Manual:CHR
Cloud Hosted Router
Cloud Hosted Router (CHR) is a RouterOS version intended for running as a virtual machine. It supports the x86 64-bit architecture and can be used on most of the popular hypervisors such as VMWare, Hyper-V, VirtualBox, KVM and others. CHR has full RouterOS features enabled by default but has a different licensing model than other RouterOS versions.
System Requirements
Minimal requirements:
- Package version: RouterOS v6.34 or newer
- Host CPU: 64-bit with virtualization support
- RAM: 128MB or more
- Disk: 128MB disk space for the CHR virtual hard drive (Max: 16GB)

Note: The minimum required RAM depends on interface count and CPU count. You can get an approximate number by using the following formula: RAM = 128 + ( 8 × (CPU_COUNT) × (INTERFACE_COUNT - 1) )
CHR has been tested on the following platforms:
- VirtualBox 5 on Linux and OS X
- VMWare Fusion 7 and 8 on OS X
- VMWare ESXi 6.5
- Qemu 2.4.0.1 on Linux and OS X
- Hyper-V on Windows Server 2008r2, 2012 and Windows 10 (Only Generation 1 Hyper-V virtual machine is supported at the moment)
- Xen Project 4.6.5
- Xen Server 7.1
Usable Network and Disk interfaces on various hypervisors:
- ESX:
- Network: vmxnet3, E1000
- Disk: IDE, VMware paravirtual SCSI, LSI Logic SAS, LSI Logic Parallel
- Hyper-V:
- Network: Network adapter, Legacy Network adapter
- Disk: IDE, SCSI
- Qemu/KVM:
- Network: Virtio, E1000, vmxnet3 (optional)
- Disk: IDE, Sata, Virtio
- Xen Project:
- Network: E1000, rtl8193, netfront
- Disk: IDE, Sata
- VirtualBox
- Network: E1000, rtl8193
- Disk: IDE, Sata, SCSI, SAS

Note: SCSI controller Hyper-V and ESX is usable just for secondary disks, system image must be used with IDE controller!

Warning: We do not recommend using E1000 network interface if better synthetic interface options are available on specific Hypervisor!
How to Install CHR
We provide 4 different virtual disk images to choose from. Note that they are only disk images, and you can't simply run them.
- RAW disk image (.img file)
- VMWare disk image (.vmdk file)
- Hyper-V disk image (.vhdx file)
- VirtualBox disk image (.vdi file)
Steps to install CHR
- Download virtual disk image for your hypervisor
- Create a guest virtual machine
- Use previously downloaded image file as a virtual disk drive
- Start the guest CHR virtual machine
- Log in to your new CHR. Default user is 'admin', without password
Please note that running CHR systems can be cloned and copied, but the copy will be aware of the previous trial period, so you cannot extend your trial time by making a copy of your CHR. However, you are allowed to license both systems individually. To make a new trial system, you need to make a fresh installation and reconfigure RouterOS.
Installing CHR
- VMWare Fusion / Workstation and ESXi 6.5
- VirtualBox
- Hyper-V
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Linode
- Google Compute Engine
- ProxMox
CHR Licensing
The CHR has 4 license levels:
- free
- p1 perpetual-1 ($45)
- p10 perpetual-10 ($95)
- p-unlimited perpetual-unlimited ($250)
60-day free trial license is available for all paid license levels. To get the free trial license, you have to have an account on MikroTik.com as all license management is done there.
Perpetual is a lifetime license (buy once, use forever). It is possible to transfer a perpetual license to another CHR instance. A running CHR instance will indicate the time when it has to access the account server to renew it's license. If the CHR instance will not be able to renew the license it will behave as if the trial period has ran out and will not allow an upgrade of RouterOS to a newer version.
