Manual:Tools/Traffic Generator
Summary
Traffic Generator is a tool that allows to generate and send RAW packets over specific ports. Tool also collects latency and jitter values, tx/rx rates, it also counts lost packets and detects Out-of-Order packets. Traffic Generator can be used similar to bandwidth test tool as well as generate packets that will be routed back to packet generator for advanced status collection.
suggest
General
Sub-menu /tool traffic-generator
This menu allows to set general traffic generator properties and contains commands to quickly start and stop the tool.
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| latency-distribution-scale (integer [0..28]; Default: 10) | |
| test-id (integer [0..255]; Default: 0) |
Read-Only Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| latency-distribution-samples (integer) | |
| latency-distribution-measure-interval (time) | |
| running (yes | no) | Shows whether traffic generator tool is started. |
Commands
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| quick () | This command allows to quickly start packet generator and print the stats output to the terminal. Command also accept several parameters that overrides settings in packet template and stream settings. Accepted parameters are duration, entries-to-show, freeze-frame-interval, mbps, num, packet-size, port, pps, stream, test-id, tx-template
The rest of the parameters are not command specific and are described elsewhere. Parameters specified when running quick command overrides configured values. In case if parameter is specified only for one header then value is multiplied for all the other headers (if required). |
| start () | Commands starts the traffic generator tool in the background. It accepts one parameter test-id |
| stop () | Command stops the started traffic generator tool by start command. |
Packet Template
Sub-menu /tool traffic-generator packet-template
This sub menu allows to build packet based on provided parameters. Based on parameters you can build ip packet with vlan tags and set udp ports. Raw packet template is generated based on provided parameters.
If you require more low level packet or take full advantage of traffic generator, then please use raw-packet-template builder to build the packet.
If same type of header is present in packet more than once then header field values are passed as comma separated list. (For example if there are two ip
headers then source addresses are given like "ip-src=1.1.1.1,2.2.2.2").
For quicker header construction many of the header field values are assumed. For example if header stack is "mac,ip" then traffic generator can assume that mac-protocol value is "ip". Or if "port" or "interface" setting is specified traffic generator can assume "mac-src" to be MAC address of interface).
Assumed values have distinct names that start with "assumed-" and are read only. Manually specified values override assumed ones.

Note: Assumed values are not automatically updated. New values are assumed after template edit. "packet-template set 0" is enough to trigger new assumed values
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| comment (string; Default: ) | Short description of packet you are building. |
| data (incrementing | random | specific-byte | uninitialized; Default: uninitialized) | Specifies how packet payload will be filled:
|
| data-byte (hex [0..FF]]; Default: 0) | Byte that will be used to fill packet payload. |
| interface (string; Default: ) | Optional parameter of packet template. This is mutually exclusive with "port" setting. Specifying "interface" allows user not to create a port entry for interface in port menu. In fact a port entry is created dynamically. This is useful for running quick tests. |
| ip-dscp (list of integer[0..255] (max 16 times); Default: ) | Single DSCP or list of DSCP values that will be set in IP header |
| ip-dst (list of IP/Netmask (max 16 times); Default: ) | List of destination IP addresses that will be used when generating IP headers. |
| ip-frag-off (list of integer[0..65535] (max 16 times); Default: ) | List of fragmentation offsets in IP header. |
| ip-gateway (IP; Default: ) | In situations when sender and receiver is the same device, it is impossible to determine nexthop automatically from ip-dst. If ip-gateway is specified packet template will assume destination mac address based on resolved ip-gateway. |
| ip-id (list of integer [0..65535]; Default: ) | |
| ip-protocol (list of IP protocols (max 16 times); Default: ) | |
| ip-src (list of IP/Mask (max 16 times); Default: ) | |
| ip-ttl (list of integer [0..255] (max 16 times); Default: ) | |
| mac-dst (list of MAC/MASK (max 16 times); Default: ) | |
| mac-protocol (list of mac protocols (max 16 times); Default: ) | |
| mac-src (list of MAC/MASK (max 16 times); Default: ) | |
| name (string; Default: ) | Descriptive name of the template. |
| port (string; Default: ) | Optional parameter of packet template. This suggests a port through which packets generated using this template should be sent out. Port can also be specified in other places such as in stream settings. This is mutually exclusive with interface setting. |
| raw-header (string (max 16 times); Default: ) | Raw packet header as string in hexadecimal format. |
| udp-dst-port (list of port [0..65535]/mask [0..FFFF] (max 16 times); Default: ) | |
| udp-src-port (list of port [0..65535]/mask [0..FFFF] (max 16 times); Default: ) | |
| vlan-id (; Default: ) | |
| vlan-priority (; Default: ) | |
| vlan-protocol (; Default: ) | |
| header-stack (list of ip | mac | raw | udp | vlan (max 16 times); Default: ip) | Sequence of headers that a generated packet should have.
