic configuration of the aggregates, so minimal configuration of the switch is needed. This standard also mandates that frames will be delivered in order and connections should not see mis-ordering of packets. Also standard mandates that all devices in the aggregate must operate at the same speed and duplex and works only with MII link monitoring.
balance-rr
If this mode is set, packets are transmitted in sequential order from the first available slave to the last.
Balance-rr is the only mode that will send packets across multiple interfaces that belong to the same TCP/IP connection.
When utilizing multiple sending and multiple receiving links, packets often are received out of order, which result in segment retransmission, for other protocols such as UDP it is not a problem if client software can tolerate out-of-order packets.
If switch is used to aggregate links together, then appropriate switch port configuration is required, however many switches do not support balance-rr.
Quick setup guide demonstrates use of the balance-rr bonding mode. As you can see, it is quite simple to set up. Balance-rr is also useful for bonding several wireless links, however it requires equal bandwidth for all bonded links. If bandwidth of one bonded link drops, then total bandwidth of bond will be equal to bandwidth of the slowest bonded link.
active-backup
This mode uses only one active slave to transmit packets. Different slave becomes active only if primary slave fails. Mac address of the bonding interface is visible only on active port to avoid confusing of the switch. Active-backup is best choice in high availability setups with multiple switches that are interconnected.
ARP monitoring in this mode will not work correctly if both routers are directly connected. In such setups mii-type1 or mii-type2 monitoring must be used or switch should be put between routers.
balance-xor
Packets will be sent over the same interface if destined for specific peer.
broadcast
balance-tlb
This mode balances outgoing traffic by peer. Each link can be a different speed and duplex and no specific switch configuration is required as in other modes. Downside of this mode is that only MII link monitoring is supported and incoming traffic is not balanced. Incoming traffic will use the link that is configured as "primary".
Configuration example
Lets assume than router has two links - ether1 max bandwidth is 10Mbps and ether2 max bandwidth is 5Mbps.
First link has more bandwidth so we set it as primary link
/interface bonding add mode=balance-tlb slaves=ether1,ether2 primary=ether1
No additional configuration is required for the switch.
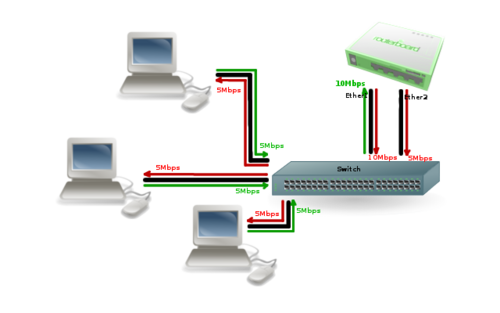
Image above illustrates how balance-tlb mode works. As you can see router can communicate to all the clients connected to switch with total bandwidth of both links (15Mbps). But as you already know, balance-tlb is not balancing incoming traffic. In our example clients can communicate to router with total bandwidth of primary link which is 10Mbps in our configuration.
balance-alb
Mode is basically the same as balance-tlb but incoming traffic is also balanced. Only additional downside of this mode is that it requires device driver capability to change mac address. Most of the cheap cards do not support this mode.
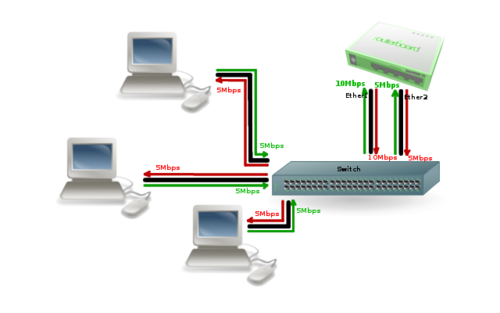
Image above illustrates how balance-alb mode works. Compared to balance-tlb traffic from clients also can use secondary link to communicate with router.
Property Description
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| arp (disabled | enabled | proxy-arp | reply-only; Default: enabled) | Address Resolution Protocol for the interface.
|
| arp-interval (time; Default: 00:00:00.100) | time in milliseconds which defines how often to monitor ARP requests |
| arp-ip-targets (IP addres; Default: ) | IP target address which will be monitored if link-monitoring is set to arp. You can specify multiple IP addresses, separated by comma |
| down-delay (time; Default: 00:00:00) | if a link failure has been detected, bonding interface is disabled for down-delay time. Value should be a multiple of mii-interval |
| lacp-rate (1sec | 30secs; Default: 30secs) | Link Aggregation Control Protocol rate specifies how often to exchange with LACPDUs between bonding peer. Used to determine whether link is up or other changes have occurred in the network. LACP tries to adapt to these changes providing failover. |
| link-monitoring (arp | mii-type1 | mii-type2 | none; Default: none) | method to use for monitoring the link (whether it is up or down)
|
| mii-interval (time; Default: 00:00:00.100) | how often to monitor the link for failures (parameter used only if link-monitoring is mii-type1 or mii-type2) |
| mode (802.3ad | active-backup | balance-alb | balance-rr | balance-tlb | balance-xor | broadcast; Default: balance-rr) | Specifies one of the bonding policies
|
| mtu (integer; Default: 1500) | Maximum Transmit Unit in bytes |
| name (string; Default: ) | descriptive name of bonding interface |
| primary (string; Default: ) | Interface is used as primary output interface. If primary interface fails, only then others slaves will be used. This value works only with active-backup mode |
| slaves (string; Default: none) | at least two ethernet-like interfaces separated by a comma, which will be used for bonding |
| up-delay (time; Default: 00:00:00) | if a link has been brought up, bonding interface is disabled for up-delay time and after this time it is enabled. Value should be a multiple of mii-interval |
| transmit-hash-policy (layer-2 | layer-2-and-3 | layer-3-and-4; Default: layer-2) | Selects the transmit hash policy to use for slave selection in balance-xor and 802.3ad modes
|
Notes
Link failure detection and failover is working significantly better with expensive network cards, for example, made by Intel, then with more cheap ones. For example, on Intel cards failover is taking place in less than a second after link loss, while on some other cards, it may require up to 20 seconds. Also, the Active load balancing (mode=balance-alb) does not work on some cheap cards.