After licensing a running trial system, you must manually run the /system license renew function from the CHR to make it active. Otherwise the system will not know you have licensed it in your account. If you do not do this before the system deadline time, the trial will end and you will have to do a complete fresh CHR installation, request a new trial and then license it with the license you had obtained.
| License | Speed limit | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Free | 1Mbit | FREE |
| P1 | 1Gbit | $45 |
| P10 | 10Gbit | $95 |
| P-Unlimited | Unlimited | $250 |
Paid licenses
p1
p1 (perpetual-1) license level allows CHR to run indefinitely. It is limited to 1Gbps upload per interface. All the rest of the features provided by CHR are available without restrictions. It is possible to upgrade p1 to p10 or p-unlimited After the upgrade is purchased the former license will become available for later use on your account.
p10
p10 (perpetual-10) license level allows CHR to run indefinitely. It is limited to 10Gbps upload per interface. All the rest of the features provided by CHR are available without restrictions. It is possible to upgrade p10 to p-unlimited After the upgrade is purchased the former license will become available for later use on your account.
p-unlimited
The p-unlimited (perpetual-unlimited) license level allows CHR to run indefinitely. It is the highest tier license and it has no enforced limitations.
Free licenses
There are several options to use and try CHR free of charge.
free
The free license level allows CHR to run indefinitely. It is limited to 1Mbps upload per interface. All the rest of the features provided by CHR are available without restrictions. To use this, all you have to do is download disk image file from our download page and create a virtual guest.
60-day trial
In addition to the limited Free installation, you can also test the increased speed of P1/P10/PU licenses with a 60 trial.
You will have to have an account registered on MikroTik.com. Then you can request the desired license level for trial from your router that will assign your router ID to your account and enable a purchase of the license from your account. All the paid license equivalents are available for trial. A trial period is 60 days from the day of acquisition, after this time passes, your license menu will start to show "Limited upgrades", which means that RouterOS can no longer be upgraded.
If you plan to purchase the selected license, you must do it within 60 days of the trial end date. If your trial ends, and there are no purchases within 2 months after it ended, the device will no longer appear in your MikroTik account. You will have to make a new CHR installation to make a purchase within the required time frame.
To request a trial license, you must run the command "/system license renew" from the CHR device command line. You will be asked for the username and password of your mikrotik.com account.

Warning: If you plan to use multiple virtual systems of the same kind, it may be possible that the next machine has the same systemID as the original one. This can happen on certain cloud providers, such as Linode. To avoid this, after your first boot, run the command "/system license generate-new-id" before you request a trial license. Note that this feature must be used only while CHR is running on free type of RouterOS license. If you have already obtained paid or trial license, do not use regenerate feature since you will not be able to update your current key any more
Getting the License
After the initial setup a CHR instance will have a free license assigned. From there, it is possible to upgrade the license to a higher tier. Once you have a trial license all the work with the license is done on the account server where it is possible to upgrade license to a higher tier unless it is p-unlimited already.
Upgrade from free to p1 or higher
Initial upgrade from the free tier to anything higher than that incurs CHR instance registration on the account server. To do that you have to enter your MikroTik.com username and password and a desired license level you want to acquire. As a result, a CHR ID number will be assigned to your account on the account server and 60-day trial created for that ID. There are 2 ways to obtain a license - using WinBox or RouterOS command line interface:
Using WinBox (Sytem -> License menu):
Using command line interface:
[admin@MikroTik] > /system license print
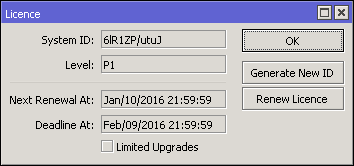
system-id: 6lR1ZP/utuJ
level: free
[admin@MikroTik] > /system license renew
account: mymikrotikcomaccount
password: *********************
level: p1
status: done
[admin@MikroTik] > /system license print
system-id: 6lR1ZP/utuJ
level: p1
next-renewal-at: jan/10/2016 21:59:59
deadline-at: feb/09/2016 21:59:59
To acquire a higher level trial, set up a new CHR instance, renew the license and select the desired level.
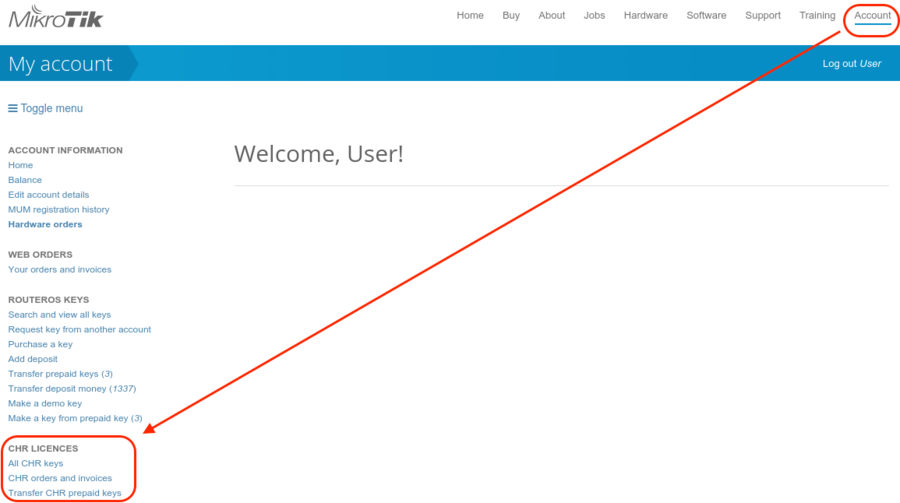
To upgrade from a Trial license to Paid go to MikroTik.com account server and choose 'all keys' in Cloud Hosted Router (CHR) section:
You will be presented with a list of your CHR machines and licenses:
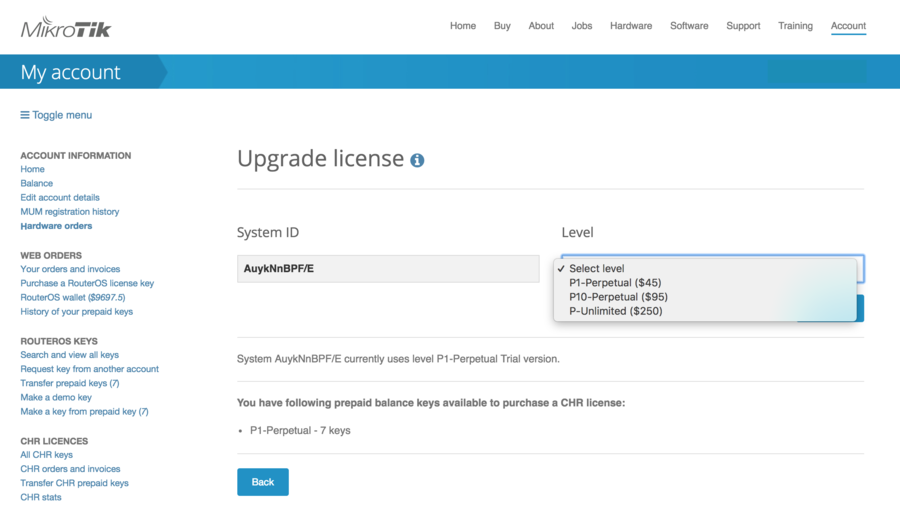
To upgrade from a Trial to a Paid license click 'Upgrade', choose the desired license level (it can be different than the level of the trial license) and click 'Upgrade key':
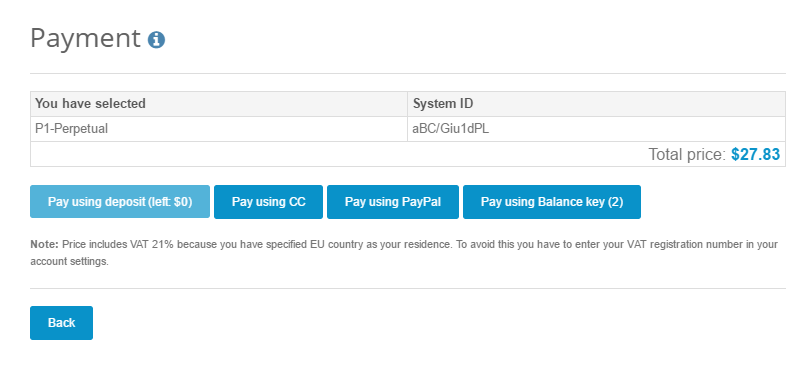
Choose the payment method:
It is possible to pay using account balance (deposit), credit card (CC), PayPal or using Balance (prepaid) key (if you have any).
Upgrade from higher tier up
Only an upgrade to a higher tier is possible at the moment (for paid licenses only) and that is done in the account server. For changes to take place on the router itself renew command should be issued. When the router already has any kind of trial or paid license, the license level you set for the renew command is not important anymore, it is mandated by the account server. Possible upgrades are as follows:
- p1 upgrade to p10
- p1 upgrade to p-unlimited
- p10 upgrade to p-unlimited
License Update
In '/system license' menu router will indicate the time next-renewal-at when it will attempt to contact server located on licence.mikrotik.com. Communication attempts will be performed once an hour after the date on next-renewal-at and will not cease until the server responds with an error. If deadline-at date is reached without successfully contacting the account server, the router will consider that license has expired and will disallow further software updates. However, router will continue to work with the same license tier as before.
Troubleshooting
Running on VMware ESXi
Changing MTU
VMware ESXi supports MTU of up to 9000 bytes. To get the benefit of that, you have to adjust your ESXi installation to allow a higher MTU. Virtual Ethernet interface added after the MTU change will be properly allowed by the ESXi server to pass jumbo frames. Interfaces added prior to MTU change on the ESXi server will be barred by the ESXi server (it will still report old MTU as maximum possible size). If you have this, you have to re-add interfaces to the virtual guests.
Example. There are 2 interfaces added to the ESXi guest, auto-detected MTU on the interfaces show MTU size as it was at the time when the interface was added:
[admin@chr-vm] > interface ethernet print Flags: X - disabled, R - running, S - slave # NAME MTU MAC-ADDRESS ARP 0 R ether1 9000 00:0C:29:35:37:5C enabled 1 R ether2 1500 00:0C:29:35:37:66 enabled
Using bridge on Linux
If Linux bridge supports IGMP snooping, and there are problems with IPv6 traffic it is required to disable that feature as it interacts with MLD packets (multicast) and is not passing them through.
echo -n 0 > /sys/class/net/vmbr0/bridge/multicast_snooping
Packets not passing from guests
The problem: after configuring a software interface (VLAN, EoIP, bridge, etc.) on the guest CHR it stops passing data to the outside world beyond the router.
The solution: check your VMS (Virtualization Management System) security settings, if other MAC addresses allowed to pass if packets with VLAN tags allowed to pass through. Adjust the security settings according to your needs like allowing MAC spoofing or certain MAC address range. For VLAN interfaces, it is usually possible to define allowed VLAN tags or VLAN tag range.
Using vlans on CHR in various Hypervisors
In some of hypervisors before Vlans can be used on VMs they need to first be configured on hypervisor it self.
ESXI
Enable Promiscuous mode in port group or virtual switch that you will use for specific VM.
ESX documentation:
Hyper-V
Hyper-V documentation:
bhyve hypervisor
It wont be possible to run CHR on this hypervisor. CHR cannot be run as paravirtualized platform.
Linode
When creating multiple Linodes with the same disk size, new Linodes will have the same systemID. This will cause issues to get a Trial/Paid license. To avoid this, run the command /system license generate-new-id after the first boot and before you request a trial or paid license. This will make sure the ID is unique.
Some useful articles:
Specific vlan is untagged by nic interface:
- https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/adamfazio/2008/11/14/understanding-hyper-v-vlans/
- http://www.aidanfinn.com/?p=10164
Allow passing other vlans:
Guest tools
VMWare
Time synchronization
Must be enabled from GUI ('Synchronize guest time with host'). Backwards synchronization is disabled by default - if guest is ahead of host by more than ~5 seconds, synchronization is not performed
Power operations
- poweron and resume scripts are executed (if present and enabled) after poweron and resume operations respectively.
- poweroff and suspend scripts are executed before poweroff and suspend operations respectively.
- If scripts take longer than 30 seconds or contain errors, the operation fails
- In case of failure, retrying the same operation will ignore any errors and complete successfully
- Failed script output is saved to file (e. g. 'poweroff-script.log', 'resume-script.log' etc)
- Scripts can be enabled/disabled from hypervisor GUI ('run VMware Tools Scripts') or by enbaling/disabling scripts from console
Quiescing/backup
Guest filesystem quiescing is performed only if requested.
- freeze script is executed before freezing the filesystem
- freeze-fail script is executed if hypervisor failed to prepare for snapshot or if freeze script failed
- thaw script is executed after snapshot has been taken
- Script run time is limited to 60 seconds
- freeze script timeouts and errors result in backup operation being aborted
- FAT32 disks are not quiesced
- Failed script output is saved to file (e. g. 'freeze-script.log', 'freeze-fail-script.log', 'thaw-script.log')
Guest info
Networking, disk, and OS info is reported to hypervisor every 30 seconds (GuestStats (memory) are disabled by default, can be enabled by setting 'guestinfo.disable-perfmon = "FALSE"' in VM config).
- The order, in which network interfaces are reported, can be controlled by setting 'guestinfo.exclude-nics', 'guestinfo.primary-nics' and 'guestinfo.low-priority-nics' options. Standard wildcard patterns can be used.
Provisioning
Can use the ProcessManager from vim API to execute scripts. Python bindings are available
- Main data structure: GuestProgramSpec
- The workingDirectory and envVariables members are ignored
- programPath must be set to either 'inline' or 'import'
- If programPath is 'inline', arguments are interpreted as script text
- If programPath is 'import', arguments are interpreted as file path
After using GuestProgramSpec together with an instance of GuestAuthentication as arguments to StartProgramInGuest unique JobID is obtained.
Script progress can be tracked by using the ListProcessesInGuest command. ListProcessesInGuest accepts an array of job id's; passing an empty array will report on all jobs started from API
- ListProcessesInGuest returns an array of GuestProcessInfo instances:
- pid field is set to JobID
- endTime is only set after completion
- exitCode is set to 0 on success and -1 on error
- name is set to 'inline' or 'import' (same as programPath in GuestProgramSpec)
Information about completed jobs is kept around for ~1 minute, or untill ListProcessesInGuest (with the corresponding JobID) is called. If the script fails, a file named 'vix_job_$JobID$ .txt' containing the script output is created. Script run time is limited to 120 seconds and script output is not saved on timeout,
- The vmrun command runScriptInGuest can also be used
- The PowerCLI cmdlet Invoke-VMScript is not supported
- Host/guest file transfer is not supported
Python example
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import sys,time
from pyVim import connect
from pyVmomi import vmodl,vim
def runInline(content,vm,creds,source):
''' Execute script source on vm '''
if isinstance(source, list):
source = '\n'.join(source)
ps = vim.vm.guest.ProcessManager.ProgramSpec(
programPath = 'console',
arguments = source
)
return content.guestOperationsManager.processManager.StartProgramInGuest(vm,creds,ps)
def runFromFile(content,vm,creds,fileName):
''' Execute script file located on CHR '''
ps = vim.vm.guest.ProcessManager.ProgramSpec(
programPath = 'import',
arguments = fileName
)
return content.guestOperationsManager.processManager.StartProgramInGuest(vm,creds,ps)
def findDatastore(content,name):
sessionManager = content.sessionManager
dcenterObjView = content.viewManager.CreateContainerView(content.rootFolder, [vim.Datacenter], True)
datacenter = None
datastore = None
for dc in dcenterObjView.view:
dstoreObjView = content.viewManager.CreateContainerView(dc, [vim.Datastore], True)
for ds in dstoreObjView:
if ds.info.name == name:
datacenter = dc
datastore = ds
break
dstoreObjView.Destroy()
dcenterObjView.Destroy()
return datacenter,datastore
def _FAILURE(s,*a):
print(s.format(*a))
sys.exit(-1)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
if __name__ == '__main__':
host = sys.argv[1] # ip or something
user = 'root'
pwd = 'MikroTik'
vmName = 'chr-test'
dataStoreName = 'datastore1'
service = connect.SmartConnectNoSSL(host=host,user=user,pwd=pwd)
if not service:
_FAILURE("Could not connect to the specified host using specified username and password")
content = service.RetrieveContent()
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Find datacenter and datastore
datacenter,datastore = findDatastore(content,dataStoreName)
if not datacenter or not datastore:
connect.Disconnect(service)
_FAILURE('Could not find datastore \'{}\'',dataStorename)
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Locate vm
vmxPath = '[{0}] {1}/{1}.vmx'.format(dataStoreName, vmName)
vm = content.searchIndex.FindByDatastorePath(datacenter, vmxPath)
if not vm:
connect.Disconnect(service)
_FAILURE("Could not locate vm")
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Setup credentials from user name and pasword
creds = vim.vm.guest.NamePasswordAuthentication(username = 'admin', password = '')
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Run script
pm = content.guestOperationsManager.processManager
try:
# Run script
src = [':ip address add address=192.168.0.1/24 interface=ether1;']
jobID = runInline(content, vm, creds, src)
# Or run file (from FTP root)
# jobID = runFromFile(content,vm,creds, 'scripts/provision.rsc')
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Wait for job to finish
pm = content.guestOperationsManager.processManager
jobInfo = pm.ListProcessesInGuest(vm, creds, [jobID])[0]
while jobInfo.endTime is None:
time.sleep(1.0)
jobInfo = pm.ListProcessesInGuest(vm, creds, [jobID])[0]
if jobInfo.exitCode != 0:
_FAILURE('Script failed!')
except:
raise
else:
connect.Disconnect(service)
Xen
Network, disk, memory and OS info is reported to hypervisor every 30 seconds
- On older hosts (pre 21.06.2017) only the first ipv4 address assigned to interface is visible
Provisioning
Base-64 encoded strings written to (domain local) xenstore path ('vm-data/provision/script') are decoded and interpreted a script-text. Status ('ready', 'running', 'error') is reported in 'vm-data/provision/script/status'. Scripts are accepted only if 'status' != 'running'. Base 64 encoded script output (if any) is written to 'vm-data/provision/script/otuput'.
- When creating a VM scripts can be provided by using xenapi (VM.add_to_xenstore_data)
KVM
QEMU guest agent is available. Supported agent commands can be retrieved by using guest-info command. Host-guest file transfer can be performed by using guest-file-* commands. Guest networking information can be retrieved by using the guest-network-get-interfaces command.
