Manual:VLANs on Wireless: Difference between revisions
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
=Examples= | =Examples= | ||
[[File:vlan-wlan1.jpg|740px|center|alt=Alt text|Vlan forwarding over wireless interface]] | [[File:vlan-wlan1.jpg|740px|center|alt=Alt text|Vlan forwarding over wireless interface]] | ||
| Line 57: | Line 55: | ||
{{ Warning | Some devices have a built-in switch chip that can switch packets between Ethernet ports with wire-speed performance. Bridge VLAN filtering disables hardware offloading (except on CRS3xx series switches), which will prevent packets from being switched, this does not affect Wireless interfaces as traffic through them cannot be offloaded to the switch chip either way. }} | {{ Warning | Some devices have a built-in switch chip that can switch packets between Ethernet ports with wire-speed performance. Bridge VLAN filtering disables hardware offloading (except on CRS3xx series switches), which will prevent packets from being switched, this does not affect Wireless interfaces as traffic through them cannot be offloaded to the switch chip either way. }} | ||
{{ Note | VLAN filtering is not required in this setup, but is highly recommended due to security reasons. Without VLAN filtering it is possible to forward unknown VLAN IDs in certain scenarios. Disabling VLAN filtering does have performance benefits. }} | |||
'''R3:''' | '''R3:''' | ||
Revision as of 10:53, 18 July 2019
Summary
RouterOS supports VLAN on wireless interfaces. Configuration examples contain information about VLAN cooperation with wireless interface features. Described cases work in the same way but examples show different approaches how to forward VLANs over wireless interfaces. For example we use wlan1 (Cafe Wifi users) and VirtualAP wlan2 (Wifi for company employees) on one device, and we want to separate both traffics with VLANs. The configurations are sorted by precedence of recommended usage.
Examples
Bridge VLAN Filtering since RouterOS v6.41 provides VLAN aware Layer2 forwarding and VLAN tag modifications within the bridge.
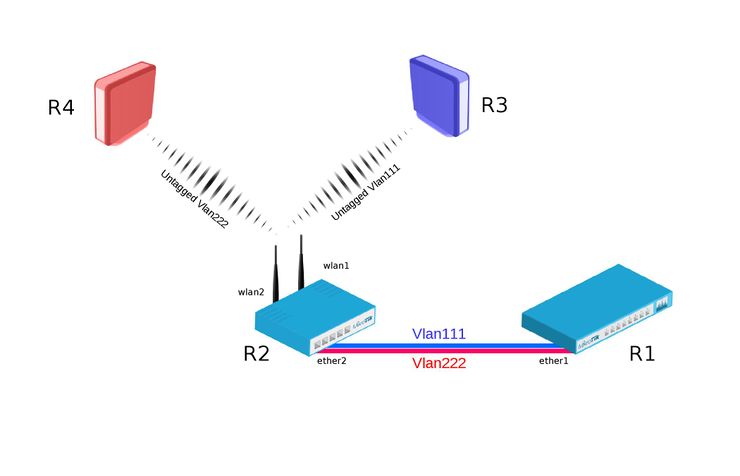
R1:
- Add necessary VLAN interfaces on ethernet interface to make it as a VLAN trunk port. Add ip addresses on VLAN interfaces.
[admin@R1] > /interface vlan add interface=ether1 name=vlan111 vlan-id=111 add interface=ether1 name=vlan222 vlan-id=222 /ip address add address=192.168.1.1/24 interface=vlan111 add address=192.168.2.1/24 interface=vlan222
R2:
- Add VirtualAP under wlan1 interface and create wireless security-profiles for wlan1 and wlan2
[admin@R2] > /interface wireless set [ find default-name=wlan1 ] disabled=no mode=ap-bridge security-profile=vlan111 ssid=vlan111 vlan-id=111 vlan-mode=use-tag add disabled=no master-interface=wlan1 name=wlan2 security-profile=vlan222 ssid=vlan222 vlan-id=222 vlan-mode=use-tag
- Create bridge with vlan-filtering=yes
- Add necessary bridge ports
- Add tagged interfaces under interface bridge vlan section with correct vland-ids
[admin@R2] > /interface bridge add fast-forward=no name=bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes /interface bridge port add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether2 add bridge=bridge1 interface=wlan1 add bridge=bridge1 interface=wlan2 /interface bridge vlan add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2,wlan1 vlan-ids=111 add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2,wlan2 vlan-ids=222
Warning: Some devices have a built-in switch chip that can switch packets between Ethernet ports with wire-speed performance. Bridge VLAN filtering disables hardware offloading (except on CRS3xx series switches), which will prevent packets from being switched, this does not affect Wireless interfaces as traffic through them cannot be offloaded to the switch chip either way.
Note: VLAN filtering is not required in this setup, but is highly recommended due to security reasons. Without VLAN filtering it is possible to forward unknown VLAN IDs in certain scenarios. Disabling VLAN filtering does have performance benefits.
R3:
- Add IP address on wlan1 interface.
- Create wireless security-profile compatible with R2 wlan1.
[admin@R3] > /ip address add address=192.168.1.3/24 interface=wlan1 /interface wireless set [ find default-name=wlan1 ] disabled=no security-profile=vlan111
R4:
- Add ip address on wlan1 interface.
- Create wireless security-profile compatible with R2 wlan2.
[admin@R4] > /ip address add address=192.168.2.4/24 interface=wlan1 /interface wireless set [ find default-name=wlan1 ] disabled=no security-profile=vlan222