Currently supports:
|
Port Configuration
Sub-menu /tool packet-generator port
This menu allows to configure ports that will be associated to specific interface and will be used to receive/send generated packets.
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Whether port is disabled and does not participate in receiving/sending of the packets |
| name (string; Default: ) | Descriptive name of the port |
| interface (string; Default: ) | Name of the interface associated with the port. |
Read-Only Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| dynamic (yes | no) | Whether port configuration is generated automatically. |
| first-header (ip | mac | raw | udp | vlan) | Shows suggested first header for packets to be sent out of specified interface. This is information can be used when creating packet templates. |
| inactive (yes | no) | Whether port is inactive and can't participate in tx/rx of the packets. |
Stats
Sub-menu /tool traffic-generator stats
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| (; Default: ) |
Streams
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| disabled (yes | no; Default: no) | Whether stream is disabled |
| mbps (integer [0..4294967295]; Default: 0) | Value in Mega bits per second that stream will try to generate. |
| name (string; Default: ) | Descriptive name of the stream. |
| num (integer [0..15]; Default: 0) | |
| packet-size (integer[1..65535] [-integer[1..65535]]; Default: 0) | Generated size of the packets in bytes. Can be set as the range for random packet size generation. |
| port (string; Default: ) | Name of the port from Port menu that will be used to transmit packets. |
| pps (integer [0..4294967295]; Default: 0) | Packets per second that stream will try to generate. |
| tx-template (string; Default: ) | Name of the packet template from packet-template or raw-packet-template menus used as the packet content source. |
Configuration Examples
IpSec tunnel performance test
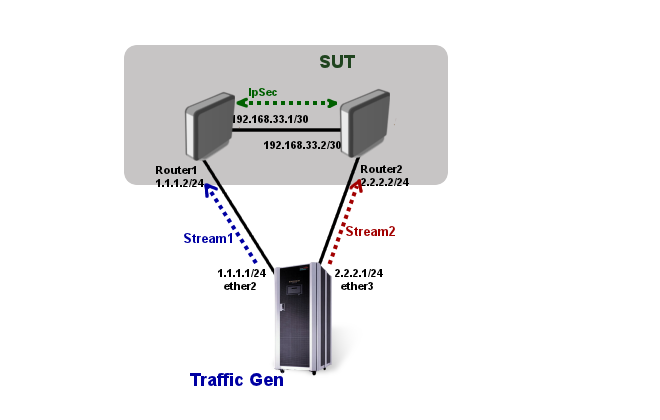
Consider following test setup
System Under Test (SUT) consists of two routers connected to traffic generator server. Connection between both SUT routers are IPSec encrypted.
Traffic generator will run two streams:
- in direction from 1.1.1.0/24 network to 2.2.2.0/24 network
- in direction from 2.2.2.0/24 network to 1.1.1.0/24 network.
R1 routing and ipsec setup
/ip address
add address=192.168.33.1/30 interface=ether1
add address=1.1.1.2/24 interface=ether2
/ip route
add dst-address=2.2.2.0/24 gateway=192.168.33.2
/ip ipsec proposal
set default enc-algorithms=aes-128
/ip ipsec peer
add address=192.168.33.2 secret=123
/ip ipsec policy
add sa-src-address=192.168.33.1 sa-dst-address=192.168.33.2 \
src-address=1.1.1.0/24 dst-address=2.2.2.0/24 tunnel=yes
R2 routing and ipsec setup
/ip address
add address=192.168.33.2/30 interface=ether1
add address=2.2.2.2/24 interface=ether2
/ip route
add dst-address=1.1.1.0/24 gateway=192.168.33.1
/ip ipsec proposal
set default enc-algorithms=aes-128
/ip ipsec peer
add address=192.168.33.1 secret=123
/ip ipsec policy
add sa-src-address=192.168.33.2 sa-dst-address=192.168.33.1 \
src-address=2.2.2.0/24 dst-address=1.1.1.0/24 tunnel=yes
Traffig generator server setup
/ip address add address=1.1.1.1/24 interface=ether2 add address=2.2.2.1/24 interface=ether3
First we will define which ports will be used as traffic generator tx/rx ports
/tool traffic-generator port add disabled=no interface=ether2 name=port0 add disabled=no interface=ether3 name=port1
To construct actual packet that will be generated packet-template is used.
/tool traffic-generator packet-template
add header-stack=mac,ip,udp ip-dst=2.2.2.1/32 ip-gateway=1.1.1.2 ip-src=1.1.1.1/32 \
name=routing-1 port=port0
add header-stack=mac,ip,udp ip-dst=1.1.1.1/25 ip-gateway=2.2.2.2 ip-src=2.2.2.1/32 \
name=routing-2 port=port1
Notice that mac addresses was not specified since template generator can assume next-hop mac address automatically by sending ARP messages. Since we are doing routing and destination IP is not directly reachable, we set up ip-gateway parameter do determine next-hop mac-address.
When doing print you can see all assumed (detected) values including mac addresses.
[admin@test-host] /tool traffic-generator packet-template> print 0 name="routing-1" header-stack=mac,ip,udp port=port0 assumed-mac-dst=00:0C:42:00:38:9D assumed-mac-src=00:0C:42:40:94:25 assumed-mac-protocol=ip assumed-ip-dscp=0 assumed-ip-id=0 assumed-ip-frag-off=0 assumed-ip-ttl=64 assumed-ip-protocol=udp ip-src=1.1.1.1/32 ip-dst=2.2.2.1/32 assumed-udp-src-port=100 assumed-udp-dst-port=200 ip-gateway=1.1.1.2 data=uninitialized data-byte=0 1 name="routing-2" header-stack=mac,ip,udp port=port1 assumed-mac-dst=00:0C:42:00:38:D1 assumed-mac-src=00:0C:42:40:94:26 assumed-mac-protocol=ip assumed-ip-dscp=0 assumed-ip-id=0 assumed-ip-frag-off=0 assumed-ip-ttl=64 assumed-ip-protocol=udp ip-src=2.2.2.1/32 ip-dst=1.1.1.1/32 assumed-udp-src-port=100 assumed-udp-dst-port=200 ip-gateway=2.2.2.2 data=uninitialized data-byte=0
For example if routers in SUT change, assumed mac-addresses will not be updated automatically. To update packet templates simply issue command :
/tool traffic-generator packet-template set [find]
Last part is to configure streams
/tool traffic-generator stream
add disabled=no mbps=500 name=str1 num=3 packet-size=1450 port=port0 pps=0 \
tx-template=routing-1
add disabled=no mbps=500 name=str3 num=4 packet-size=1450 port=port1 pps=0 \
tx-template=routing-2
Notice that each stream has unique num value. This value identifies stream packets, otherwise traffic generator will not work.
Now we are ready to run the test. In this case quick mode will be used:
[admin@test-host] /tool traffic-generator> quick mbps=450 SEQ NUM TX-PACKET TX-RATE RX-PACKET RX-RATE RX-OOO LOST-PACKET LOST-RATE 37 4 39 488 458.0Mbps 39 270 455.5Mbps 15 509 218 2.5Mbps 37 TOT 78 976 916.1Mbps 76 485 887.2Mbps 22 529 2 491 28.8Mbps 38 3 38 957 451.9Mbps 37 657 436.8Mbps 7 078 1 300 15.0Mbps 38 4 38 958 451.9Mbps 38 402 445.4Mbps 14 763 556 6.4Mbps 38 TOT 77 915 903.8Mbps 76 059 882.2Mbps 21 841 1 856 21.5Mbps 39 3 38 816 450.2Mbps 37 893 439.5Mbps 7 307 923 10.7Mbps 39 4 38 815 450.2Mbps 38 642 448.2Mbps 15 110 173 2.0Mbps 39 TOT 77 631 900.5Mbps 76 535 887.8Mbps 22 417 1 096 12.7Mbps 40 3 39 779 461.4Mbps 37 415 434.0Mbps 7 136 2 364 27.4Mbps 40 4 39 780 461.4Mbps 39 567 458.9Mbps 15 908 213 2.4Mbps 40 TOT 79 559 922.8Mbps 76 982 892.9Mbps 23 044 2 577 29.8Mbps 41 3 39 218 454.9Mbps 37 089 430.2Mbps 7 075 2 129 24.6Mbps 41 4 39 218 454.9Mbps 38 663 448.4Mbps 15 752 555 6.4Mbps 41 TOT 78 436 909.8Mbps 75 752 878.7Mbps 22 827 2 684 31.1Mbps 42 3 39 188 454.5Mbps 37 906 439.7Mbps 6 729 1 282 14.8Mbps 42 4 39 187 454.5Mbps 38 954 451.8Mbps 15 565 233 2.7Mbps 42 TOT 78 375 909.1Mbps 76 860 891.5Mbps 22 294 1 515 17.5Mbps TOT 3 1 645 468 454.4Mbps 1 568 201 433.1Mbps 280 174 77 267 21.3Mbps TOT 4 1 645 464 454.4Mbps 1 626 896 449.3Mbps 627 480 18 568 5.1Mbps TOT TOT 3 290 932 908.9Mbps 3 195 097 882.4Mbps 907 654 95 835 26.4Mbps
Stats shows throughput of each stream and total throughput of both streams, Out-of-order packet count, Lost rate, latency and jitter.
[ Top | Back to Content ]