- Scripts can be executed by using the guest-exec command together with the GuestExec data structure:
- If the path member is provided, the corresponding file is executed
- If the path member is not set and input-data member is provided, input-data value is used as script input
- If capture-output is set, script output is reported back
- args and env members are not used
- Script job progress can be monitored with guest-exec-status command. The GuestExecStatus data structure is populated as follows:
- On success exitcode member is set to 0
- If the script timed out exitcode is set to 1
- If the script contained errors exitcode is set to -1
- signal member is not set
- The err-data member is not used
- If capture-output was true, Base64 encoded script output is stored in out-data
- Enabling guest agent in libvirt
- An additional agent channel ('chr.provision_channel') is also available
Proxmox
Some agent commands can be issued by using Proxmox REST api. Guest filesystem quiescing is automatically performed when taking a snapshot
- Enabling 'chr.provision-agent' for remote access on port 1234
In host shell:
vmid=256 hostip=192.168.0.1 portnum=1234 qm set $vmid --args "-chardev 'socket,host=$hostip,port=$portnum,id=chr-agent,server,nowait' -device 'virtio-serial,bus=pci.0,addr=0x9' -device 'virtserialport,chardev=chr-agent,name=chr.provision_agent'"
- Disabling 'chr.provision-agent'
In host shell:
vmid=256 qm set $vmid --delete args
- Providing remote access to default agent on port 1234
In host shell:
vmid=256 portnum=1234 socat TCP-LISTEN:$portnum,reuseaddr,fork UNIX-CLIENT:/run/qemu-server/$vmid.qga
Guest agent python example
import os,time,base64,json,socket,select,errno
class GuestAgent(object):
'''
Qemu guest agent interface
runScript and runFile commands are tailored for ROS agent implementation
Transport provided by derived classes (transact method)
'''
def __init__(self,**kwargs):
# Due to file contents being passed as base64 inside json:
# - large chunk sizes may slow down guest-side parsing.
# - small chunk sizes result in additional message fragmentation overhead.
# Default value is a guestimate.
self.__chunkSize = kwargs.get('chunkSize', 4096)
def _qmpError(self,cls,msg):
''' Generic callback to log qmp errors before (optionally) raising an exception '''
print(cls)
for line in msg.split('\n'):
print(line)
# raise RuntimeError()
def _error(self,msg,*a):
''' Generic callback to misc errors before (optionally) raising an exception '''
print(msg.format(*a))
# raise RuntimeError()
def _info(self,msg,*a):
''' Generic callback to log info '''
print(msg.format(*a))
def _monitorJob(self,pid):
''' Block untill script job completes, echo output. Returns None on failure '''
ret = self.transact('guest-exec-status',{'pid':pid})
if ret is None:
return None
while not bool(ret['exited']):
time.sleep(1)
ret = self.transact('guest-exec-status',{'pid':pid})
if ret is None:
return None
# err-data is never sent
out = []
if 'out-data' in ret.keys():
out = base64.b64decode(ret['out-data']).decode('utf-8').split('\n')
if not out[-1]:
out = out[:-1]
exitcode = int(ret['exitcode'])
return exitcode, out
def putFile(self,src,dst):
''' Upload file '''
src = os.path.expanduser(src)
if not os.path.exists(src) or not os.path.isfile(src):
self._error('File does not exist: \'{}\'', src)
return None
ret = self.transact('guest-file-open', {'path':dst,'mode':'w'})
if ret is None:
return None
handle = int(ret)
file = open(src, 'rb')
for chunk in iter(lambda : file.read(self.__chunkSize), b''):
count = len(chunk)
chunk = base64.b64encode(chunk).decode('ascii')
ret = self.transact('guest-file-write',{'handle':handle,'buf-b64':chunk,'count':count})
if ret is None:
return None
self.transact('guest-file-flush',{'handle':handle})
ret = self.transact('guest-file-close',{'handle':handle})
return True
def getFile(self,src,dst):
''' Download file '''
dst = os.path.expanduser(dst)
ret = self.transact('guest-file-open',{'path':src,'mode':'rb'})
if ret is None:
return None
handle = int(ret)
data = ''
size = 0
while True:
ret = self.transact('guest-file-read',{'handle':handle,'count':self.__chunkSize})
if ret is None:
return None
data += ret['buf-b64']
size += int(ret['count'])
if bool(ret['eof']):
break
ret = self.transact('guest-file-close',{'handle':handle})
data = base64.b64decode(data.encode('ascii'))
with open(dst,'wb') as f:
f.write(data)
return True
def runFile(self,fileName):
''' Execute file (on guest) as script '''
ret = self.transact('guest-exec',{'path':fileName, 'capture-output':True})
if ret is None:
return None
pid = ret['pid']
return self._monitorJob(pid)
def runSource(self,cmd):
''' Execute script '''
if isinstance(cmd,list):
cmd = '\n'.join(cmd)
cmd += '\n'
cmd = base64.b64encode(cmd.encode('utf-8')).decode('ascii')
ret = self.transact('guest-exec',{'input-data':cmd, 'capture-output':True})
if ret is None:
return None
pid = ret['pid']
return self._monitorJob(pid)
def shutdown(self,mode='powerdown'):
'''
Execut shutdown command
mode == 'reboot' - reboot guest
mode == 'shutdown' or mode == 'halt' - shutdown guest
'''
ret = self.transact('guest-shutdown',{'mode':mode})
return ret
class SocketAgent(GuestAgent):
'''
GuestAgent using unix/tcp sockets for communication.
