Manual:Spectral scan
The spectral scan can scan all frequencies supported by your wireless card, and plot them directly in console. Exact frequency span depends on card. Allowed ranges on r52n: [4790; 6085], [2182; 2549].
Wireless card can generate 4us long spectral snapshots for any 20mhz wide channel. This is considered a single spectral sample.
To improve data quality spectrum is scanned with 10mhz frequency increments, which means doubled sample coverage at each specific frequency (considering 20mhz wide samples).
Currently this feature is supported only for Atheros Merlin chips. (ie. AR9220, AR9280, AR9223).
Currently tested models: RouterBOARD R52N and R2N only.
Console
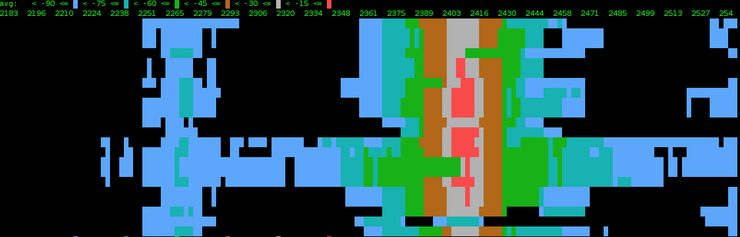
Spectral History
/interface wireless spectral-history <wireless interface name>
Plots spectrogram. Legend and frequency ruler is printed every 24 lines. Numbers in the ruler correspond to the value at their leftmost character position. Power values that fall in different ranges are printed as different colored characters with the same foreground and background color, so it is possible to copy and paste terminal output of this command.
- value -- select value that is plotted on the output. 'interference' is special as it shows detected interference sources (affected by 'classify-samples' parameter) instead of power readings, and cannot be made audible.
- interval -- interval at which spectrogram lines are printed.
- duration -- terminate command after specified time. default is indefinite.
- buckets -- how many values to show in each line of spectrogram. This value is limited by the number of columns in terminal. It is useful to reduce this value if using 'audible'.
- average-samples -- Number of 4us spectral snapshots to take at each frequency, and calculate average and maximum energy over them. (default 10)
- classify-samples -- Number of spectral snapshots taken at each frequency and processed by interference classification algorithm. Generally more samples gives more chance to spot certain type of interference (default 50)
- range --
- 2.4ghz - scan whole 2.4ghz band
- 5ghz - scan whole 5ghz band
- current-channel - scan current channel only (20 or 40 mhz wide)
- range - scan specific range
- audible=yes -- play each line as it is printed. There is a short silence between lines. Each line is played from left to right, with higher frequencies corresponding to higher values in the spectrogram.
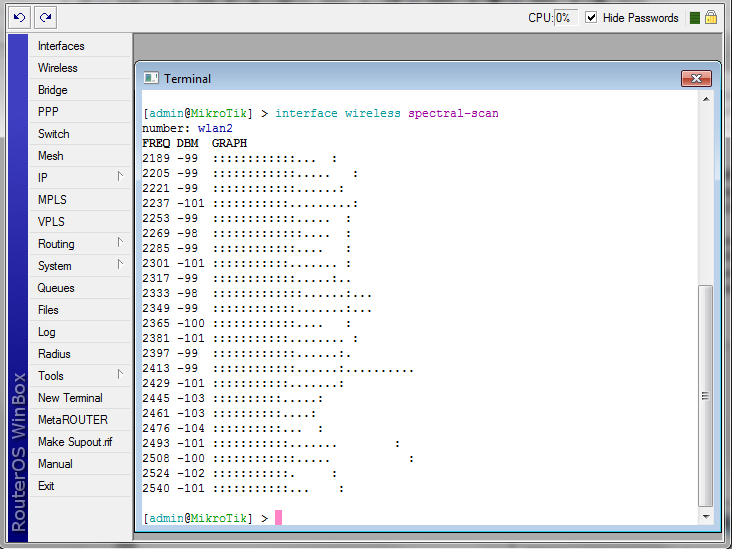
Spectral Scan
/interface wireless spectral-scan <wireless interface name>
Continuously monitor spectral data. This command uses the same data source as 'spectral-history', and thus shares many parameters.
Each line displays one spectrogram bucket -- frequency, numeric value of power average, and a character graphic bar. Bar shows average power value with ':' characters and average peak hold with '.' characters. Maximum is displayed as a lone floating ':' character.
- show-interference -- add column that shows detected interference sources.
Types of possibly classified interference:
- bluetooth-headset
- bluetooth-stereo
- cordless-phone
- microwave-oven
- cwa
- video-bridge
- wifi
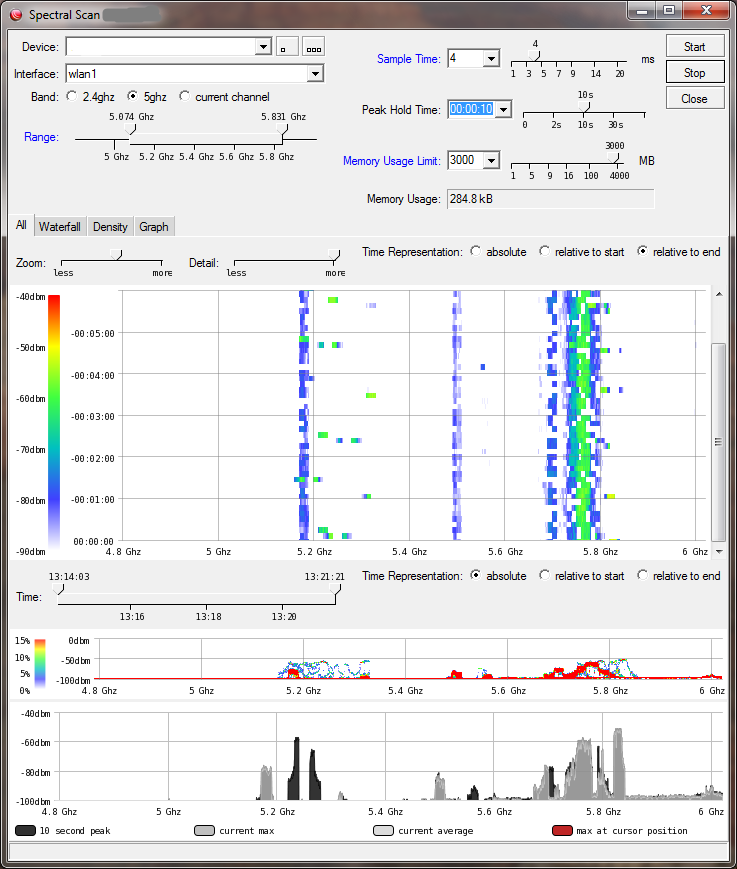
The Dude
The Dude is a free network monitoring and management program by MikroTik. You can download it here.
The Dude has a built-in capability to run graphical Spectral Scan from any of your RouterOS devices with a supported wireless card. Simply select this device in your Dude map, right click and choose Tools -> Spectral Scan.
This will bring up the Spectral Scan GUI with various options and different view modes: