Manual:IP/TFTP
Summary
Standards: RFC 1350 RFC 2348
TFTP is a very simple protocol used to transfer files. It is from this that its name comes, Trivial File Transfer Protocol or TFTP. Each nonterminal packet is acknowledged separately. RouterOS has a built-in TFTP server since v3.22

Warning: Since version 4.4 to set up tftp rules you will have to have policy sensitive enabled for your account.

Note: since RouterOS 5.6 sequence number roll-over is supported by TFTP server. That has to be set specifically for TFTP rule that allows it.
TFTP access rules
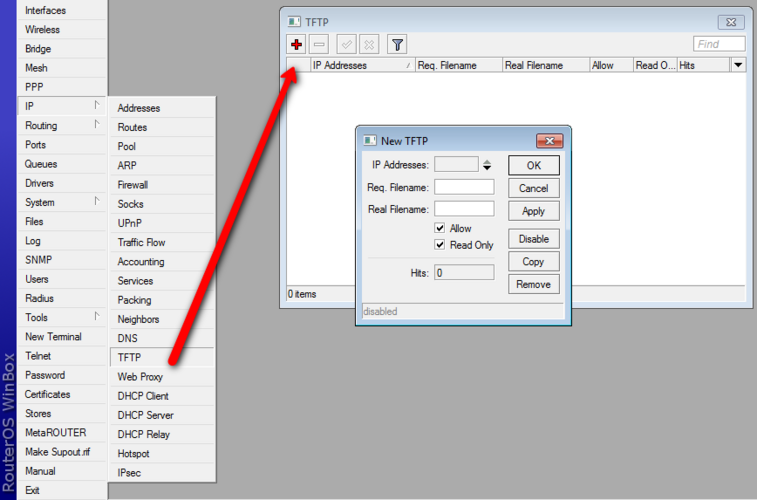
Menu: /ip tftp This menu contains all TFTP access rules. If in this menu are no rules, TFTP server is not started when RouterOS boots. This menu only shows 1 additional attribute compared to what you can set when creating rule, see explanations of attribute descriptions lower.
| Property | Desciption |
|---|---|
| hits | how many times this access rule entry has been used (read-only) |
Add new access rule
Expansion of command: /ip tftp add
To add new tftp access rule you will have to issue command add under /ip tftp menu with attributes as follows:
| Property | Desciption |
|---|---|
| ip-address (required) | range of IP addresses accepted as clients if empty 0.0.0.0/0 will be used |
| allow-rollover (Default:No) | if set to yes TFTP server will allow sequence number to roll over when maximum value is reached. This is used to enable large downloads using TFTP server. |
| req-filename | requested filename as regular expression (regex) if field is left empty it defaults to .* |
| real-filename | if req-filename and real-filename values are set and valid, the requested filename will be replaced with matched file. This field has to be set. If multiple regex are specified in req-filename, with this field you can set which ones should match, so this rule is validated. real-filename format for using multiple regex is filename\0\5\6 |
| allow (default: yes) | to allow connection if above fields are set. if no, connection will be interrupted |
| read-only (default: no) | sets if file can be written to, if set to "no" write attempt will fail with error |
req-filename field allowed regexp
allowed regexps in this field are
- brackets () - marking subsection
example 1 a(sd|fg) will match asd or afg
- asterisk "*" - match zero or more times preceding symbol,
example 1 a* will match any length name consisting purely of symbols a or no symbols at all
example 2 .* will match any length name, also, empty field
example 3 as*df will match adf, asdf, assdf, asssdf etc.
- plus "+" will match one or more times preceding symbol,
example: as+df will match asdf, assdf etc.
- dot "." - matches any symbol
example as.f will match asdf, asbf ashf etc.
- square brackets [] - variation between
example as[df] will match asd and asf
- question mark "?" will match one or none symbols,
example asd?f will match asdf and asf
- caret "^" - used at the beginning of the line means that line starts with,
- dollar "$" - means at the end of the line
Examples
- example 1 if file is requested return file from store called sata1:
/ip tftp add req-filename=file.txt real-filename=/sata1/file.txt allow=yes read-only=yes
- example 2 if we want to give out one specific file no matter what user is requesting:
/ip tftp add req-filename=.* real-filename=/sata1/file.txt allow=yes read-only=yes
- example 3 if user requests aaa.bin or bbb.bin then give them ccc.bin:
/ip tftp add req-filename="(aaa.bin)|(bbb.bin)" real-filename="/sata1/ccc.bin\\0" allow=yes read-only=yes