'''
def __init__(self):
GuestAgent.__init__(self,chunkSize= 32 * 65536)
@staticmethod
def unix(dev):
''' Connect using unix socket '''
self = SocketAgent()
self.__af = socket.AF_UNIX
self.__args = dev
self.__wait = False
return self
@staticmethod
def tcp(ip,port,wait = True):
''' Connect using tcp socket '''
self = SocketAgent()
self.__af = socket.AF_INET
self.__args = (ip,port)
self.__wait = wait
return self
def __enter__(self):
self._sock = socket.socket(self.__af, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
if self.__wait:
self._info('Waiting for guest ...')
# Wait for hyper to create channel
while True:
try:
self._sock.connect(self.__args)
break
except socket.error as e:
if e.errno == errno.EHOSTUNREACH or e.errno == errno.ECONNREFUSED:
time.sleep(1)
else:
self._sock.close()
raise
#Wait for guest agent to initialize and sync
while True:
import random
key = random.randint(0, 0xffffffff)
msg = json.dumps({'execute':'guest-sync-delimited','arguments':{'id':key}},separators=(',',':'),sort_keys=True)
self._sock.send(msg.encode('ascii'))
self._sock.setblocking(0)
response = b''
if (select.select([self._sock],[],[])[0]):
response += self._sock.recv(65536)
else:
raise RuntimeError()
self._sock.setblocking(1)
sentinel = b'\xff'
response = response.split(sentinel)[-1]
if not response:
time.sleep(3)
continue
response = json.loads(response.decode('utf-8').strip())
if 'return' in response.keys():
if int(response['return']) == key:
break
time.sleep(3)
else:
self._sock.connect(self.__args)
return self
def __exit__(self,*a):
self._sock.close()
def transact(self,cmd,args={}):
''' Exchange a single command with guest agent '''
timeout = 2
msg = json.dumps({'execute':cmd,'arguments':args},separators=(',',':'),sort_keys=True)
self._sock.send(msg.encode('ascii'))
self._sock.setblocking(0)
response = b''
if (select.select([self._sock],[],[],timeout)[0]):
response += self._sock.recv(65536)
self._sock.setblocking(1)
if not response:
response = None
else:
if response[0] == 255: # sync
response = response[1:]
response = json.loads(response.decode('utf-8').strip())
if 'error' in response.keys():
self._qmpError(response['error']['class'],response['error']['desc'])
response = None
elif 'return' in response:
response = response['return']
return response
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
if __name__ == '__main__':
script = [':log info "hello world";']
ip = '192.168.0.1'
port = 1234
# can also use unix sockets
#with SocketAgent.unix('/dev/something') as agent:
with SocketAgent.tcp(ip, port) as agent:
ret,out = agent.runSource(script)
print('ret = {}'.format(ret))
for line in out:
print(line)
[ Top | Back to Content ]